Leaves play a pivotal role in the life of a plant, engaging in processes vital for survival such as photosynthesis, transpiration, and gas exchange. Yet, beyond these essential functions, leaves vary widely in appearance, with some displaying plain green surfaces and others showcasing a spectrum of colors in variegated patterns. This variety not only adds to the visual appeal of plants but also speaks to a diversity of underlying biological mechanisms.
Variegated leaves differ from simple leaves primarily in their coloration. Variegated leaves feature streaks, patches, or patterns of multiple colors, typically including white or yellow alongside green. This is contrasted by simple leaves, which are uniformly green. The main difference lies in the presence of non-green pigments in variegated leaves, which can affect the leaf’s function and plant’s overall health.
In the plant world, these variations are not just cosmetic. They can influence the plant’s photosynthetic efficiency, growth rate, and adaptability to its environment. Variegated leaves, often prized for their beauty in horticultural circles, may require more specific care conditions due to their unique pigment configuration and reduced chlorophyll content.
Leaf Basics
What is a Leaf?
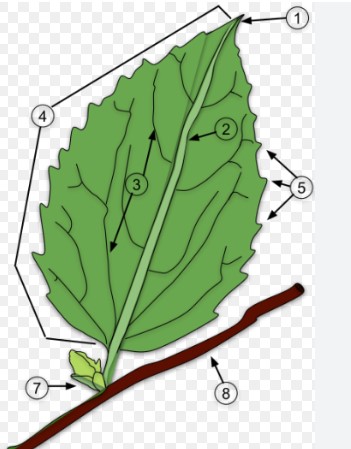
A leaf is a vital organ of a plant, primarily involved in the process of photosynthesis, where sunlight is converted into chemical energy. It is usually green and flat, attached to the plant’s stem directly or via a stalk known as the petiole. The typical leaf consists of three main parts: the blade, the petiole, and sometimes, small leaf-like structures called stipules.
Functions of Leaves
Leaves perform several critical functions that are essential for the survival and growth of plants:
- Photosynthesis: Leaves are the primary site for photosynthesis, absorbing light and carbon dioxide to produce oxygen and glucose.
- Transpiration: They help in the process of transpiration, where water evaporated from the leaf surfaces drives the uptake of water and nutrients from the roots.
- Gas Exchange: Leaves facilitate gas exchange by opening and closing their stomata, tiny openings on their surface, to take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen.
- Storage: Some leaves also serve as storage organs for water and food.
Variegated Leaves
Definition
Variegated leaves are those that have different colors in discrete areas—unlike the uniform green of typical leaves. This variegation can appear as stripes, spots, borders, or an intermixture of colors, primarily white, yellow, and green.
Explanation of Variegation in Leaves
Variegation happens when leaves display zones of different colors due to uneven distribution of chlorophyll. The areas without green pigment allow other colors, caused by different pigments such as carotenoids and anthocyanins, to be visible.
Causes
Genetic Factors
Some plants naturally exhibit variegation as a genetic trait. This pattern can be stable and passed down to new generations, showing consistent patterns across the species.
Environmental Factors
Environmental conditions like light exposure, temperature, and chemical mutagens can also cause variegation. Sometimes, such environmental variegation is reversible if conditions change.
Types
Chimeral Variegation
This type of variegation occurs when there are two different types of genetic makeup in the plant cells. Chimeral variegation can result from a mutation during cell division, leading to a sector of cells that differ genetically from the rest of the plant.
Pattern-Gene Variegation
Pattern-gene variegation is determined by genetic factors that cause specific patterns. These are controlled by plant genetics and typically follow predictable rules within the species.
Reflective Variegation
Reflective variegation is due to the presence of air spaces within the leaf that reflect light, giving the leaf a silvery or white appearance. This type is less about pigment and more about the leaf structure.
Benefits
Aesthetic Value
Variegated leaves are highly valued in horticulture and interior decorating for their striking appearances. They add visual interest and contrast in gardens and indoor spaces.
Possible Adaptive Advantages
Although variegated leaves may absorb less sunlight, the lighter parts of the leaves can help reduce the chances of sunburn in intensely sunny environments, potentially a protective adaptation.
Challenges
Growth Issues
Plants with variegated leaves often grow more slowly than their non-variegated counterparts due to reduced chlorophyll. Less chlorophyll means less energy production, impacting overall growth.
Care Requirements
Variegated plants might need more care regarding light exposure and nutrient supply. They require specific lighting conditions to maintain their coloration and avoid reverting to a fully green form.
