Genetic inheritance has fascinated scientists and laypeople alike for centuries, serving as the foundation for understanding how traits are transmitted from parents to offspring. While many theories have attempted to explain these mechanisms, two contrasting concepts, blending inheritance and particulate inheritance, have historically dominated the field. These theories propose different methods for how genetic traits are passed down, influencing not just scientific research but also how we perceive human and animal breeding.
Blending inheritance suggests that parental traits are mixed and permanently integrated to produce intermediate offspring characteristics, much like mixing colors of paint. On the other hand, particulate inheritance, as established by Gregor Mendel, posits that traits are inherited as discrete units, unchanged and recombined in various ways across generations. This principle forms the basis of modern genetics, emphasizing the predictability and recombination of traits without any blending.
Historically, the distinction between these theories has been pivotal in advancing our understanding of genetics. Blending inheritance was once a widely accepted model, believed to explain the continuous variation observed in many traits. However, as particulate inheritance gained scientific backing, it offered a more accurate and predictive framework, leading to groundbreaking developments in genetic research and practical applications in breeding and medical genetics.
Historical Perspectives
Early Theories of Inheritance
The quest to understand how traits are passed from one generation to the next predates modern science, with ideas rooted deeply in folklore, agriculture, and early biology. Initially, many cultures believed in a form of inheritance where traits were a blend or mix from parents, akin to mixing liquids. This concept was intuitive, reflecting everyday experiences where mixing substances resulted in a combination of properties.
Aristotle, the ancient Greek philosopher, proposed one of the earliest scientific theories of inheritance. He believed that male and female parents contributed different types of material, forming a new individual through mixture. This set the stage for future theories that grappled with explaining the mechanics behind trait transmission.
Gregor Mendel’s Contributions
The Father of Genetics
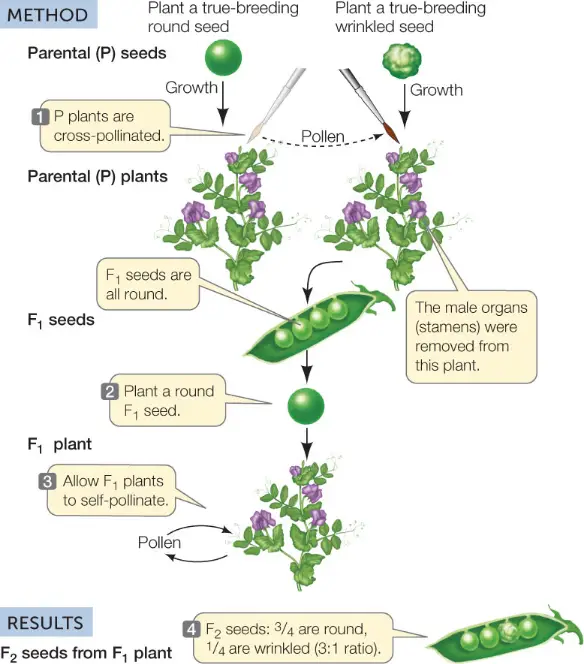
Gregor Mendel, an Augustinian monk, revolutionized our understanding of inheritance in the mid-19th century. Conducting meticulous pea plant experiments, Mendel observed that traits were not blended but instead passed as discrete units, later termed genes. His approach was methodical:
- Mendel controlled pollination between plants with different traits.
- He recorded traits like plant height and flower color across several generations.
Mendel’s Laws
From these experiments, Mendel derived the foundational laws of inheritance:
- Law of Segregation: Each individual has two alleles for a trait, and these alleles separate during the formation of gametes.
- Law of Independent Assortment: Different traits are passed independently of one another.
These insights laid the groundwork for particulate inheritance, providing a clear, predictive model that countered the prevailing blending theories.
