Neural communication forms the backbone of the human nervous system, orchestrating a symphony of signals that enable thought, sensation, movement, and emotion. Central to this complex interplay are the refractory periods, critical intervals that dictate the timing and frequency of these neural signals. Understanding the difference between relative and absolute refractory periods sheds light on the fundamental mechanics of neuronal activity and its effects on our daily lives.
The absolute refractory period is a brief phase following an action potential during which a neuron is completely incapable of firing a second action potential, regardless of the stimulus strength. Conversely, the relative refractory period is the subsequent phase where a neuron can initiate another action potential but requires a stronger-than-normal stimulus. These periods ensure orderly propagation of neural signals and prevent the overload of neural circuits, playing a vital role in the coding and processing of information within the nervous system.
Refractory periods are not just abstract concepts; they are essential mechanisms that ensure our nervous system operates efficiently and reliably. By regulating the pace at which neurons can fire, they prevent the chaotic overlap of signals, allowing for clear, precise communication across vast neural networks. This regulation is crucial for everything from basic sensory processing to complex cognitive functions, highlighting the intricate balance and precision inherent in human physiology.

Refractory Period Basics
Definition and Role
The refractory period refers to a span of time during which a neuron is either completely unable to fire another action potential or requires a greater than normal stimulus to do so. This concept is fundamental in the realm of neural communication, ensuring that signals within the nervous system are sent in an orderly and manageable fashion.
Significance in Neural Function
Refractory periods play a critical role in maintaining the directionality of nerve impulses and the rhythmic pattern of neuronal firing. By doing so, they prevent the chaotic overlap of signals, ensuring clear and efficient communication across the vast networks of the nervous system. This mechanism is pivotal for everything from basic sensory processing to the execution of complex movements and cognitive functions.
Types of Refractory Periods
General Overview
There are two main types of refractory periods: absolute and relative. Each serves a unique function in the regulation of neural activity, contributing to the precise timing of action potentials, the electrical impulses that carry information along neurons.
Distinguishing Absolute from Relative
- The absolute refractory period is a phase immediately following an action potential during which a neuron is completely incapable of firing again, regardless of stimulus strength.
- The relative refractory period occurs right after the absolute phase, where a neuron can fire again but requires a stimulus stronger than usual.
Absolute Refractory Period
Conceptual Understanding
Definition
The absolute refractory period is the time during which a second action potential is impossible, no matter how strong the incoming signal might be. This phase ensures that each neural signal is a discrete event, facilitating clear signal transmission.
Physiological Basis
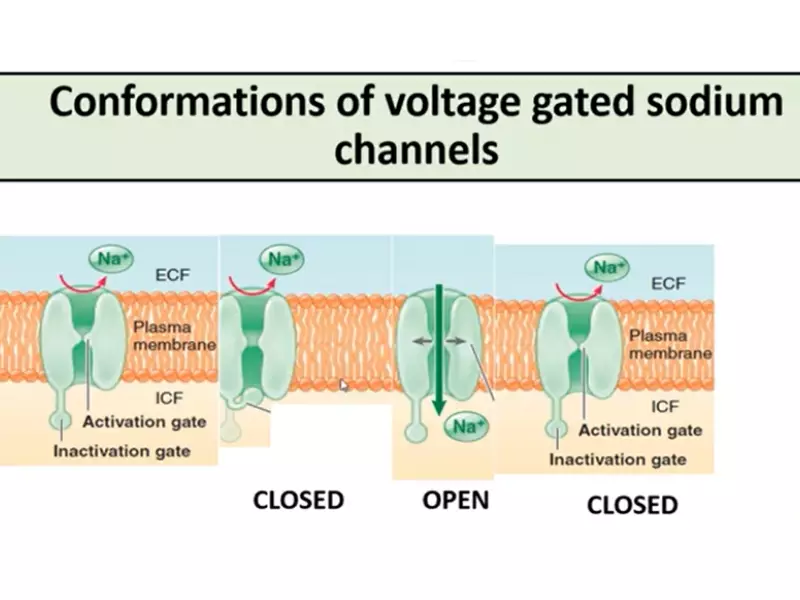
This period is largely governed by the status of sodium channels in the neuron’s membrane, which, after opening to initiate an action potential, must close and reset before they can open again. This process is essential for the neuron to “recharge” and be ready for the next signal.
