The human body is an intricate network of systems functioning in harmony, with bones playing a pivotal role in providing structure, protection, and support. Among the microscopic elements that contribute to the complexity and efficiency of bones are lacunae and osteocytes. These components, often overlooked, are fundamental to bone health and functionality.
Lacunae are small cavities in bone tissue that house osteocytes, the most abundant cells in mature bone. Osteocytes, derived from osteoblasts, are entombed in these lacunae and play a crucial role in maintaining bone density and regulating mineral content. They act as the bone’s command centers, directing the remodeling process, which is vital for bone strength and health.
Understanding the difference between lacunae and osteocytes is essential for comprehending how bones maintain their integrity over time. While lacunae serve as the residence for osteocytes, osteocytes themselves monitor and signal the needs for bone repair and remodeling. This symbiotic relationship ensures that our bones remain strong, flexible, and capable of supporting our body’s demands.
Bone Basics
Structure
Overview of Bone Tissue
Bone tissue, or osseous tissue, is a hard, dense connective tissue that forms the structural elements of the skeleton. It is a composite material, both rigid and flexible, consisting mainly of collagen fibers and calcium phosphate. This composition allows bones to withstand compression forces while also providing a degree of flexibility, vital for their protective roles and mechanical functions.
Types of Bone Cells
There are three primary types of bone cells, each playing a unique role in bone health and functionality:
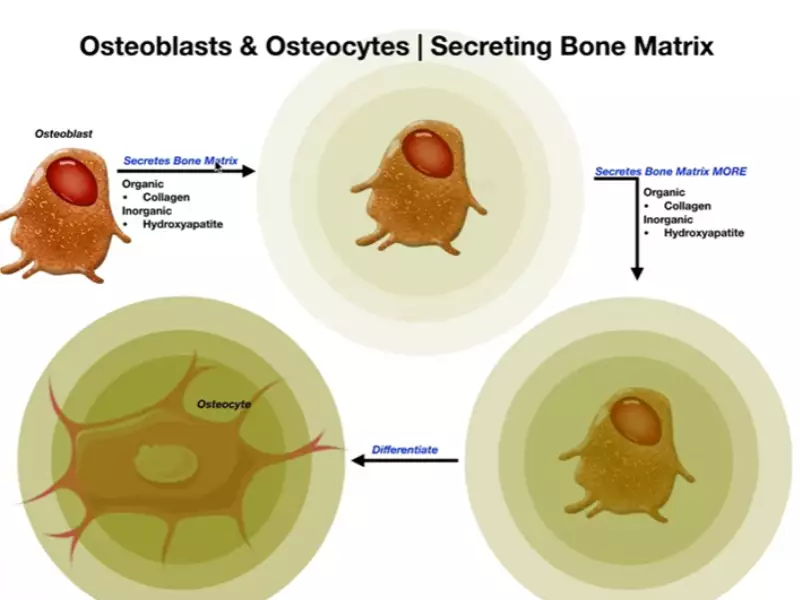
- Osteoblasts – These cells are responsible for forming new bone tissue. They synthesize and secrete the collagen matrix and calcium salts.
- Osteoclasts – In contrast to osteoblasts, osteoclasts break down bone tissue. This process is critical for bone remodeling and calcium regulation.
- Osteocytes – Osteocytes are mature bone cells that originated from osteoblasts. They maintain bone tissue and regulate mineral content. Osteocytes reside in lacunae, small cavities within the bone matrix.
Function
Role in Support and Protection
Bones provide a framework for the body, supporting the structure and shape of the organism. They support soft tissues, protect vital organs by encasing them (e.g., the skull protects the brain, and the ribcage protects the heart and lungs), and facilitate movement by serving as leverage points for muscles.
Mineral Storage and Blood Cell Production
Bones act as reservoirs for minerals, most notably calcium and phosphate. These minerals are essential for various bodily functions, including nerve conduction, muscle contraction, and blood coagulation. Additionally, bones contain marrow, which produces blood cells – a process known as hematopoiesis.
