Solids are a cornerstone of the material world, presenting a fascinating array of properties and applications that stem from their atomic and molecular structures. The way atoms or molecules are held together in a solid dictates its hardness, melting point, electrical conductivity, and many other characteristics. Among the various types of solids, molecular solids and covalent network solids stand out due to their distinct bonding and structural differences.
Molecular solids are composed of molecules held together by relatively weak forces, such as Van der Waals forces or hydrogen bonds, leading to low melting points and poor electrical conductivity. Covalent network solids, on the other hand, are characterized by a continuous network of covalent bonds, resulting in materials with high melting points, exceptional hardness, and varying electrical conductivities. This stark contrast highlights the profound impact of atomic and molecular arrangements on the properties of solid materials.
The distinction between molecular solids and covalent network solids lies in their bonding and structure. Molecular solids, with their discrete molecular units, and covalent network solids, with their endless covalent bonds, embody the diverse nature of solid materials. This variance not only influences their physical and chemical properties but also determines their suitability for different applications, from everyday products to advanced technological devices.
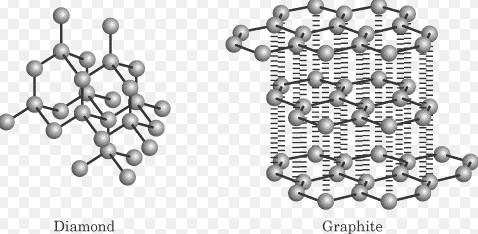
Solid State Basics
Types of Solids
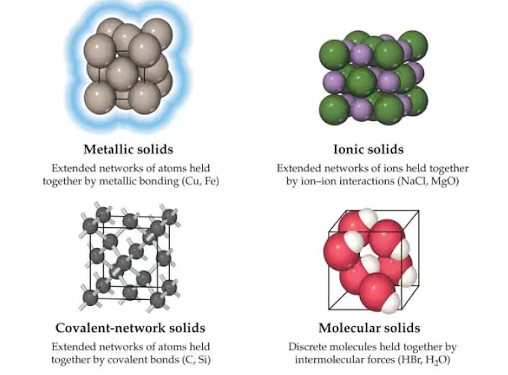
The classification of solids is based on the nature of the atomic or molecular interactions that hold them together. These can be broadly categorized into metallic, ionic, molecular, and covalent network solids.
Metallic Solids
Metallic solids are characterized by a sea of electrons that freely moves around the positively charged metal ions. This unique bonding results in properties such as high electrical conductivity, malleability, and ductility.
Ionic Solids
In ionic solids, ions of opposite charges are bound together by electrostatic forces. These solids are typically hard and brittle, with high melting points and good electrical conductivity when molten or dissolved in water.
Molecular Solids
Molecular solids consist of molecules held together by intermolecular forces such as Van der Waals forces, dipole-dipole interactions, or hydrogen bonds. They often have low melting points and are poor electrical conductors.
Covalent Network Solids
Covalent network solids are formed from atoms connected by covalent bonds in a continuous network across the material. These solids are distinguished by their extreme hardness, high melting points, and in some cases, semiconductor properties.
Bonding and Properties
The bonding in a solid affects its physical properties in several ways:
- Melting Point: The strength of the bonds between particles influences the temperature at which a solid becomes a liquid. Stronger bonds result in higher melting points.
- Hardness: This property is a measure of a solid’s resistance to deformation. Solids with strong atomic or molecular bonds tend to be harder.
- Electrical Conductivity: The presence of free-moving electrons or ions in a solid facilitates electrical conductivity. Solids with delocalized electrons (like metals) or ions (in the case of ionic solids in solution) conduct electricity well.
Molecular Solids
Characteristics
Molecular solids are notable for their weak intermolecular forces holding the molecules in place. These forces include London dispersion, dipole-dipole interactions, and hydrogen bonds. As a result, molecular solids tend to have low melting and boiling points and are generally soft.
Examples
Water ice, dry ice (solid CO2), and sugar are familiar examples of molecular solids. These substances demonstrate the typical properties of molecular solids, such as low melting points and poor conductivity.
Properties
- Melting Points: Molecular solids melt at lower temperatures due to the weak intermolecular forces.
- Electrical Conductivity: They are typically poor conductors because they lack free electrons or ions.
- Hardness: These solids are relatively soft compared to ionic or covalent network solids.
- Solubility: Molecular solids are often soluble in organic solvents, depending on the nature of the intermolecular forces.
Covalent Network Solids
Characteristics
Covalent network solids are characterized by their continuous network of covalent bonds. This extensive bonding network results in materials that are exceptionally hard, have high melting points, and can vary in their electrical conductivity.
Examples
Diamond, quartz (SiO2), and silicon carbide (SiC) are prime examples of covalent network solids. Each demonstrates the unique properties that result from their covalent network structure.
Properties
- High Melting Points: The strong covalent bonds require a great deal of energy to break, resulting in high melting points.
- Electrical Properties: Depending on the structure, some covalent network solids (like diamond) are excellent insulators, while others (such as silicon) are semiconductors.
- Hardness: The continuous network of covalent bonds makes these solids among the hardest materials known.
