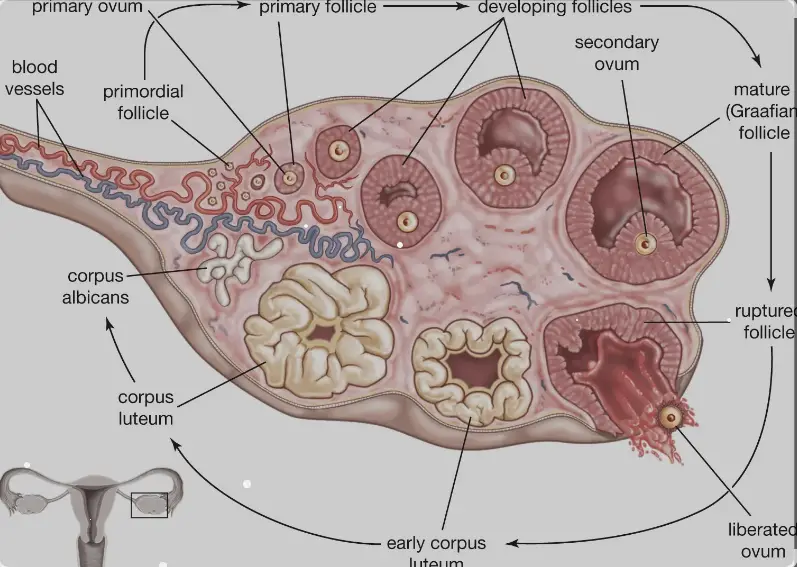
The human body operates through a series of complex and finely tuned processes, among which the ovarian cycle plays a critical role in female reproductive health. This cycle involves several stages, each characterized by specific changes and developments. Two key players in this process are the Corpus Luteum and Corpus Albicans, which are structures formed in the ovaries and have distinct functions and lifespans.
The Corpus Luteum is a temporary gland formed in the ovary after the release of an egg during ovulation. It secretes hormones such as progesterone and estrogen, which are crucial for maintaining pregnancy and regulating the menstrual cycle. If pregnancy does not occur, the Corpus Luteum degenerates into the Corpus Albicans, a scar tissue that signifies the end of a menstrual cycle.
The formation and regression of these structures are pivotal in the reproductive cycle, influencing fertility and overall reproductive health. The Corpus Luteum and Corpus Albicans play specific roles that ensure the body is prepared for conception and, when necessary, returning to a non-pregnant state. These processes are governed by hormonal changes that are essential for a healthy menstrual cycle.
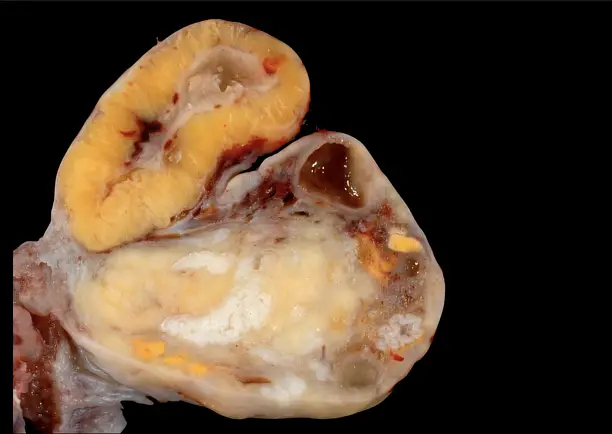
Corpus Luteum Explained
Formation and Role
The Corpus Luteum is a vital structure within the ovaries, developing from what was once a follicle that has released an egg during the process known as ovulation. After the egg is ejected, the ruptured follicle undergoes a transformation, turning into the Corpus Luteum. This change is pivotal as it marks the body’s preparation for a potential pregnancy.
The primary role of the Corpus Luteum is to produce hormones, primarily progesterone and small amounts of estrogen. These hormones are crucial because they prepare the uterine lining for the possible implantation of a fertilized egg, ensuring that the uterus is receptive and ready to support embryonic development. If fertilization does not occur, the hormonal levels will decline, leading to the onset of menstruation.
Hormonal Contributions
The hormonal contributions of the Corpus Luteum are significant:
- Progesterone: This hormone stabilizes the uterine lining and is essential for maintaining a pregnancy. It prevents further ovulation during pregnancy and modifies the immune system to prevent rejection of the developing embryo.
- Estrogen: Although in smaller quantities, the estrogen produced also aids in maintaining the uterine lining and regulates various bodily functions related to reproductive health.
These hormones also influence other body systems, indicating the systemic importance of the Corpus Luteum beyond the reproductive process.
Life Span and Regression
The life span of the Corpus Luteum is typically around 14 days in a non-pregnant cycle. If pregnancy occurs, it receives a signal (human chorionic gonadotropin hormone) from the developing placenta to continue its hormone production, extending its life span until the placenta can take over this function around the 10th week of pregnancy.
If no pregnancy occurs, the Corpus Luteum will regress, meaning it ceases hormone production and is eventually replaced by scar tissue known as the Corpus Albicans.
Corpus Albicans Overview
Definition and Formation
The Corpus Albicans is essentially the remnants of the Corpus Luteum after it has regressed. It forms when the Corpus Luteum ceases its hormone production due to the absence of pregnancy. This structure is fibrous and whitish, marking a phase where the once-active gland becomes a scar within the ovary.
