Teichoic acids are crucial components found in the cell walls of most gram-positive bacteria, playing significant roles in cellular processes and pathogenesis. These substances, primarily composed of glycerol phosphate or ribitol phosphate residues, are integral to bacterial physiology and morphology. Their study sheds light on the intricate mechanisms of bacterial life and their interactions with host organisms.
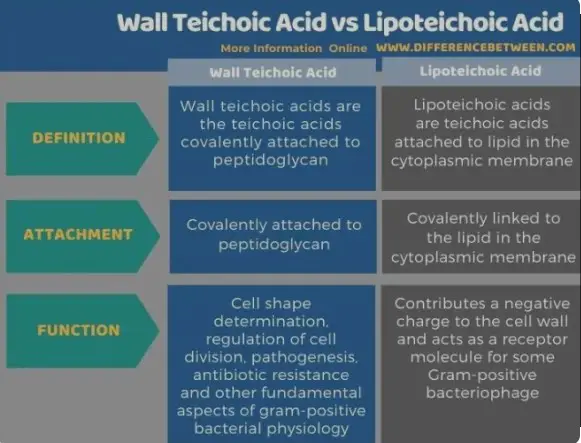
Wall teichoic acid (WTA) and lipoteichoic acid (LTA) differ mainly in their location and molecular structure within the bacterial cell. WTA is covalently bound to the peptidoglycan layer of the cell wall, whereas LTA is anchored in the cytoplasmic membrane. These differences profoundly impact their functions, from providing structural integrity to playing roles in host-pathogen interactions.
The distinction between WTA and LTA is not merely structural but extends to their biosynthetic pathways and functional contributions in bacterial ecology and pathogenicity. Understanding these differences is crucial for developing targeted antibiotics and therapeutic strategies, particularly as antibiotic resistance becomes an increasing concern.
Teichoic Acids Basics
Definition and Roles
Teichoic acids are polymers composed predominantly of glycerol phosphate or ribitol phosphate, which are linked via phosphodiester bonds. These molecular compounds are integral to the structure and function of gram-positive bacteria, serving several crucial roles. Firstly, they maintain the cell wall integrity, providing rigidity and shape to the bacterial cell. Secondly, teichoic acids play a pivotal part in the cell’s adherence to surfaces and other cells, facilitating the formation of biofilms. This ability is particularly significant in the context of infections, as it aids bacterial colonies in evading the host’s immune system. Moreover, teichoic acids are involved in the regulation of ion movement across the cell wall, essential for maintaining an appropriate internal environment in bacterial cells.
Types of Teichoic Acids
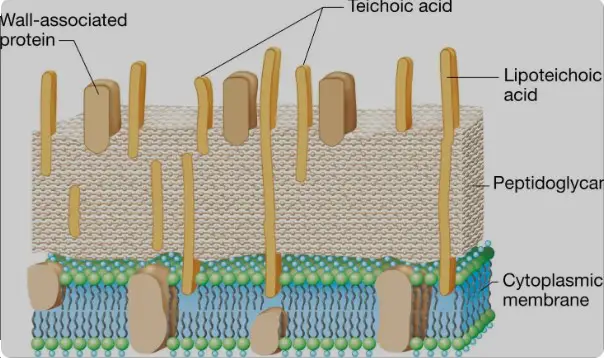
Teichoic acids can be classified mainly into two types: Wall Teichoic Acid (WTA) and Lipoteichoic Acid (LTA). Both types are found in the cell envelopes of most gram-positive bacteria but differ in their structure and location within the cell.
Wall Teichoic Acid (WTA)
Structure and Composition
WTA is a polymer that is covalently linked to the peptidoglycan layer of the bacterial cell wall. Its backbone typically consists of repeated units of phosphodiester-linked poly(glycerol phosphate) or poly(ribitol phosphate). These chains are often modified with D-alanine esters and sugars, which can vary depending on the bacterial species, thereby affecting the properties of the WTA and its cell wall.
Biosynthesis Process
The biosynthesis of WTA is a complex, enzyme-driven process that involves multiple steps:
- Initiation: It starts in the cytoplasm where the precursors of the teichoic acid backbone are synthesized.
- Polymerization: Enzymes like glycerol phosphate transferase add glycerol or ribitol phosphate units to the growing polymer.
- Modification: Specific residues like D-alanines are added to the polymer, which can affect the overall charge and hydrophilicity of the molecule.
- Transport and Attachment: Once synthesized, WTA is transported out of the cytoplasm and anchored onto the peptidoglycan framework of the cell wall.
Functions in Bacteria
WTA has several essential functions in bacterial life cycles:
- Structural Support: It provides structural integrity and rigidity to the cell wall.
- Protection: WTA contributes to the cell’s resistance against environmental stresses, such as changes in pH and ionic strength.
- Host Interaction: It plays a crucial role in adhesion to host tissues, a key factor in the pathogenicity of many bacteria.
Lipoteichoic Acid (LTA)
Composition Details
LTA is similarly constructed from glycerol phosphate or ribitol phosphate units; however, unlike WTA, LTA is anchored directly into the lipid membrane. It often has a simpler structure and may carry different modifications, such as lipids or additional carbohydrates, which impact its function and interaction with the environment.
