Energy measurement in the field of engineering and environmental science is pivotal for determining the efficiency and sustainability of various fuels. Heating values are fundamental parameters in this assessment, encapsulated by two primary metrics: Higher Heating Value (HHV) and Lower Heating Value (LHV). These measures provide critical insight into the potential energy release of fuels during combustion.
The distinction between HHV and LHV lies primarily in their consideration of water vapor produced during combustion. HHV represents the total energy release, assuming all water remains in vapor form and retains heat, whereas LHV assumes that water vapor condenses, and the latent heat is not utilized. This difference is crucial for accurately calculating fuel efficiency and environmental impact.
In practice, the choice between HHV and LHV can influence decision-making in power generation, automotive efficiency, and other industrial applications. Each value offers unique insights into the energy potential of fuels, affecting everything from regulatory compliance to operational strategies and technological development.
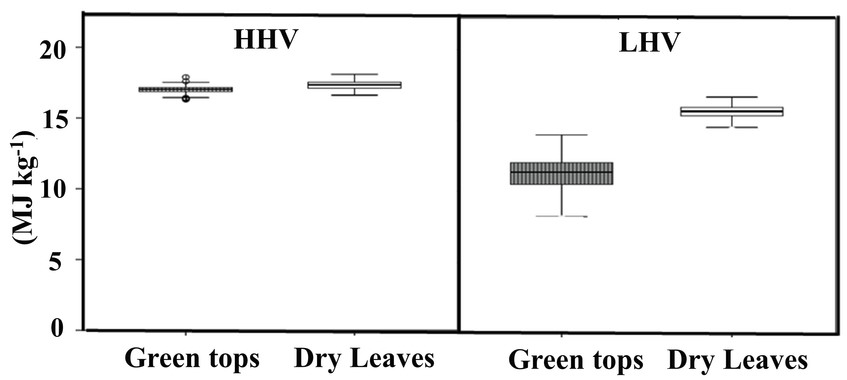
Basic Concepts
What is HHV?
Higher Heating Value (HHV), often referred to as the gross calorific value, is a measure of the total energy content of a fuel. It includes the energy contained in the water vapor produced during combustion, assuming this water remains as vapor and retains its latent heat. HHV provides a comprehensive measure of a fuel’s potential energy release when all produced water is condensed and the heat contained in the water vapor is fully recovered.
Definition and Explanation
HHV is a critical parameter for energy evaluation, especially in contexts where every bit of energy output from a fuel is accounted for. It reflects the maximum energy available from a fuel and is used in settings where energy recovery is optimized, such as in laboratory conditions or theoretical calculations.
How HHV is Measured
The measurement of HHV is typically conducted in a bomb calorimeter. The steps involved are:
- Sample Preparation: A known quantity of the fuel is prepared and placed in the calorimeter.
- Combustion: The fuel is ignited and burned in an oxygen-rich environment to ensure complete combustion.
- Heat Capture: The heat released by combustion is absorbed by a known mass of water surrounding the combustion chamber.
- Temperature Measurement: The rise in water temperature is measured, which correlates directly to the energy released by the fuel.
What is LHV?
Lower Heating Value (LHV), also known as net calorific value, measures the energy release from combustion but excludes the energy contained in the water vapor. It assumes that the water vapor produced during combustion escapes and the latent heat is not recovered.
Definition and Explanation
LHV is a more practical measure for most real-world applications where the condensation of water vapor is not feasible or its heat is not recovered. It provides a realistic view of the energy that can actually be harnessed in most combustion systems.
How LHV is Measured
LHV is measured similarly to HHV but with a key difference in accounting for the heat of vaporization of the water produced:
- Combustion in a Calorimeter: Like HHV, the fuel is burned in a controlled environment.
- Temperature Change Recorded: The increase in temperature of the surrounding water is noted.
- Adjustment for Water Vapor: The heat that would be required to condense the water vapor is subtracted from the total heat measured.
Key Differences
Energy Content Analysis
The energy values of HHV and LHV are pivotal for different applications. HHV will always be higher than LHV because it includes the heat of condensation of water vapor which is not considered in LHV.
Measurement Techniques
The procedures for measuring HHV versus LHV differ primarily in the treatment of water vapor:
- HHV Measurement: Includes all the energy from the burning fuel.
- LHV Measurement: Subtracts the energy used to vaporize water during the combustion process.
Application Relevance
HHV and LHV have practical uses in various industries:
- Energy Sector: HHV is used when evaluating the maximum energy potential of fuels for power generation.
- Automotive: LHV is often used to gauge the real-world efficiency of fuels in engines where exhaust heat recovery is minimal.
Factors Influencing HHV and LHV
Moisture Content
Moisture in fuels significantly impacts both HHV and LHV:
- Higher Moisture Content: Leads to lower HHV and LHV because energy is consumed in evaporating the water content.
- Impact on Calculations: More moisture means more energy is directed away from fuel combustion towards moisture evaporation.
Chemical Composition
The elements like carbon and hydrogen within the fuel profoundly affect HHV and LHV:
- Carbon and Hydrogen: High contents lead to higher HHV and LHV as these elements have high energy content.