Structural Changes
During its transformation, the Corpus Luteum collapses and the cells within it undergo a process called apoptosis, or programmed cell death. The area is then invaded by fibroblasts that lay down collagen, turning the structure into the Corpus Albicans.
Role in the Ovarian Cycle
The Corpus Albicans has no hormonal function, which signals the end of the current ovarian cycle and allows the next cycle to begin with the development of new follicles. Its presence is a normal part of the ovarian cycle and indicates the body’s readiness to start the process anew.
Comparative Analysis
Structural Differences
The Corpus Luteum and Corpus Albicans differ markedly in appearance and structure. The Corpus Luteum is initially rich with blood vessels and glandular, secreting important hormones, whereas the Corpus Albicans is avascular, containing mainly fibrous tissue without active secretion.
Functional Distinctions
Functionally, the Corpus Luteum and Corpus Albicans are at opposite ends of the spectrum:
- The Corpus Luteum is active, secreting hormones that are critical for pregnancy and the regulation of the menstrual cycle.
- The Corpus Albicans serves as a sign that the ovarian cycle is resetting, with no active hormonal role.
Hormonal Differences
While the Corpus Luteum produces significant levels of progesterone and estrogen, the Corpus Albicans does not produce any hormones. The hormonal shift accompanying the transition from the Corpus Luteum to Corpus Albicans is a critical regulatory mechanism in the menstrual cycle, leading to the shedding of the uterine lining if pregnancy does not occur.
Clinical Significance
Implications in Fertility
The roles of the Corpus Luteum and Corpus Albicans are critical in determining a woman’s fertility. The Corpus Luteum’s ability to produce sufficient levels of progesterone is essential for the maintenance of early pregnancy. If the Corpus Luteum does not function adequately, it may lead to luteal phase deficiency, a condition where the uterine lining is not adequately prepared for pregnancy, potentially resulting in infertility or early pregnancy loss.
Associated Conditions
Several reproductive conditions are associated with the dysfunction of the Corpus Luteum, including:
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): This condition can disrupt the formation of the Corpus Luteum and thus interfere with normal hormone production.
- Luteal Phase Defect: Insufficient progesterone production by the Corpus Luteum can prevent the successful implantation of an embryo.
- Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS): Excessive stimulation of the ovaries during fertility treatments can lead to an overproduction of structures similar to the Corpus Luteum, leading to severe symptoms.
Diagnostic Relevance
The health and function of the Corpus Luteum can be evaluated through various diagnostic methods, crucial for treating infertility and managing reproductive health:
- Blood tests to measure hormone levels, such as progesterone and estrogen.
- Ultrasound examinations to observe the structure and size of the Corpus Luteum.
These diagnostics help in understanding the underlying causes of menstrual irregularities and reproductive issues, guiding appropriate treatments.
Research and Advances
Recent Studies on Ovarian Cycle
Recent research in the field of reproductive biology has provided deeper insights into the ovarian cycle, particularly the roles and mechanisms of the Corpus Luteum and Corpus Albicans. Studies have explored:
- The molecular triggers for the transformation of the Corpus Luteum to the Corpus Albicans.
- The impact of environmental and genetic factors on the efficiency of these structures.
These studies are essential for developing targeted therapies that could enhance fertility treatments and improve outcomes for women with reproductive disorders.
Future Implications in Reproductive Health
The ongoing advancements in understanding the ovarian cycle hold promising implications for the future of reproductive health:
- Personalized Medicine: Improved understanding of the Corpus Luteum and Corpus Albicans can lead to more personalized approaches in fertility treatments, tailoring interventions based on individual hormonal profiles.
- Preventive Strategies: Identifying women at risk of luteal phase defects or other conditions associated with the dysfunction of the Corpus Luteum could allow for earlier interventions.
- Technological Innovations: New technologies, such as advanced imaging and hormone monitoring devices, are on the horizon, potentially offering more precise assessments of ovarian health and function.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Corpus Luteum?
The Corpus Luteum is a structure formed in the ovary from the follicle that has released an egg. Its primary function is to produce hormones, mainly progesterone and some estrogen, which are essential for establishing and maintaining pregnancy if fertilization occurs.
How does the Corpus Albicans form?
The Corpus Albicans forms following the regression of the Corpus Luteum if pregnancy does not occur. This involves the replacement of the luteal cells by fibrous tissue, turning the once hormone-secreting gland into a non-functional scar-like structure within the ovary.
What role does progesterone play in the ovarian cycle?
Progesterone, mainly produced by the Corpus Luteum, is crucial in preparing the uterine lining for a potential pregnancy and maintaining it in the early stages of gestation. It also regulates the menstrual cycle and affects the release of other hormones within the pituitary gland.
How do changes in these structures affect fertility?
The normal function and timely regression of the Corpus Luteum and the transformation into the Corpus Albicans are vital for regular menstrual cycles. Any disruptions in these processes can lead to menstrual irregularities and impact fertility, highlighting their importance in reproductive health.
Conclusion
The intricate dynamics between the Corpus Luteum and Corpus Albicans underscore their significance in the ovarian cycle. These structures not only facilitate reproductive processes but also illustrate the body’s ability to prepare for and conclude a potential pregnancy. Understanding their roles offers insights into broader aspects of reproductive health and fertility management.
By appreciating the complex interplay of hormones and ovarian structures, one gains a deeper understanding of how crucial balanced and timely transitions between these stages are for maintaining reproductive health. This knowledge is essential for anyone looking to understand the nuances of female fertility and hormonal regulation.