Genetic crosses are a cornerstone of understanding how traits are passed from one generation to the next. They reveal the intricate dance of genes and alleles that determine everything from the color of our eyes to our susceptibility to certain diseases. At the heart of this exploration are two fundamental concepts: monohybrid and dihybrid crosses. These methods, developed from the pioneering work of Gregor Mendel, serve as the bedrock for the field of genetics.
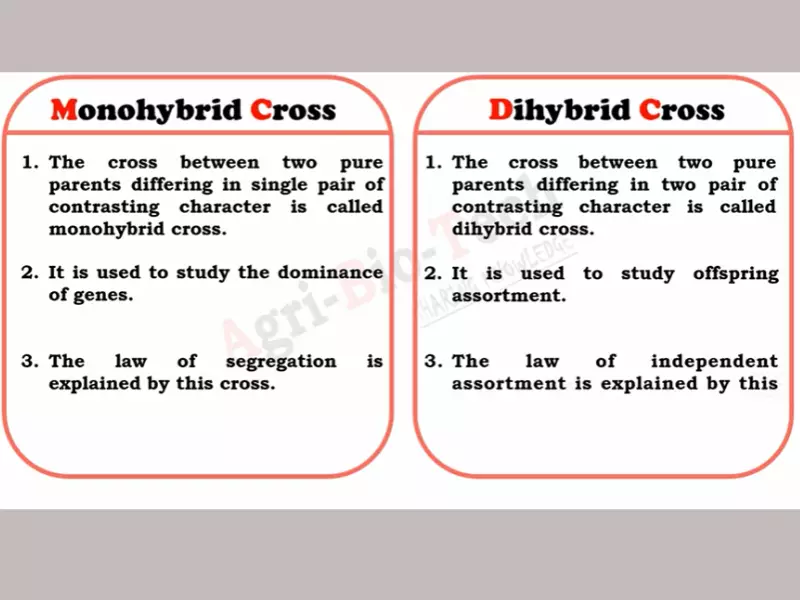
Monohybrid crosses involve the study of a single trait, examining how alleles from two parents combine and manifest in their offspring. In contrast, dihybrid crosses delve into the inheritance of two distinct traits simultaneously. The difference lies not only in the number of traits examined but also in the complexity of the genetic interactions and the patterns of inheritance that emerge.
These concepts extend far beyond academic curiosity, influencing everything from agricultural breeding programs to medical genetic counseling. Understanding the difference between monohybrid and dihybrid crosses illuminates the fundamental principles of inheritance, laying the groundwork for advancements in genetic engineering, biotechnology, and our grasp of human genetics.
Basics of Genetic Crosses
Genes and Alleles
Definition of Genes
Genes are the basic units of heredity found in the DNA of living organisms. They act as instructions for the production of proteins, which in turn influence individual traits such as hair color, height, and susceptibility to certain diseases. Each gene resides at a specific location on a chromosome.
Concept of Alleles
Alleles are different versions of the same gene. While genes determine the general framework for an organism’s traits, alleles dictate the variations in how these traits manifest. For example, a gene for eye color may have alleles for blue, green, or brown eyes. Organisms inherit two alleles for each gene, one from each parent, which interact to determine the organism’s physical characteristics.
Mendelian Genetics
Gregor Mendel’s Contributions
Gregor Mendel, a 19th-century monk, is known as the father of modern genetics. His experiments with pea plants laid the foundation for the understanding of genetic inheritance. Mendel discovered that traits are inherited in discrete units (genes), not through a blend of parental traits, revolutionizing the study of genetics.
Principles of Inheritance
Mendel identified several key principles of inheritance:
- Law of Segregation: Each individual has two alleles for each gene, which separate during gamete formation, ensuring that offspring inherit one allele from each parent.
- Law of Independent Assortment: Genes for different traits are inherited independently of one another, provided they are on different chromosomes.
Monohybrid Crosses
Definition
A monohybrid cross is a breeding experiment between two organisms that are heterozygous for a single trait of interest. This type of cross examines the inheritance of one particular gene.
Explanation of Monohybrid Crosses
In a monohybrid cross, scientists track the inheritance of a single trait. This allows them to understand how alleles interact (dominant vs. recessive) and predict the ratios of the offspring’s phenotypes and genotypes.
Key Features
- Single Trait Focus: Concentrates on one trait at a time.
- Genotype and Phenotype Ratios: Predictable ratios emerge, typically 3:1 for phenotypes and 1:2:1 for genotypes in a simple dominant-recessive allele scenario.
Process
- Select parental organisms with known genotypes for the trait of interest.
- Cross the parents to produce offspring (F1 generation).
- Analyze the offspring’s phenotypes and genotypes.
Punnett Square Illustration
A Punnett Square is a diagram that predicts the outcome of a genetic cross. It shows the possible combinations of alleles that the offspring can inherit from the parents.
Examples
Real-world scenarios of monohybrid crosses include breeding plants to obtain a desired flower color or crossing animals to achieve a specific coat pattern.
Dihybrid Crosses
Definition
A dihybrid cross involves a study of the inheritance patterns of two different traits that are controlled by different genes. The parents in the cross are typically heterozygous for both traits.
Explanation of Dihybrid Crosses
Dihybrid crosses allow scientists to observe the inheritance of two traits simultaneously and to understand how genes located on different chromosomes assort independently during gamete formation.
Key Features
- Two-Trait Focus: Examines the inheritance of two traits.
- Independent Assortment Principle: Demonstrates that alleles of different genes are distributed independently of one another.