Simple Leaves
Definition
Simple leaves are defined by their single, undivided blade attached to the stem with a stalk, known as a petiole. Unlike variegated leaves, simple leaves exhibit a uniform color, usually green, which is due to the consistent presence of chlorophyll throughout the leaf’s surface.
Characteristics of Simple Leaves
Simple leaves are known for their uniformity and simplicity in design, making them the archetype of foliage in plant biology. These leaves have a single, coherent blade, which can vary in shape and size but lacks the complex patterns found in variegated types.
Common Types
Simple leaves come in various shapes and edges, each adapted to specific environmental conditions:
- Oval: Common in environments where water conservation is essential.
- Lanceolate: Narrow and long, typical of windy areas.
- Serrated or Toothed Edges: Ideal for deterring pests.
Advantages
Photosynthesis Efficiency
Simple leaves are highly efficient at photosynthesis due to their extensive green area, which allows for maximum light absorption. This efficiency supports quicker growth and higher overall energy production.
Growth and Maintenance
Simple leaves require less maintenance than variegated leaves because their care does not involve managing light to preserve color patterns. Their robust growth and adaptability make them ideal for a variety of climates and soils.
Comparative Analysis
Photosynthesis
The efficiency of photosynthesis in simple leaves is generally higher than in variegated leaves. This is because simple leaves have a full quota of chlorophyll cells, maximizing the conversion of sunlight into energy.
Efficiency in Variegated vs. Simple Leaves
While variegated leaves are aesthetically pleasing, they often possess less chlorophyll than simple leaves, leading to reduced photosynthetic capacity. Simple leaves, with their full chlorophyll coverage, are more adept at sustaining the plant’s energy needs.
Aesthetic Appeal
Preferences in gardening and landscaping vary greatly:
- Variegated Leaves: Often chosen for their striking appearance and unique patterns.
- Simple Leaves: Valued for their lush, green appearance and natural simplicity.
Plant Health
Simple leaves tend to be less susceptible to diseases compared to variegated leaves, as their uniform pigment distribution and structure make them less prone to environmental stress and damage.
Practical Considerations
Gardening with Variegated Leaves
When incorporating variegated plants into your garden, consider these tips:
- Selection Tips:
- Choose varieties known for stability in variegation.
- Avoid plants with very light leaves, as they may burn easily.
- Care and Maintenance:
- Provide partial shade to prevent sunburn.
- Prune regularly to encourage the growth of variegated sections.
Choosing Simple Leaves
For those looking to enhance their garden with minimal maintenance, simple leaves offer distinct advantages:
- Advantages in Landscape Design:
- The uniform color and shape provide a cohesive look.
- Easy to integrate with a variety of plant types.
- Ease of Care:
- Less sensitive to fluctuations in light and watering.
- Generally more resilient to pests and diseases.
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes leaf variegation?
Leaf variegation occurs due to genetic mutations or environmental conditions that alter the distribution of chlorophyll and other pigments. In some plants, this is an inherited trait, while in others, it can result from viral infections or cultural practices.
How do simple leaves differ from variegated ones?
Simple leaves are uniformly colored, typically green, due to the consistent presence of chlorophyll across their surface. This uniformity aids in maximizing photosynthesis. Variegated leaves have patches without chlorophyll, which can slightly reduce their photosynthetic efficiency.
Can variegated leaves revert to being simple?
Yes, variegated leaves can revert to being simple green leaves. This reversion can occur if the variegated parts of the plant do not survive well or if environmental conditions favor the growth of the plant’s green parts.
Are variegated plants less healthy than those with simple leaves?
Not necessarily, but variegated plants often have reduced chlorophyll levels, which can impair photosynthesis and slow growth. However, with proper care tailored to their needs, variegated plants can thrive just as well as those with simple leaves.
Is it harder to care for variegated plants?
Variegated plants may require more attention regarding light conditions and pruning to ensure that the variegated areas are maintained and the plant remains healthy overall. They can be more sensitive to poor lighting conditions and nutrient deficiencies.
Conclusion
The distinction between variegated and simple leaves offers more than an aesthetic choice for gardeners and plant enthusiasts; it reflects significant biological variations that can impact a plant’s growth, health, and environmental adaptation. While variegated leaves bring striking colors and patterns to gardens and homes, they require understanding and specific care to maintain their vibrant appearance.
In choosing between variegated and simple leaves, one should consider not only the visual impact but also the environmental conditions and care requirements. Whether your preference leans towards the understated elegance of green or the dramatic flair of variegation, both choices enrich our surroundings and offer unique advantages in the world of plants.
