Cell disruption techniques such as sonication and homogenization are crucial in laboratory settings where the extraction of intracellular contents is required. These methods break down cell walls and membranes to release proteins, DNA, and other cellular components essential for research and industrial applications. The choice between sonication and homogenization depends on several factors, including the nature of the sample and the desired outcome.
Sonication utilizes ultrasonic energy to agitate particles in a sample, causing cell disruption. Homogenization, on the other hand, employs mechanical force to physically break cells open. While both methods are effective, they differ significantly in their mechanisms, applications, and the scale at which they operate, making each suitable for specific types of samples and purposes.
Understanding the specific advantages and limitations of sonication and homogenization helps scientists and researchers select the most appropriate method for their needs. The efficacy of these techniques can influence the purity and yield of extracted materials, impacting the overall success of scientific experiments and production processes.
What is Sonication?
Definition and Basics
Sonication refers to the process of applying sound energy, specifically ultrasonic waves, to agitate particles in a sample. This method is widely used for disrupting cell membranes and walls in biological samples. The sound waves create rapid pressure changes in the liquid medium, resulting in the formation and violent collapse of small bubbles or cavities, a phenomenon known as cavitation. This process generates intense local heating and high shear forces, which disrupt the cellular structures.
Equipment Used
The primary equipment used in sonication is the ultrasonic processor, sometimes known as a sonicator. This device typically consists of:
- Generator: Produces the high-frequency electrical energy.
- Transducer: Converts electrical energy into mechanical vibrations.
- Probe or Horn: Directs the ultrasonic energy into the sample.
Sonicators come in various forms, from handheld models for small lab samples to industrial-sized units designed for large-scale processes.
Common Applications
Sonication is employed in a range of applications across different fields:
- DNA, RNA, and Protein Extraction: Disrupts cells to release genetic material and proteins.
- Liposome Preparation: Used in pharmaceuticals to prepare carrier molecules.
- Nanoparticle Dispersion: Breaks up aggregates and disperses particles evenly.
What is Homogenization?
Definition and Basics
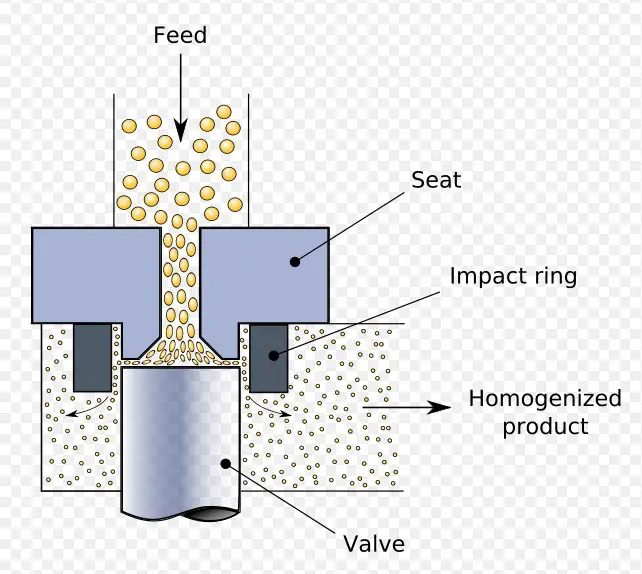
Homogenization involves applying mechanical force to blend two non-mixable liquids into a stable emulsion or to disrupt cellular structures. Unlike sonication, homogenization does not rely on sound waves but physical force to achieve cell disruption or to create emulsions.
Equipment Used
Homogenization equipment varies depending on the application but generally includes:
- High-Pressure Homogenizers: Force liquid through a narrow space under high pressure, breaking down particle sizes.
- Bead Mills: Use small, spherical beads to mechanically grind the sample.
- Rotor-Stator Homogenizers: Feature a rotating blade and a stationary outer ring to shear the sample.
Common Applications
Homogenization is crucial in many sectors, including:
- Food Processing: Creates smooth, uniform mixtures in dairy products, sauces, and creams.
- Pharmaceuticals: Ensures uniform distribution of active ingredients in topical ointments, creams, and injectables.
- Cosmetics: Produces consistent and stable emulsions in creams and lotions.
Key Differences
Mechanism of Action
The fundamental difference between sonication and homogenization lies in their mechanisms. Sonication disrupts cells primarily through cavitation caused by ultrasonic vibrations. Homogenization, meanwhile, achieves disruption through physical force, whether by crushing, grinding, or shearing.
Efficiency and Scale
Efficiency varies significantly between the two methods. Sonication can be particularly effective for small to medium batches and delicate samples that require precise control over the energy input. Homogenization is typically more efficient for larger volumes and can be scaled up easily.
Sample Integrity
Sample integrity is another critical consideration. Sonication can sometimes generate heat that might denature sensitive molecules, although this can be mitigated with pulse sonication techniques. Homogenization might cause less heat but can potentially shear DNA or damage fragile components in a sample.