Process
- Identify parental genotypes for two traits.
- Create a Punnett Square for a dihybrid cross, which is more complex than for a monohybrid cross due to the consideration of two traits.
- Determine the phenotypic and genotypic ratios of the offspring.
Punnett Square Complexity
The Punnett Square for a dihybrid cross involves 16 boxes, representing the possible allele combinations the offspring can inherit.
Examples
An example of a dihybrid cross could be crossing pea plants with different pea shapes (round vs. wrinkled) and colors (yellow vs. green), revealing the patterns of inheritance for these traits.

Comparing Monohybrid and Dihybrid
Trait Number
Single vs. Multiple Traits
Monohybrid crosses focus on one trait, such as flower color in pea plants, allowing for straightforward genetic analysis. Dihybrid crosses, however, delve into two traits simultaneously, like seed shape and color, revealing how different genes interact during inheritance.
Genetic Ratios
Phenotypic and Genotypic Ratios Comparison
In monohybrid crosses, the phenotypic ratio typically emerges as 3:1 for dominant to recessive traits, and the genotypic ratio stands at 1:2:1. Dihybrid crosses, considering two traits, result in a more complex 9:3:3:1 phenotypic ratio under simple dominant-recessive allele scenarios.
Complexity
Analysis of Process Complexities
The complexity of predicting outcomes increases significantly from monohybrid to dihybrid crosses. Dihybrid crosses require understanding of independent assortment and more intricate Punnett Squares, making the prediction process more complex but also more informative about genetic behavior.
Predictive Power
Use in Predicting Offspring Traits
Both monohybrid and dihybrid crosses have predictive power. Monohybrid crosses help predict the inheritance of a single trait, while dihybrid crosses extend this prediction to the simultaneous inheritance of two traits, offering a broader genetic perspective.
Practical Applications
Agricultural Breeding
Enhancing Crop Traits
Genetic crosses, particularly dihybrid crosses, are vital in agricultural science for developing crops with desired traits such as drought resistance and improved yield. These practices allow for the selective breeding of plants to meet human needs more effectively.
Medical Genetics
Predicting Genetic Disorders
Understanding the principles behind monohybrid and dihybrid crosses is crucial in medical genetics for predicting the likelihood of hereditary diseases. This knowledge aids in genetic counseling and the development of treatment plans for conditions with genetic bases.
Conservation Biology
Biodiversity through Genetic Variation
In conservation biology, genetic crosses inform efforts to preserve biodiversity. By understanding how traits are passed down, conservationists can manage breeding programs for endangered species, ensuring genetic diversity and the survival of species.
Challenges and Limitations
Epistasis
Interaction Between Genes
Epistasis occurs when the effect of one gene is modified by one or more other genes, which can complicate the outcomes of genetic crosses. This interaction can mask or alter phenotypic ratios, making predictions more challenging.
Polygenic Inheritance
Multiple Genes Affecting a Trait
Unlike the simple inheritance patterns seen in monohybrid and dihybrid crosses, many traits are influenced by multiple genes (polygenic inheritance), such as skin color and height. This complexity requires an understanding beyond basic Mendelian genetics to predict outcomes accurately.
Environmental Influence
Genes vs. Environment Debate
The debate between the influence of genes and the environment on an organism’s traits underscores the complexity of predicting phenotypic outcomes. While genetic crosses provide insights into heredity, environmental factors often play a significant role, indicating that genetics is only part of the equation in determining an organism’s characteristics.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a Monohybrid Cross?
A monohybrid cross is a genetic cross between two individuals focusing on a single trait of interest. This method tracks how alleles for a particular trait are inherited by offspring from their parents. The outcomes, often represented in a Punnett square, provide insight into the possible genotypes and phenotypes, highlighting the basic patterns of Mendelian inheritance.
What is a Dihybrid Cross?
A dihybrid cross examines the inheritance of two distinct traits simultaneously. This type of cross involves individuals that are heterozygous for two traits, allowing geneticists to observe how alleles for each trait segregate and assort independently across generations. The results unveil the complexity of genetic variation and the principle of independent assortment.
How Do Monohybrid and Dihybrid Crosses Differ?
The primary difference between monohybrid and dihybrid crosses lies in the number of traits studied. Monohybrid crosses focus on a single trait, offering a simpler view of inheritance patterns, while dihybrid crosses involve two traits, showcasing the independent assortment of alleles and more complex genetic interactions. This distinction is crucial for understanding the diversity of genetic outcomes.
Why are Genetic Crosses Important?
Genetic crosses are vital for deciphering the laws of inheritance that govern how traits are transmitted from parents to offspring. They provide foundational knowledge essential for fields like agriculture, where breeders aim to enhance crop traits, and medicine, where understanding genetic disorders can lead to better treatments and counseling. Moreover, these crosses help in conserving biodiversity by understanding genetic variations.
Conclusion
The exploration of monohybrid and dihybrid crosses provides a window into the fundamental mechanisms of inheritance, revealing the intricate ways in which traits are passed down through generations. This understanding is not just academically enriching but also has practical implications across a myriad of fields, from agriculture to medicine. It empowers us to harness the power of genetics for the betterment of society and the natural world.
As we continue to unravel the complexities of genetic inheritance, the knowledge gleaned from studying these crosses will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in the advancement of genetic research and biotechnology. The principles of monohybrid and dihybrid crosses are the keystones upon which much of modern genetics is built, guiding us toward a future where the potential of genetic understanding is fully realized.