Characteristics
Non-negotiability
The absolute refractory period is non-negotiable in the sense that no additional action potential can be generated in a neuron during this time, ensuring the unidirectional flow of neural impulses.
Duration Specifics
Typically, this period lasts about 1-2 milliseconds but can vary depending on the type of neuron and physiological conditions.
Biological Significance
Prevention of Backward Propagation
By making it impossible for a neuron to fire a second action potential immediately, the absolute refractory period prevents the backward propagation of signals, ensuring that neural communication only moves in one direction.
Role in Action Potential Spacing
It also helps in spacing out the action potentials, preventing them from bunching up too closely, which could lead to signal overlap and neural dysfunction.
Relative Refractory Period
Conceptual Understanding
Definition
Following the absolute refractory period, the relative refractory period is a phase where a neuron can fire again but requires a higher-than-normal stimulus. This period allows for some degree of control over the frequency and timing of action potentials.
Physiological Basis
During this time, potassium channels are still returning to their resting state, and a greater than normal internal negativity must be overcome for an action potential to be initiated.
Characteristics
Conditional Neuron Firing
Neuron firing in this phase is conditional on the strength of the stimulus. Only stimuli that are significantly stronger than usual can generate an action potential during the relative refractory period.
Duration Specifics
The duration of this period can vary widely, often lasting several milliseconds and extending the window during which the timing and frequency of neuron firing are influenced by the intensity of incoming signals.
Biological Significance
Modulation of Action Potential Frequency
The relative refractory period allows the nervous system to modulate the frequency of action potentials in response to the strength of stimuli, enabling a form of signal intensity coding.
Influence on Signal Intensity
This modulation plays a crucial role in how information is encoded and processed within the brain, affecting everything from the perception of sensory input to the initiation of motor responses.
Comparative Analysis
Key Differences
Trigger Conditions
The absolute refractory period is triggered by the initiation of an action potential, specifically when sodium channels open, allowing for the influx of sodium ions and the depolarization of the neuron. In contrast, the relative refractory period begins as the neuron starts repolarizing, marked by the closing of sodium channels and the opening of potassium channels, which work to restore the neuron’s resting state. This distinction in trigger conditions underpins the fundamental differences in neuron responsiveness during these periods.
Physiological Implications
The physiological implications of these differences are profound. During the absolute refractory period, the neuron’s inability to fire again ensures the unidirectional flow of signals, a critical feature for the orderly transmission of neural impulses. On the other hand, the relative refractory period’s requirement for a stronger-than-normal stimulus to initiate another action potential allows for the graded response of neurons, reflecting the intensity of stimuli and contributing to the dynamic range of neural signaling.
Duration and Thresholds
Comparison of Timelines
The absolute refractory period typically lasts about 1-2 milliseconds, whereas the relative refractory period can extend for several milliseconds beyond this. The precise duration of these periods can vary significantly among different types of neurons and is influenced by the physiological state of the neuron and its environment.
Impact on Neuron Excitability
These variations in duration have a direct impact on neuron excitability. A shorter absolute refractory period may lead to a higher potential firing rate, allowing neurons to respond more rapidly to successive stimuli. Conversely, a longer relative refractory period can modulate the firing rate in response to stimulus intensity, enabling neurons to participate in complex processing and coding mechanisms based on the strength and timing of inputs.