Advantages of Sonication
Precision in Disruption
Sonication offers high precision in targeting and disrupting specific cells or particles, making it ideal for applications requiring fine control, such as in genetic engineering and microbiology.
Energy Efficiency
It is also more energy-efficient for small-scale laboratory operations, as it directly transfers energy to the sample without significant loss.
Applications in DNA, RNA Isolation
For DNA and RNA isolation, sonication provides a quick and effective method to shear nucleic acids, facilitating subsequent extraction and purification steps without significant chemical modifications.

Advantages of Homogenization
Versatility
Homogenization is recognized for its versatility across a range of industries. This method can process various types of samples, from delicate biological tissues to robust chemical mixtures. The ability to adjust the intensity and method of force application makes homogenization suitable for a broad spectrum of materials, ensuring its adaptability to different scientific and commercial needs.
Scalability
Another significant advantage of homogenization is its scalability. Equipment designed for homogenization can handle small laboratory samples to large industrial batches without compromising efficiency or outcome. This scalability is particularly crucial in sectors such as pharmaceuticals and food production, where large volumes of products are processed.
Use in Protein Extraction
In the field of protein extraction, homogenization proves to be exceptionally effective. It facilitates the breakdown of cellular structures to release proteins and other macromolecules efficiently. This method is preferred for its ability to maintain the integrity of proteins during extraction, which is vital for subsequent analytical procedures.
Choosing the Right Method
Factors to Consider
Selecting the right method for cell disruption involves considering various factors:
- Purpose of Extraction: Whether the goal is to obtain nucleic acids, proteins, or other intracellular components.
- Physical and Chemical Properties of the Sample: Some methods may be more suitable for fluid samples, while others are better for solid tissues.
Cost Implications
Economic factors often dictate the choice of method. Sonication equipment can be expensive and less cost-effective for processing large volumes, whereas homogenization systems may offer a more economical solution for bigger batches.
Sample Type and Size
The type and size of the sample are crucial in deciding between sonication and homogenization. Sonication might be more appropriate for small, delicate samples sensitive to heat and physical stress, while homogenization might be better for larger, tougher samples.
Industry Applications
Biotechnology
In biotechnology, both sonication and homogenization are employed to extract genetic material, synthesize biofuels, and more. Each method supports the advancement of biotechnological solutions by ensuring high-purity samples for research and development.
Pharmaceutical Development
During pharmaceutical development, consistency and reproducibility are key. Homogenization is particularly valuable in this industry for its ability to produce uniform and stable emulsions, essential for creating creams, ointments, and injectables.
Food Science
Homogenization is integral to food science, where it is used to improve the stability and texture of products such as milk, dressings, and sauces. The process ensures that emulsions do not separate, extending the shelf life and enhancing the quality of food products.
Future Trends
Technological Advancements
The ongoing technological advancements in both sonication and homogenization are set to improve their efficiency and applications. Innovations such as more precise energy controls and automated systems enhance the reproducibility and scalability of these methods.
Environmental Impact
As the global emphasis on sustainability grows, the environmental impact of these technologies is being scrutinized. Future developments are likely to focus on reducing energy consumption and minimizing waste production during the cell disruption process.
Market Growth
The market for cell disruption methods is projected to grow significantly. This growth is driven by the increasing demand in fields such as biotechnology, pharmaceuticals, and nutraceuticals. The expansion of these sectors is pushing the advancements in sonication and homogenization technologies, aiming to cater to more specialized and efficient processing needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Sonication?
Sonication is a process where ultrasonic waves are used to disrupt cell structures. This method is especially useful for breaking down cellular walls at a microscopic level, facilitating the extraction of intracellular substances without significant heat generation.
How does Homogenization Work?
Homogenization involves applying physical force to break down cellular structures. This can be achieved through various equipment that grinds, blends, or presses the sample under high pressure, effectively rupturing the cell walls to release the contents.
When to Use Sonication Over Homogenization?
Sonication is preferred when dealing with small volume samples that require delicate handling to prevent heat degradation. It is ideal for sensitive applications like DNA or RNA extraction where the integrity of the material is paramount.
What are the Advantages of Homogenization?
Homogenization excels in its versatility and scalability, making it suitable for handling large volumes of samples efficiently. It is widely used in industries like food and pharmaceuticals where the consistency and stability of the product are critical.
Conclusion
Choosing between sonication and homogenization hinges on understanding their distinct benefits and limitations. Each method offers unique advantages that cater to different scientific needs and industrial applications. By selecting the appropriate technique, researchers can optimize the extraction process, enhance sample quality, and ensure the success of their experimental and production goals.
In conclusion, the decision to use sonication or homogenization should be guided by the specific requirements of the sample and the desired outcome of the process. As technological advances continue to evolve, the efficiency and application of both methods are likely to expand, providing even more options for scientists and industry professionals.