What Are Lacunae?
Definition
Lacunae, in the context of bone tissue, are small cavities that serve as the homes for osteocytes. These spaces are essential for the maintenance and regulation of the bone.
Characteristics
Physical Description
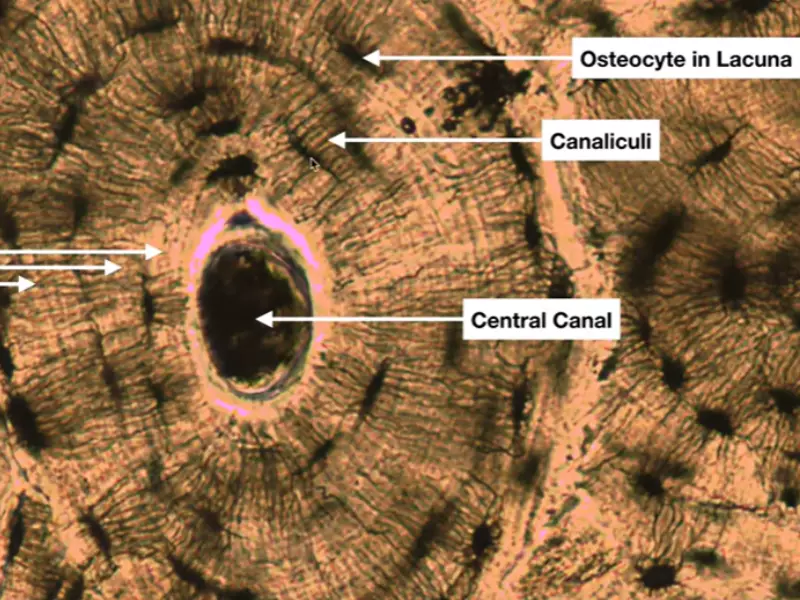
Lacunae are oval-shaped cavities embedded within the bone matrix. They are interconnected by canaliculi, tiny canals that allow for the exchange of nutrients and waste products between osteocytes and the blood supply.
Location Within Bone
Lacunae are found throughout the cortical (compact) and cancellous (spongy) layers of bone. Their distribution is strategic, ensuring that osteocytes can efficiently regulate mineral content and communicate mechanical stresses throughout the bone.
What Are Osteocytes?
Definition
Osteocytes are mature bone cells that play a pivotal role in maintaining bone tissue. They originate from osteoblasts and are the most abundant cell type found in bone.
Characteristics
Development from Osteoblasts
Osteocytes develop from osteoblasts once these bone-forming cells become entombed in the bone matrix they’ve created. This encasement process results in the transformation of an osteoblast into an osteocyte, which then resides in a lacuna.
Functions in Bone
Osteocytes perform several critical functions within the bone:
- Regulate mineral content – They help maintain the balance between bone formation and resorption, crucial for bone density and strength.
- Mechanosensation – Osteocytes can sense mechanical stresses and strains, signaling other cells to deposit or resorb bone as needed.
- Regulation of bone remodeling – Through their extensive network of canaliculi, osteocytes communicate with surface osteoblasts and osteoclasts, directing bone remodeling in response to mechanical and metabolic needs.
Lacunae vs Osteocytes
Location
Lacunae and osteocytes are both integral to the bone matrix, but their positions within this structure are distinct yet interconnected. Lacunae are tiny cavities or spaces within the bone matrix. These spaces are not randomly distributed; rather, they are strategically located to house osteocytes. Osteocytes reside within these lacunae, extending their long, dendritic processes through canaliculi, which are tiny channels in the bone matrix. This arrangement facilitates communication between osteocytes and the surface of the bone, as well as among the osteocytes themselves.
Function
The functions of lacunae and osteocytes are distinct but complementary in maintaining bone health. Lacunae, by providing a residence for osteocytes, play a passive but crucial role in bone biology. They are the structural feature that allows osteocytes to be optimally positioned within the bone to perform their functions.