Blending Inheritance Explained
Definition and Basic Concept
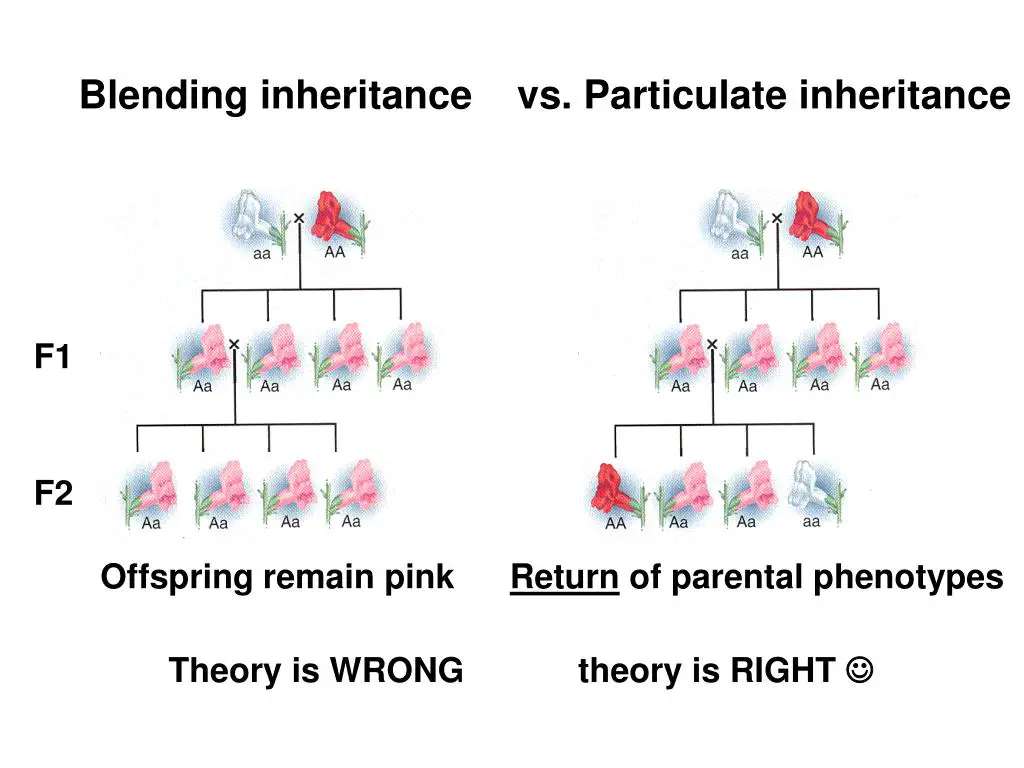
Blending inheritance was once a dominant theory that posited traits from parents are mixed in their offspring, resulting in a permanent, intermediate form. This theory likened heredity to mixing paint, where once two colors blend, the original hues cannot be separated.
Historical Examples and Beliefs
Historically, blending inheritance was used to explain why children often appear to have a mix of physical characteristics from both parents. It seemed logical and observable, straightforward in its explanation of continuous variation in traits such as skin color, height, and intelligence. For centuries, this model was unchallenged, supported by the observable blending of traits in domestic animals and plants.
Particulate Inheritance Explained
Mendelian Genetics Overview
Particulate inheritance, as proposed by Mendel, introduces the concept that traits are inherited as “particles” (today known as genes), maintaining their integrity across generations. This theory asserts that genes come in pairs and are separated during the production of gametes, which leads to the recombination of different traits from both parents in their offspring.
Key Principles and Laws
Mendel’s work distilled into several key principles that form the basis of classical genetics:
- Dominance: Some traits dominate over others, determining phenotype when two different alleles are present.
- Recessive Traits: These traits only appear when an individual has two copies of the recessive allele.
These principles explain why some traits skip generations or reappear, challenging the blending inheritance model which could not account for such patterns.
Key Differences
Genetic Transmission Methods
The fundamental difference between blending and particulate inheritance lies in the transmission of genetic material:
- Blending Inheritance: Traits are mixed and the resulting combination is permanent.
- Particulate Inheritance: Traits are passed as discrete units that do not blend but segregate and assort independently.
Impact on Offspring Variation
Blending inheritance would lead to a homogenization of traits over generations, diminishing variation. In contrast, particulate inheritance explains the rich diversity observed within species, as it allows for new trait combinations and the maintenance of variation through sexual reproduction. This principle is crucial for understanding both evolution and breeding practices.
Scientific Evidence
Studies Supporting Particulate Inheritance
Since Gregor Mendel’s pioneering work, numerous studies have reinforced the theory of particulate inheritance. Key research includes experiments with fruit flies in the early 20th century by Thomas Hunt Morgan, which identified specific genes linked to eye color, establishing the chromosome theory of inheritance. This body of work not only supported Mendel’s findings but also expanded them to demonstrate that genes are located on chromosomes and that they determine specific traits.
