Weather metrics such as dew point and humidity are pivotal in forecasting conditions, impacting everything from what we wear to how we plan our day. These terms frequently pop up in weather reports, yet their nuanced differences and interconnectedness often go unexplored by the general public. Grasping the relation between these two can significantly enhance our understanding of weather phenomena.
The relation between dew point and humidity is a fundamental concept in meteorology that defines how moisture in the air contributes to our perception of the weather. In essence, while humidity measures the air’s moisture content, the dew point is the temperature at which air becomes saturated and moisture begins to condense. This relationship provides a clear indicator of how humid it feels outside, affecting comfort levels and weather conditions.
Diving into the specifics, humidity and dew point offer insights into the atmospheric conditions that influence daily weather patterns. For instance, a higher dew point indicates more moisture in the air, often leading to muggier conditions. Conversely, lower humidity levels can signify dryer air, affecting everything from skin hydration to the spread of wildfires. Understanding these concepts not only enriches our knowledge of the weather but also aids in making informed decisions related to health, agriculture, and daily activities.

Basics of Humidity
What is Humidity?
Humidity is a measure of the water vapor content in the air. Water vapor is the gaseous state of water and is invisible to the human eye. Humidity plays a crucial role in how we perceive the weather and our comfort levels.
Types of Humidity
Absolute Humidity
This measures the actual amount of water vapor in the air, regardless of the air’s temperature. It’s usually expressed in grams of water vapor per cubic meter of air (g/m³).
Relative Humidity
A more familiar term, relative humidity, expresses the current amount of moisture in the air as a percentage of the maximum amount of moisture the air can hold at that temperature. For example, a relative humidity of 50% means the air is holding half the moisture it can hold at that temperature.
Specific Humidity
Specific humidity is the ratio of the mass of water vapor to the total mass of the air parcel, including the water vapor. This is a useful measure in scientific studies and meteorology.
Measuring Methods
To gauge humidity, various tools and techniques are employed:
- Hygrometers are instruments designed to measure the moisture content in the environment.
- Psychrometers consist of two thermometers, one dry and one covered with a moist cloth. By comparing temperatures, the humidity level can be deduced.
- Dew point hygrometers measure the temperature at which dew forms, giving insights into moisture content.
Dew Point Explained
What is Dew Point?
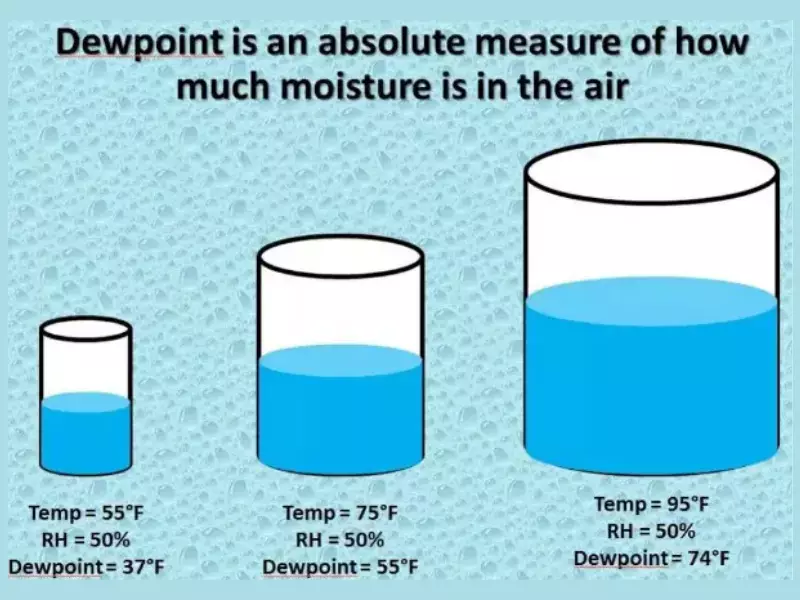
The dew point is the temperature at which air must be cooled for water vapor to condense into dew. It is a direct indicator of the moisture content in the air. A higher dew point means more moisture in the air.
How It’s Measured
Measuring the dew point requires observing the point at which dew forms under controlled conditions. This can be achieved through:
- Chilled mirror technology, where air is cooled until condensation forms on a mirror, and the temperature at this point is the dew point.
- Electronic sensors that calculate the dew point based on humidity and temperature readings.
Relevance to Weather
The dew point provides valuable insights into weather conditions. High dew points indicate muggy weather, while low dew points suggest dry conditions. It helps in predicting fog, frost, and precipitation chances.
Humidity vs. Dew Point
Key Differences
While both humidity and dew point relate to moisture in the air, they measure different aspects:
- Humidity is about the air’s moisture capacity at a given temperature.
- Dew point is the absolute measurement of moisture in the air, indicating the temperature at which dew forms.
Interconnection
Despite their differences, humidity and dew point are interconnected. High humidity levels can lead to a high dew point, signaling saturated air. Understanding both metrics gives a complete picture of the air’s moisture content.
Impact on Weather Forecasting
Forecasters use humidity and dew point to predict weather patterns. High dew points are associated with uncomfortable weather and potential for heavy rain or storms. Humidity levels help anticipate heat index values, critical for heat advisories.
Factors Influencing Dew Point
Temperature
Temperature changes can dramatically affect the dew point. Warmer air can hold more moisture, raising the dew point. Conversely, cooling air can lower the dew point, leading to dew formation or even frost.
