Quiescence and dormancy are two distinct states of being that are often confused with one another. In this blog post, we will explore the differences between quiescence and dormancy, and discuss how each state can have an effect on both individual organisms and entire ecosystems.
We will also examine some of the advantages and disadvantages of each state and look at some real-world examples of how quiescence and dormancy are used in nature.
Definition of quiescence

Quiescence and dormancy are two terms that are often used interchangeably, but they actually refer to two different states. Quiescence is a state of inactivity or suppression of activity, while dormancy is a state of suspended animation or suspended metabolic activity. Quiescence is typically associated with a type of relaxation or restfulness, while dormancy is associated with a state of suspended development.
Quiescence is typically associated with a type of relaxation or restfulness, while dormancy is associated with a state of suspended development. Quiescence is often used to describe a temporary state, while dormancy is usually used to describe a longer-term state. Generally speaking, quiescence is characterized by a lack of activity, while dormancy is characterized by a lack of development.
In addition, quiescence is often used to describe a period of rest or relaxation, while dormancy is typically used to describe a period of suspended development.
Definition of dormancy
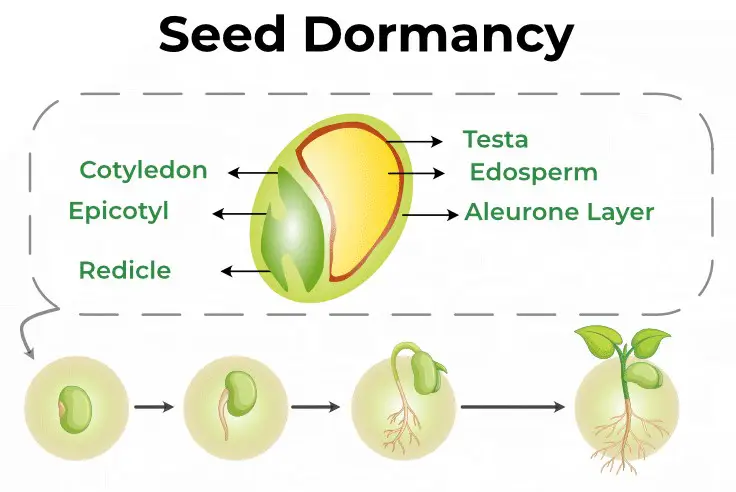
Dormancy is a state of physiological inactivity in which an organism reduces its metabolic rate and enters a state of suspended animation or reduced activity in order to survive in unfavorable environmental conditions. It is different from quiescence, which is a more active state of reduced metabolic activity associated with a longer period of suspended animation.
Quiescence is a way for the organism to conserve energy and prepare for a future period of increased activity. Dormancy, on the other hand, is a state of complete inactivity where the organism is unable to respond to external stimuli and undergoes a period of prolonged dormancy in order to survive in harsh environmental conditions.
Similarities between quiescence and dormancy
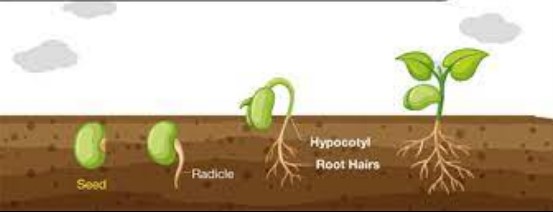
When it comes to quiescence and dormancy, there is often confusion around the difference between the two. Quiescence and dormancy are similar in that they both involve a period of inactivity, but there are some key differences.
Quiescence is usually a short-term form of inactivity, while dormancy is a long-term form of inactivity. Quiescence is usually used as a way to conserve energy and resources, while dormancy is used as a way to survive unfavorable environmental conditions.
Quiescence is usually voluntary, while dormancy is involuntary. Ultimately, both quiescence and dormancy can help organisms survive, but the key difference is the level of metabolic activity and the length of inactivity.
Differences between quiescence and dormancy

The difference between quiescence and dormancy might be subtle, but it’s an important distinction to understand. Quiescence is a state of rest or inactivity, a period of dormancy without growth or development.
It’s a temporary pause in activity that can be triggered by environmental cues or part of an organism’s natural life cycle. Dormancy, on the other hand, is a period of suspended animation where an organism slows its metabolic rate and enters a state of reduced activity. This can be a response to unfavorable environmental conditions, such as cold temperatures, drought, or lack of food.
Both quiescence and dormancy can help an organism conserve energy and survive difficult times, but dormancy is a more extreme state that can last for months or even years.
Examples of quiescence and dormancy
Quiescence and dormancy are two terms that may appear similar but have distinct differences. Quiescence is a state of inactivity or suspended animation in which an organism or cell reduces its metabolic activity and energy consumption. Dormancy, on the other hand, is a state of slowed development in which an organism or cell temporarily suspends its growth and development until environmental conditions become more favorable.
Dormancy, on the other hand, is a state of slowed development in which an organism or cell temporarily suspends its growth and development until environmental conditions become more favorable. An example of quiescence is when a plant enters a state of suspended animation during winter months. A form of dormancy is seen when eggs remain undeveloped until the right temperature and moisture levels are present.
While both quiescence and dormancy may result in a decrease in an organism’s activity level, the main difference between the two is that quiescence is a result of reduced metabolic activity, while dormancy is a result of slowed development.
Conclusion
In conclusion, quiescence and dormancy are two different states of reduced activity or inactivity in organisms. While quiescence refers to the temporary suspension of growth and metabolism, dormancy is a state of prolonged inactivity where the metabolic rate is reduced and the organism may remain dormant for a long period of time. Dormancy is usually triggered by environmental factors such as temperature and light while quiescence is a response to the internal environment.
Dormancy is usually triggered by environmental factors such as temperature and light while quiescence is a response to the internal environment. Quiescence is usually a reversible state while dormancy is a more permanent state and may be irreversible.

