Organic chemistry, a branch of science devoted to the study of carbon-based compounds, has seen tremendous growth through the development of numerous chemical reactions. Among these, the Woodward and Prevost reactions stand out due to their unique applications and mechanisms. These reactions are pivotal in synthesizing complex organic molecules, essential in various scientific advancements.
The Woodward reaction, primarily known for constructing sterically strained alkenes, utilizes the photochemical generation of ketenes. In contrast, the Prevost reaction involves the stereospecific conversion of alcohols into alkenes through a two-step process involving organohalide intermediates. These methods are fundamental tools in organic synthesis, offering precise control over molecular architecture.
The importance of these reactions extends beyond their definitions, touching on their mechanisms, applications, and role in advancing organic synthesis. This discussion seeks to explore their intricacies and utility in modern chemistry, providing a clear view of their impact and relevance in the scientific community.
Woodward Reaction
Definition and Mechanism
The Woodward reaction is a prominent chemical process named after Robert Burns Woodward, a Nobel Prize-winning chemist. This reaction involves the photochemical conversion of α-diketones into ketenes, which subsequently undergo intramolecular addition to form cyclic ketones. The mechanism is initiated by ultraviolet light, which cleaves the carbon-carbon bond between the carbonyl groups of the α-diketone. This cleavage results in the formation of highly reactive ketene intermediates. These intermediates quickly react with nearby molecules, often resulting in the formation of cyclobutanones or other cyclic structures.
Key Features
Key features of the Woodward reaction include:
- Photochemical Activation: This reaction requires ultraviolet light to initiate the chemical process, distinguishing it from thermal or catalytic methods.
- Formation of Cyclobutanones: One of the most common products of this reaction is cyclobutanones, which are valuable in various synthetic applications.
- Stereospecificity: The reaction can be controlled to yield products with specific stereochemical configurations, crucial for creating biologically active compounds.
Applications in Synthesis
The applications of the Woodward reaction in chemical synthesis are diverse and impactful:
- Synthesis of Complex Molecules: Used in the synthesis of complex organic molecules, particularly those with strained rings, which are challenging to produce through other methods.
- Pharmaceuticals: Many pharmaceutical compounds benefit from the unique structures that can be built using this reaction.
- Material Science: Organic materials with specific properties can be synthesized using the architectural control afforded by this reaction.
Examples and Case Studies
- Synthesis of Vitamin D: Woodward’s reaction has been utilized in the synthesis of analogs of Vitamin D, which are used to study bone growth and calcium metabolism.
- Creation of Natural Products: Several complex natural products have been synthesized using modifications of the Woodward reaction, showcasing its versatility in organic synthesis.
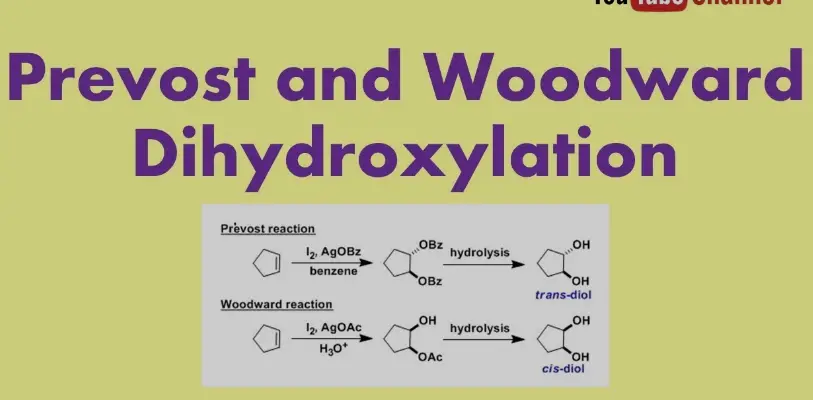
Prevost Reaction
Definition and Mechanism
The Prevost reaction, named after Charles Prevost, involves the stereospecific conversion of alcohols into alkenes. This transformation is achieved through the formation of an organohalide intermediate by reacting the alcohol with a halogenating agent. The organohalide then undergoes an elimination reaction, typically promoted by a strong base, to form the alkene. This method allows for precise control over the geometry of the resulting double bond, making it particularly valuable for synthesizing alkenes with desired stereochemistry.
Distinctive Characteristics
- Control Over Stereochemistry: The ability to dictate the E or Z configuration of the alkene product.
- High Yield and Selectivity: This reaction is known for its high efficiency and selectivity, making it a preferred method in synthetic organic chemistry.
Applications in Chemical Synthesis
- Synthesis of Steroids: Widely used in the synthesis of steroids and other complex molecules where double bond configuration is critical.
- Petrochemicals: Plays a role in the manufacture of petrochemicals where alkenes serve as key intermediates.
Examples and Case Studies
- Manufacture of Insect Pheromones: The reaction has been used in the synthesis of pheromones where specific double bond configurations are crucial for biological activity.
- Synthesis of Terpenes: Terpenes, important in both natural and synthetic chemistry for their aromatic qualities, are often synthesized using the Prevost reaction.