Functional Implications
Signal Propagation Speed
The differences between the absolute and relative refractory periods directly influence the speed at which signals are propagated through neural circuits. A shorter absolute refractory period can facilitate faster signal transmission, essential for rapid reflexes and acute sensory processing. In contrast, the relative refractory period, by requiring stronger stimuli for additional action potentials, ensures that only the most significant signals are propagated, contributing to the selective processing of information.
Neural Coding and Information Processing
The interplay between these refractory periods is central to neural coding strategies, determining how information is represented and processed within the brain. The absolute refractory period ensures clarity and fidelity in signal transmission, while the relative refractory period allows for the dynamic modulation of signal intensity and frequency, enabling the nervous system to encode a wide range of sensory inputs and cognitive processes.
Practical Implications
In Medical Research
Understanding Neurological Disorders
Disruptions in the normal functioning of refractory periods can lead to or exacerbate neurological disorders. For example, alterations in the duration of refractory periods can contribute to the hyperexcitability seen in epilepsy, where neurons fire excessively and uncontrollably. Research into the mechanisms governing refractory periods offers insights into the pathophysiology of such conditions, paving the way for novel therapeutic targets.
Impacts on Treatment Approaches
Understanding the nuances of refractory periods has also led to advances in treatment strategies for neurological conditions. For instance, certain antiepileptic drugs work by extending the absolute refractory period of neurons, thereby reducing their likelihood of abnormal firing. This illustrates how insights into refractory period dynamics can inform the development of more effective and targeted interventions.
In Neurotechnology
Applications in Brain-Computer Interfaces
The principles of refractory periods are applied in the design and optimization of brain-computer interfaces (BCIs). By understanding how neurons respond during these periods, researchers can develop more precise algorithms for decoding neural signals, leading to BCIs that offer improved speed and accuracy for users, including those with motor impairments or communication difficulties.
Enhancements in Neural Prosthetics
Similarly, knowledge of refractory period dynamics is crucial for the development of advanced neural prosthetics. Prosthetics that can mimic or respond to the natural timing of neural signals can offer more naturalistic control and feedback to the user. This involves designing systems that can interpret and replicate the nuanced patterns of neural firing, including the recognition of relative and absolute refractory periods, thereby enhancing the functionality and user experience of prosthetic limbs and organs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What triggers the absolute refractory period?
The absolute refractory period is triggered immediately after a neuron fires an action potential. It is the result of the sodium channels’ inactivation, which temporarily prevents any possibility of the neuron firing again, ensuring that each neural signal is distinct and sequentially ordered.
How long does the relative refractory period last?
The duration of the relative refractory period can vary but generally follows the absolute refractory period and can last from a few milliseconds to several milliseconds longer. The exact length depends on the neuron’s type, the intensity of the initial action potential, and the physiological context.
Why is the relative refractory period important?
The relative refractory period allows for the modulation of the firing rate of neurons based on the strength of incoming stimuli. This adaptability is crucial for the processing of varying signal intensities, enabling the nervous system to respond appropriately to different environmental cues and demands.
Can refractory periods affect neurological disorders?
Yes, alterations in refractory periods can influence neurological disorders. For instance, shorter or improperly timed refractory periods may lead to excessive neuronal firing, which is characteristic of certain types of epilepsy. Understanding refractory dynamics is therefore critical for developing targeted therapies for such conditions.
Conclusion
The exploration of relative and absolute refractory periods illuminates the intricate dance of electrical activity that underpins neural communication. These mechanisms ensure that our nervous system functions with the precision and reliability necessary for everything from simple reflexes to the complexity of conscious thought. The distinction between these two types of refractory periods highlights the nuanced control our bodies have over the seemingly instantaneous processes that define our interactions with the world around us.
Reflecting on these concepts, we gain not only a deeper appreciation for the complexity of our neural systems but also insight into the potential for advancing our understanding and treatment of neurological disorders. By continuing to unravel the mysteries of neural signaling, we pave the way for innovations in medicine and technology that could transform our approach to health and human capability.