- Influence of Other Elements: Elements like oxygen and nitrogen may reduce the heating values by diluting the energy density of the fuel.
Calculation Methods
Step-by-Step Calculation for HHV
Calculating the Higher Heating Value (HHV) of a fuel involves a detailed process that can be illustrated through an example using a common fuel like natural gas. Here’s how it typically proceeds:
- Sample Preparation: Measure a specific amount of natural gas.
- Ignition and Combustion: Burn the gas in a bomb calorimeter, a device designed to capture all released heat.
- Heat Transfer: The heat from the combustion heats up the surrounding water.
- Temperature Measurement: Record the temperature increase of the water.
- Calculations: Calculate the energy content by using the temperature change, the mass of the water, and the heat capacity of water.
- Correction for Water Vapor: Include the energy that would be required to condense the water vapor produced during combustion.
This method ensures that all potential energy from the fuel, including that from condensing water vapor, is accounted for.
Step-by-Step Calculation for LHV
Lower Heating Value (LHV) is calculated similarly to HHV but excludes the heat content of water vapor. Using natural gas as an example, the steps would include:
- Sample Preparation: As with HHV, measure a known amount of natural gas.
- Combustion: Burn the gas in a calorimeter.
- Heat Measurement: Detect the rise in temperature of the water.
- Temperature Recording: Like HHV, note the change in temperature.
- Energy Calculation: Use the temperature rise to calculate the energy content.
- Adjustment for Vapor: Subtract the heat content that would be required to condense any water vapor produced.
This calculation provides a value representing the actual usable heat when the water remains as vapor.
Industry Applications
Power Generation
HHV and LHV in energy production are critical for designing and operating power plants:
- HHV Usage: Power plants that aim to maximize energy extraction from fuel typically use HHV to evaluate potential energy output.
- LHV Usage: In systems where exhaust heat is not recovered, like in many combustion turbines, LHV gives a more accurate measure of the energy that can be effectively used.
Automotive
In the automotive sector, understanding the difference between HHV and LHV is essential for designing engines and evaluating fuel efficiency:
- Fuel Efficiency Reporting: Automobile manufacturers often use LHV to report the fuel efficiency of their engines because it reflects the actual energy that can be utilized in typical driving conditions.
- Engine Design: Knowing the LHV helps engineers optimize engines for better fuel consumption rates by tailoring technologies to the type of energy output they can expect.
Environmental Impact
Emissions and sustainability are significantly impacted by the choice of HHV or LHV for energy calculations:
- Emission Calculations: Using HHV can sometimes overestimate the efficiency of pollution control systems by not accounting for the energy lost as water vapor.
- Sustainability Practices: Accurately reporting and using LHV helps in designing more sustainable technologies by providing a realistic measure of the energy that can be environmentally and economically recovered.
Case Studies
Case Study 1: Coal Power Plant
A coal power plant using HHV and LHV demonstrates different aspects of energy use:
- HHV Application: The plant calculates HHV to determine the maximum possible energy it can get from coal, assuming full condensation of steam.
- Impact on Operation: This value influences everything from boiler design to pollution control strategies, ensuring that all potential energy is utilized.
Case Study 2: Biofuel Production
In biofuel production, the impact of HHV and LHV is directly seen in efficiency and sustainability:
- LHV Consideration: Biofuel producers often use LHV to realistically estimate the energy their products can provide in real-world applications, like in vehicle engines.
- Efficiency Implications: Understanding the LHV helps in optimizing production processes and in marketing the fuel as a viable alternative to fossil fuels, highlighting its practical energy content.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is HHV?
Higher Heating Value (HHV) refers to the maximum amount of energy a fuel can release during combustion when the water vapor produced is condensed back into liquid, allowing the energy it contains to be recovered. It provides a complete assessment of a fuel’s energy potential.
What is LHV?
Lower Heating Value (LHV), on the other hand, measures the energy output of combustion excluding the heat absorbed by the condensation of water vapor. This value is often used when the heat from water vapor is not recoverable, giving a more practical energy value in many real-world scenarios.
How do HHV and LHV affect fuel efficiency?
The choice between using HHV or LHV can significantly impact reported fuel efficiency. For instance, using LHV, which generally reports lower energy content, might suggest greater efficiency in systems where water vapor recovery is not practical, whereas HHV gives a fuller energy profile where comprehensive energy recovery is possible.
Why do different industries prefer different values?
Industries choose HHV or LHV based on specific needs and regulatory frameworks. For example, power plants might use HHV for maximum energy gain calculations, while automotive industries might prefer LHV for more accurate fuel efficiency ratings under typical operating conditions.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between HHV and LHV is more than an academic exercise; it is a practical necessity for industries reliant on accurate and efficient energy use. These measurements not only dictate technological design but also influence environmental strategies and economic outcomes.
The nuances of HHV and LHV encapsulate the complexity of energy systems and their impacts on our world. By choosing the appropriate value for specific applications, professionals can optimize energy usage and contribute to more sustainable industrial practices. This knowledge not only fuels technological advancement but also drives us towards a more energy-efficient future.