Pathway of Synthesis
The synthesis pathway of LTA mirrors that of WTA in its complexity but differs in the final stages:
- Synthesis in Cytoplasm: Like WTA, the LTA synthesis also begins in the cytoplasm.
- Polymerization and Modification: The polymer is assembled and modified in similar ways to WTA.
- Anchoring: The critical distinction lies in its integration; LTA is attached to a lipid anchor, which embeds it into the cell membrane.
Roles in Bacterial Physiology
LTA’s roles are vital for the survival and virulence of bacteria:
- Membrane Stability: LTA contributes significantly to the stability and integrity of the bacterial membrane.
- Host Immune Response: It is a key player in interactions with the host’s immune system, often triggering inflammatory responses.
- Biofilm Formation: LTA aids in the formation and maintenance of biofilms, enhancing bacterial resistance to antibiotics.
Comparative Analysis
Structural Differences
The fundamental structural distinction between Wall Teichoic Acid (WTA) and Lipoteichoic Acid (LTA) lies in their respective locations and attachment points within the bacterial cell. WTA is covalently bound to the peptidoglycan layer of the cell wall, which provides external structural support. In contrast, LTA is anchored in the cytoplasmic membrane, interfacing directly with the cellular environment. This anchorage influences their respective physical properties and functions, with WTA often being more rigid and LTA more flexible due to its lipid component.
Biosynthetic Pathways Contrast
The biosynthetic pathways of WTA and LTA highlight significant differences:
- WTA synthesis occurs through a well-defined pathway involving multiple enzymes that construct the polymer attached to the cell wall. This process is tightly regulated to ensure correct assembly and modification.
- LTA synthesis, while similar in the initial stages, diverges as the molecule is prepared for insertion into the lipid membrane, involving different enzymes and regulatory mechanisms. This difference underscores the unique roles these molecules play within the bacterial cell.
Functional Distinctions
Functionally, WTA and LTA contribute differently to bacterial physiology:
- WTA is primarily involved in maintaining cell wall integrity and shape, crucial for bacterial growth and division.
- LTA affects the cell membrane’s properties, such as permeability and immune response interactions, which are vital for the bacteria’s adaptation to environmental stresses.
Biological Implications
Impact on Bacterial Virulence
Teichoic acids significantly impact bacterial virulence. WTA and LTA affect how bacteria interact with host tissues. For example, modifications in WTA can increase a bacterium’s ability to adhere to host cells, facilitating infections. Conversely, LTA can modulate the host immune response, enhancing the survival of bacteria within the host.
Role in Immune Evasion
One of the key roles of LTA is its involvement in immune evasion. By modifying the immune response through interaction with toll-like receptors on host immune cells, LTA can help the bacteria avoid detection and destruction by the host’s immune system. This interaction triggers a response that can be either beneficial or harmful to the host, depending on the context of the infection.
Importance in Antibiotic Resistance
The study of teichoic acids also plays a critical role in understanding and combating antibiotic resistance. Alterations in teichoic acid composition can lead to reduced efficacy of antibiotics that target the cell wall. For instance, certain bacteria can modify their WTA structure to reduce the binding effectiveness of specific antibiotics, a strategy that contributes to the growing problem of antibiotic resistance.
Research and Developments
Recent Studies on Teichoic Acids
Recent research has provided deeper insights into the function and potential of teichoic acids as targets for antibiotic development. Studies have shown that targeting the biosynthetic pathways of WTA and LTA can disrupt bacterial growth and virulence, offering a promising approach for new antibacterial therapies. Researchers are exploring inhibitors that can specifically block these pathways, potentially leading to more effective treatments for bacterial infections.
Technological Advancements in Study
Technological advancements have significantly enhanced our ability to study teichoic acids. Techniques such as CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing and advanced mass spectrometry have allowed scientists to manipulate bacterial genomes and analyze teichoic acid structures and functions with unprecedented precision. These tools have not only expanded our understanding of bacterial physiology but also accelerated the development of teichoic acid-targeted therapies.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Wall Teichoic Acid?
Wall teichoic acid (WTA) is a polymer found attached to the cell wall of gram-positive bacteria. It plays multiple roles, including providing structural integrity, shaping the cell, and regulating cell division.
What is Lipoteichoic Acid?
Lipoteichoic acid (LTA) is a glycerophosphate polymer located in the membrane of gram-positive bacteria. It is crucial for maintaining cell envelope integrity and mediating host-pathogen interactions.
How do WTAs differ from LTAs?
While both are teichoic acids, WTA is bound to the cell wall, and LTA to the cell membrane. Their chemical compositions also differ, impacting their functions and interactions within the host.
Why are teichoic acids important in medicine?
Teichoic acids are targets for novel antibacterial therapies. Understanding their structure and function helps develop drugs that can disrupt bacterial growth and colonization, crucial for treating infections.
Conclusion
Teichoic acids, specifically wall teichoic acid and lipoteichoic acid, are more than mere structural components of gram-positive bacteria; they are pivotal in the interactions between pathogens and hosts. Their study not only enhances our understanding of bacterial pathogenesis but also informs the development of antibacterial therapies.
As research continues to unravel the complex roles of WTA and LTA, the potential to develop targeted treatments that curb bacterial resistance and effectively treat infections becomes increasingly feasible. This highlights the importance of teichoic acids in the broader context of microbial research and public health.