- Chemical Stability: Covalent network solids are generally chemically inert due to the strength of the covalent bonds.
Comparative Analysis
The distinctions between molecular solids and covalent network solids lie deep within their atomic and molecular structures. These differences play a crucial role in determining the properties and applications of each solid type, affecting everything from their physical and chemical properties to their utility in both technology and everyday life.
Bonding Contrast
Molecular solids are characterized by the weak intermolecular forces such as Van der Waals forces, dipole-dipole interactions, and hydrogen bonds that hold their molecules together. These forces are significantly weaker than the covalent bonds found in covalent network solids, which consist of atoms linked in a continuous network throughout the material. This fundamental difference in bonding explains the contrasting properties observed between these two types of solids.
Physical Properties
Melting Points
Molecular solids, due to their weaker forces, have lower melting points compared to covalent network solids, which require significantly more energy to break apart their robust covalent bonds. This results in covalent network solids having much higher melting points.
Hardness
The hardness of a solid is directly influenced by the strength of the bonds that hold its structure together. Consequently, molecular solids are typically softer, as their molecules are easily displaced due to the weaker forces binding them. In contrast, the extensive covalent bonding in network solids makes them extremely hard, with materials like diamond being among the hardest substances known.
Electrical Conductivity
Electrical conductivity in solids depends on the ability to transfer charge through the movement of electrons or ions. Molecular solids are poor conductors of electricity as they lack free charge carriers. Covalent network solids vary in conductivity; some, like diamond, are insulators, while others, such as silicon, exhibit semiconductor properties due to the presence of delocalized electrons within their structure.
Chemical Stability
The chemical stability of a solid is closely linked to its internal bonding. Molecular solids are generally less chemically stable compared to covalent network solids, as the weaker intermolecular forces make them more susceptible to chemical reactions. On the other hand, the strong covalent bonds in network solids confer a high degree of chemical inertness, making substances like diamond and quartz resistant to most chemical reactions under normal conditions.
Applications and Implications
The diverse properties of molecular solids and covalent network solids have profound implications for their use in both technological applications and everyday life.
In Technology
Covalent network solids find extensive use in the technology sector due to their remarkable properties. Silicon, a semiconductor, is the backbone of the modern electronics industry, used in the manufacture of transistors, integrated circuits, and solar cells. Diamond, due to its hardness and high thermal conductivity, is used in cutting tools and heat sinks. Quartz, another covalent network solid, is pivotal in timekeeping devices due to its piezoelectric properties, which allow it to generate an electrical signal with precise frequency when mechanical stress is applied.
Molecular solids, while not as robust as covalent network solids, have their niche in technology. Organic compounds, a type of molecular solid, are crucial in the pharmaceutical industry for drug synthesis. Plastics, another form of molecular solid, are versatile materials used in a wide array of applications, from packaging to insulating materials in electrical devices.
In Everyday Life
In daily life, the presence and applications of molecular and covalent network solids are ubiquitous. Sugar and ice are common examples of molecular solids, integral to food and drink. Plastics, found in everything from bottles to furniture, demonstrate the versatility and utility of molecular solids in providing lightweight, durable, and moldable materials.
Covalent network solids also play a critical role in everyday items. Silicon carbide is used in abrasive materials such as sandpapers and cutting tools. Diamonds, beyond their aesthetic value in jewelry, serve in drill bits and saws for cutting tough materials.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Molecular Solids?
Molecular solids consist of atoms or molecules held together by intermolecular forces, such as London dispersion forces, dipole-dipole interactions, or hydrogen bonds. These forces are weaker compared to covalent or ionic bonds, resulting in solids that are relatively soft, have low melting points, and are poor conductors of electricity.
How Do Covalent Network Solids Differ From Molecular Solids?
Covalent network solids are formed from atoms connected by a continuous network of covalent bonds. This structure leads to extremely high melting points, significant hardness, and, in some cases, good electrical conductivity. Unlike molecular solids, which are composed of distinct molecules, covalent network solids lack discrete molecules, giving them their unique properties.
Can Molecular Solids Conduct Electricity?
Generally, molecular solids are poor conductors of electricity. This is because they lack free electrons or ions that can move through the structure to conduct an electric current. However, some molecular solids can conduct electricity under certain conditions, such as when they are in a molten state or dissolved in a solution.
Why Are Covalent Network Solids So Hard?
The hardness of covalent network solids arises from the strong covalent bonds that extend throughout the material. These bonds require a significant amount of energy to break, making covalent network solids extremely hard and durable compared to other types of solids.
Conclusion
The exploration of molecular solids and covalent network solids uncovers the fundamental role of bonding and structure in determining the properties of materials. By comparing these two classes of solids, we gain insight into how the microscopic arrangement of atoms and molecules can have macroscopic effects on material behavior. This understanding not only enriches our knowledge of solid-state physics but also informs the development of new materials and technologies.
Recognizing the differences between molecular solids and covalent network solids equips us with the ability to tailor materials for specific applications, pushing the boundaries of innovation. Whether it’s in creating stronger materials, improving electrical conductors, or developing novel sensors, the study of these solids is crucial for the advancement of science and technology.