Decline of Blending Inheritance Theory
The blending inheritance theory began to lose favor as it failed to explain the reappearance of traits in subsequent generations and the maintenance of diversity within populations. Crucial experiments that contradicted this theory included those on flower color inheritance in snapdragons, where red and white parents produced pink offspring, which subsequently could produce red, pink, or white offspring, defying the permanent blending hypothesis.
Modern Genetics
DNA and Gene Role in Inheritance
Modern genetics firmly anchors on the understanding that DNA carries the genetic information of living organisms and that genes, segments of DNA, dictate specific traits by coding for proteins. This knowledge has revolutionized our understanding of heredity by highlighting how information is transmitted across generations through well-defined molecular mechanisms, rather than through a vague blending process.
Blending vs. Particulate in Contemporary Science
In contemporary science, the particulate nature of inheritance is undisputed. Research into genetic inheritance now focuses on how individual genes interact, how environmental factors affect gene expression, and how genetic engineering can be used to influence these outcomes. The blending theory serves more as a historical footnote, useful only for understanding the evolution of genetic theories.
Practical Examples
Human Traits Analysis
The study of human traits such as eye color, blood type, and genetic disorders illustrates particulate inheritance. For instance, blood type inheritance, where the types A, B, AB, and O result from combinations of different alleles, showcases Mendel’s laws at work in humans and provides clear examples of dominance and codominance.
Agricultural Implications
In agriculture, the principles of particulate inheritance have profound implications. They allow for the predictive breeding of crops and livestock, aiming for desirable traits such as drought resistance in plants or milk production in cows. This selective breeding relies on the understanding that specific traits are inherited according to predictable patterns, rather than blending unpredictably.
Educational Impact
Teaching Genetics in Schools
Genetics is a cornerstone of biology education in schools. Educators emphasize Mendelian genetics to explain the fundamental mechanisms of inheritance, providing students with the tools to understand more complex genetic concepts. This includes the use of Punnett squares to predict the outcomes of genetic crosses, an essential skill in learning about biological inheritance.
Misconceptions in Educational Materials
Despite advancements in genetics education, misconceptions persist. Some educational materials may oversimplify genetics or fail to adequately explain the particulate nature of inheritance, leading to outdated notions such as blending inheritance still being taught in some contexts. Addressing these misconceptions is crucial for accurate scientific literacy.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is blending inheritance?
Blending inheritance is a genetic theory that suggests offspring are a smooth, blended mixture of their parents’ traits. This theory implies that the traits of each parent are averaged and permanently integrated, leading to offspring that exhibit a mix of characteristics without distinct separation of parental traits.
How does particulate inheritance differ?
Particulate inheritance, conceptualized by Gregor Mendel, argues that traits are inherited as distinct units, called genes, which do not blend but are passed down intact. Offspring inherit one gene for each trait from each parent, leading to the expression of one trait or another in various combinations, but not a blend of both.
Why did blending inheritance fall out of favor?
Blending inheritance fell out of favor as it could not explain how traits that disappear in one generation could reappear in subsequent ones. Particulate inheritance, with its clear explanation of genetic recombination and dominance, provided a more robust framework that could accurately predict patterns of heredity, thus becoming the preferred model in genetics.
How does modern genetics view these theories?
Modern genetics primarily supports the particulate model, as it aligns with the observed behavior of DNA and genes in heredity. The blending theory is largely considered obsolete, though it remains a useful historical context for understanding the evolution of genetic science.
Conclusion
The exploration of how traits are inherited from one generation to the next has significantly evolved from the days of blending inheritance to the more precise understandings afforded by particulate inheritance. This shift not only revolutionized genetics but also enhanced our ability to manipulate genetic outcomes in medicine and agriculture. By embracing Mendel’s principles, modern genetics continues to unlock the complexities of DNA and gene interaction, paving the way for advancements in genetic engineering and therapy.
Understanding the foundational differences between blending and particulate inheritance enriches our appreciation for the complexities and beauty of biological inheritance. It underscores the importance of precise scientific models in unraveling the intricate patterns of life that impact both our present and future generations.