Comparative Analysis
Similarities Between Reactions
Both the Woodward and Prevost reactions are essential tools in organic synthesis, particularly in the construction of molecules with complex ring systems or precise double bond configurations. They share a common goal of improving the specificity and efficiency of synthetic pathways in chemical laboratories.
Key Differences
Despite their shared goals, the Woodward and Prevost reactions differ significantly in their approach and scope:
- Mechanism: Woodward’s reaction uses photochemical energy to create reactive intermediates, whereas Prevost’s reaction utilizes halogenation followed by elimination.
- Product Type: The Woodward reaction typically yields cyclic ketones, while the Prevost reaction produces alkenes.
- Application Scope: Woodward’s reaction finds extensive use in the synthesis of cyclic and strained molecules, while Prevost’s reaction is more focused on creating alkenes with specific stereochemical properties.
Practical Implications
Impact in Organic Chemistry
The Woodward and Prevost reactions have markedly influenced organic chemistry, providing robust methods for constructing complex molecular architectures. These reactions enable chemists to synthesize compounds with a level of precision that was previously unattainable. Their introduction has led to significant advancements in the synthesis of natural products, pharmaceuticals, and materials with specific optical or physical properties. By allowing for the precise manipulation of molecular structures, these reactions contribute substantially to the field’s ability to innovate and solve complex chemical problems.
Use Cases in Industry
In the industrial sector, the applications of these reactions are extensive and varied. They play a crucial role in:
- Pharmaceuticals: Both reactions are employed to create complex molecules that serve as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). Their ability to construct specific molecular configurations is crucial for the activity of these compounds.
- Agrochemicals: The synthesis of herbicides and pesticides often requires the precise construction of organic molecules, a task well-suited to these reactions.
- Material Science: Advanced materials, including polymers and organic semiconductors, rely on the unique capabilities of these reactions to tailor molecular structures for specific functions.
Challenges and Solutions
Common Challenges
Chemists often encounter several challenges when implementing the Woodward and Prevost reactions:
- Sensitivity to Conditions: Both reactions require precise control over reaction conditions, such as temperature and light exposure, which can complicate their use on an industrial scale.
- Scalability: While effective on a laboratory scale, scaling these reactions for industrial production often introduces inefficiencies and increases the risk of side reactions.
Overcoming Obstacles
To address these challenges, several strategies have been developed:
- Advanced Reaction Monitoring: Utilizing real-time monitoring techniques to precisely control the reaction conditions, ensuring optimal yields and minimizing by-products.
- Catalyst Development: Innovations in catalyst design have improved the efficiency and selectivity of these reactions, making them more suitable for large-scale applications.
Future Prospects
Emerging Trends
The continuous evolution of organic chemistry sees emerging trends that could further enhance the utility of the Woodward and Prevost reactions. Notably, the integration of computational chemistry and machine learning offers potential to predict outcomes and optimize conditions more efficiently than ever before. Additionally, the development of greener chemistry practices is guiding modifications of these reactions to use less toxic solvents and reagents, aligning with industry-wide sustainability goals.
Potential Developments
Looking ahead, potential developments in the field include:
- Automation and Robotics: The use of automated systems and robotics in organic synthesis could standardize and scale the Woodward and Prevost reactions, reducing human error and increasing reproducibility.
- Custom Reaction Media: Research into novel solvents and reaction media that can increase the efficiency and selectivity of these reactions is ongoing. Such advancements could mitigate current limitations related to sensitivity and scalability.
FAQs
What is the Woodward Reaction?
The Woodward reaction involves the photochemical creation of ketenes from α-diketones, which then react to form cyclobutanones or other cyclic products. This reaction is significant for its role in synthesizing complex, cyclic organic structures often used in pharmaceuticals.
What is the Prevost Reaction?
The Prevost reaction converts alcohols into alkenes using a two-step mechanism that involves the formation of an organohalide and subsequent elimination. This method is prized for its ability to control stereochemistry, crucial in creating substances with desired biological activities.
How do Woodward and Prevost reactions differ?
While both reactions are used to synthesize alkenes, the Woodward reaction typically uses photochemical processes to create ketenes, whereas the Prevost reaction converts alcohols directly through halogenation and elimination processes. Each has unique utility depending on the synthesis goals and the desired molecular structure.
What are the applications of these reactions?
Both reactions are extensively used in the synthesis of complex organic molecules. The Woodward reaction is particularly useful in the creation of cyclic compounds, while the Prevost reaction is essential for forming alkenes with precise stereochemical configurations.
Why are these reactions important in organic synthesis?
The Woodward and Prevost reactions provide chemists with powerful tools to build complex molecular structures with high precision. They are crucial in drug development and materials science, where the exact arrangement of atoms can significantly affect a molecule’s properties and effectiveness.
Conclusion
The Woodward and Prevost reactions represent critical methodologies within organic chemistry, enabling the precise manipulation of molecular structures with widespread applications in science and industry. Their ability to craft complex molecules with specific configurations makes them invaluable in research and commercial synthesis.
Understanding these reactions not only enriches the field of organic chemistry but also pushes the boundaries of what can be achieved in medicinal chemistry and materials engineering. As research continues, the evolving applications of these reactions will likely play a pivotal role in future scientific breakthroughs and technological advancements.