Air Pressure
Variations in air pressure can influence the dew point. High pressure can suppress the dew point, while low pressure, associated with storm systems, can increase moisture and the dew point.
Seasonal Changes
Seasonally, dew point values fluctuate. Summer brings higher dew points due to increased evaporation and moisture. In winter, colder temperatures mean lower dew points, resulting in drier air.
Impact on Daily Life
Comfort Levels
Humidity and dew point significantly influence our comfort levels. High humidity can make temperatures feel warmer than they are, as the body struggles to cool down through sweat evaporation. Conversely, low humidity can lead to dry skin and discomfort in the respiratory system. The dew point offers a more accurate reflection of how the air feels. A dew point below 60°F generally feels comfortable, while readings above 70°F are often muggy and oppressive.
Health Implications
The relationship between humidity, dew point, and health is profound. High humidity levels can exacerbate conditions like asthma and allergies, as moist air promotes mold growth and dust mite populations. Dry air, on the other hand, can aggravate respiratory issues and increase susceptibility to colds and flu by drying out the mucous membranes. Maintaining indoor humidity between 30% and 50% is recommended for optimal health.
Agriculture and Gardening
For farmers and gardeners, understanding humidity and dew point is essential for plant health. High humidity can lead to fungal diseases in crops, while too low humidity may stress plants, leading to wilting or reduced yield. Dew points that are too high or too low can significantly affect plant growth and productivity, making monitoring these metrics crucial for agriculture management.
Measuring Tools
Hygrometers
Hygrometers are tools designed to measure the humidity level in the air. They come in various types, including digital models that offer precise readings and analog versions that provide a general humidity range. Modern hygrometers can also track changes over time, helping to maintain ideal indoor conditions.
Dew Point Calculators
Dew point calculators are digital tools or online resources that compute the dew point based on temperature and relative humidity inputs. They are invaluable for meteorologists and those interested in detailed weather analysis, providing a quick way to determine air moisture content and potential for precipitation or fog.
Applications in Meteorology
Meteorologists rely on instruments like sling psychrometers, which use wet and dry bulb thermometers to measure humidity and calculate the dew point. These measurements are critical for forecasting weather conditions, predicting precipitation, and advising on humidity-related health advisories.
Practical Applications
Weather Prediction
Accurate weather prediction hinges on understanding humidity and dew point levels. Meteorologists use these measurements to forecast precipitation, fog, and heat index values. High dew points can signal impending storms or heavy rainfall, making this data essential for early warning systems.
Climate Control in Buildings
In building management, controlling humidity and understanding dew point are vital for creating comfortable, healthy environments. HVAC systems often include humidifiers and dehumidifiers to maintain optimal humidity levels, preventing mold growth and ensuring occupant comfort. Monitoring dew point levels can also help avoid condensation and structural damage.
Agriculture Management
Farmers use humidity and dew point data to make informed decisions about irrigation, planting, and harvesting. Managing humidity levels can protect crops from pests and diseases, optimize growth conditions, and increase yield. This is particularly crucial in greenhouses, where controlled environments are key to plant health.
Case Studies
Extreme Weather Events
Studying extreme weather events, like the 1995 Chicago heatwave, reveals the deadly impact of high humidity and dew points. During this event, temperatures soared, but the high humidity levels, indicated by dew points over 80°F, significantly increased the heat index, leading to over 700 deaths. This case highlights the importance of heat advisories based on humidity and dew point readings.
Effect on Health Outbreaks
Research has shown that humidity and dew point levels can affect the spread of infectious diseases. For example, flu viruses are more stable in low humidity conditions, leading to increased transmission rates in winter. Conversely, high humidity can foster mold growth, affecting those with respiratory conditions. Monitoring and managing indoor humidity can mitigate these health risks.
Innovations in Climate Control
Advancements in climate control technology demonstrate the practical applications of understanding humidity and dew point. Innovations like smart HVAC systems, which automatically adjust based on real-time humidity and temperature readings, are improving indoor air quality and energy efficiency. Such systems can prevent the overcooling or overheating of spaces, enhancing comfort and reducing energy consumption.
FAQs
What is Humidity?
Humidity represents the concentration of water vapor present in the air. The amount of moisture air can hold varies with temperature; warmer air can hold more moisture compared to cooler air. This characteristic of humidity plays a crucial role in determining the comfort level and weather conditions we experience.
How Does Dew Point Affect Weather?
The dew point temperature has a direct impact on weather by indicating the amount of moisture in the air. A higher dew point suggests more moisture, which can lead to cloud formation, fog, or precipitation when air temperature drops to this point. It’s a key factor in predicting rain, snow, and overall atmospheric comfort.
Why Is Understanding Dew Point and Humidity Important?
Understanding the relationship between dew point and humidity is vital for accurate weather forecasting and preparing for environmental conditions. It affects everything from agriculture, where humidity levels influence crop growth and pest activity, to daily comfort and health, informing us about potential heat stress or ideal conditions for outdoor activities.
Conclusion
Grasping the intricate relationship between dew point and humidity not only demystifies weather forecasts but also equips us with the knowledge to navigate the environment more effectively. These metrics, often overlooked, play a significant role in shaping our daily experiences, from the simplest tasks to complex agricultural and health-related decisions.
In a world where climate patterns are becoming increasingly unpredictable, understanding these fundamental weather principles becomes paramount. This knowledge not only enriches our interaction with the natural world but also fosters a deeper appreciation for the delicate balance that governs our planet’s atmospheric conditions.