Osteocytes, on the other hand, are active players in bone remodeling and health. They regulate mineral balance, direct the repair of damaged bone, and signal to other cells involved in bone metabolism. Their strategic position within lacunae allows them to sense mechanical stress and trigger the necessary biochemical responses to maintain bone density and integrity.
Interconnection
The relationship between lacunae and osteocytes exemplifies the sophisticated architecture of bone. Osteocytes, through their dendritic processes, connect with each other and the bone’s surface across the lacunar-canalicular system. This network enables the osteocytes to monitor and regulate the bone’s microenvironment, ensuring the bone adapts to physical demands and maintains its strength over time.
Importance in Bone Health
Lacunae’s Role
Lacunae contribute to bone structure by providing spaces that accommodate the osteocytes. This arrangement is not merely about housing; it is about positioning the osteocytes in such a way that they can effectively perform their roles. The lacunar-canalicular system is essential for nutrient and waste exchange, crucial for osteocyte survival and function. Without lacunae, the intricate signaling processes that osteocytes conduct, which are vital for bone remodeling and health, would not be possible.
Osteocytes’ Role
Osteocytes are the chief regulators of bone health. They manage the delicate balance between bone formation and resorption. By sensing changes in mechanical stress, osteocytes can signal for more bone to be laid down where it is needed and for bone to be removed where it is not. This process ensures that bones remain strong but not overly dense, preventing fractures and other bone-related issues. Additionally, osteocytes regulate the distribution of nutrients within the bone, further highlighting their central role in bone maintenance.
Research Insights
Recent Findings
Recent studies on bone remodeling have shed light on the critical roles that both lacunae and osteocytes play in bone health. Advances in imaging techniques have allowed researchers to observe the lacunar-canalicular system in unprecedented detail, leading to a deeper understanding of how osteocytes communicate and regulate bone metabolism. These studies have also highlighted the plasticity of the bone matrix, demonstrating how osteocytes can remodel their surrounding matrix in response to mechanical stress.
Implications
The implications of these findings are vast, particularly in the treatment of osteoporosis. Osteoporosis, a condition characterized by reduced bone density and increased fracture risk, has been the focus of numerous studies aimed at understanding how bone loses its strength. Insights into the functioning of osteocytes and the structural importance of lacunae offer potential pathways for novel treatments. For instance, therapies that enhance the signaling capabilities of osteocytes or that improve the integrity of the lacunar-canalicular system could lead to breakthroughs in preventing or reversing bone density loss.
FAQs
What are lacunae?
Lacunae are small cavities found throughout the bone matrix, playing a crucial role in bone architecture. They house osteocytes, the cells responsible for bone maintenance and signaling. The presence of lacunae is critical for the communication between osteocytes and the surface of the bone, facilitating the transfer of nutrients and waste products.
How do osteocytes function within bones?
Osteocytes, once osteoblasts that have become embedded in the bone matrix, serve multiple functions. They regulate the bone’s mineral content, ensuring strength and rigidity. Additionally, they orchestrate the bone remodeling process by signaling osteoblasts and osteoclasts in response to mechanical stress or damage, maintaining bone health.
Why is the difference between lacunae and osteocytes important?
Understanding the difference between lacunae and osteocytes sheds light on the intricate processes of bone maintenance and regeneration. It helps in identifying the mechanisms behind bone diseases and devising targeted treatments. Recognizing how osteocytes, within their lacunae, regulate bone metabolism is key to advancements in bone health research and therapies.
Conclusion
The distinction between lacunae and osteocytes is not merely academic but pivotal for understanding bone physiology and pathology. Recognizing how these structures contribute individually and collectively to bone health can enlighten both medical professionals and the general public on the importance of maintaining bone integrity through diet, exercise, and lifestyle choices.
In sum, the interplay between lacunae and osteocytes highlights the sophistication of skeletal biology. As research advances, our grasp of these relationships will undoubtedly deepen, paving the way for innovative treatments for bone-related ailments and improving the quality of life for individuals affected by them.
