Triethylamine and triethanolamine are two compounds frequently utilized in various industrial applications due to their unique chemical properties. Despite the similarity in their names, these chemicals have distinct structures and functionalities that set them apart. These differences are critical to understanding their specific uses in industries ranging from pharmaceuticals to textiles.
Triethylamine is an organic compound known for its role in the synthesis of quaternary ammonium compounds, while triethanolamine is notable for its use as an emulsifier and surfactant. Essentially, triethylamine serves primarily as a base and catalyst in organic reactions, whereas triethanolamine is often found in cosmetic and skin care products due to its ability to balance pH levels and act as a buffering agent.
These chemicals are not just important for their direct applications but also for their roles in environmental safety, health considerations, and economic implications within their respective industries. They are both pivotal in the production of various consumer and industrial products, underscoring the necessity to grasp their distinct and critical characteristics.
Chemical Properties
Basic Structure
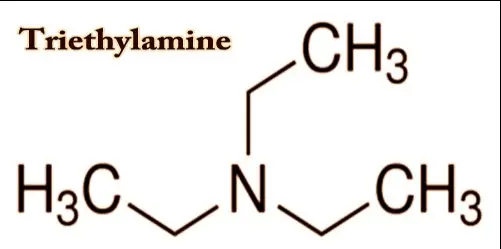
Triethylamine (TEA) and Triethanolamine (TEA) are both derived from ammonia by substituting ethyl and ethanol groups respectively for hydrogen atoms. Triethylamine consists of a nitrogen atom bonded to three ethyl groups, giving it a formula of 𝑁(𝐶𝐻2𝐶𝐻3)3N(CH2CH3)3. This structure makes it a tertiary amine. Triethanolamine, on the other hand, is composed of a nitrogen atom connected to three hydroxyethyl groups (𝑁(𝐶𝐻2𝐶𝐻2𝑂𝐻)3N(CH2CH2OH)3), classifying it as a triol and a tertiary amine. These structural differences directly influence their chemical behaviors and applications.
Molecular Differences
The key molecular difference between triethylamine and triethanolamine lies in their substituents: triethylamine has ethyl groups, while triethanolamine has ethanol groups, which contain hydroxyl (-OH) groups. This addition of hydroxyl groups to triethanolamine increases its polarity, making it more hydrophilic (water-loving) compared to the more hydrophobic (water-repelling) triethylamine. The presence of hydroxyl groups in triethanolamine also allows it to form hydrogen bonds, enhancing its ability to interact with other molecules, which is crucial in its role as an emulsifier.
Production Processes
Triethylamine Synthesis
The production of triethylamine typically involves the alkylation of ammonia with ethanol. This process occurs in the presence of an acid catalyst under elevated temperatures and pressures. The steps include:
- Mixing ammonia and ethanol: Ammonia gas is reacted with ethanol in a reactor.
- Catalysis: An acid catalyst, often aluminum oxide, facilitates the reaction.
- Distillation: The reaction mixture is distilled to separate triethylamine from other byproducts and unreacted materials.
Triethanolamine Synthesis
Triethanolamine is synthesized through a similar alkylation process, where instead of simple ethanol, ethylene oxide reacts with ammonia. This reaction typically requires precise temperature and pressure controls to ensure efficiency and safety. The process includes:
- Ammonia and ethylene oxide reaction: Ethylene oxide is reacted with liquid ammonia.
- Pressure and temperature control: Controlled conditions ensure optimal reaction rates and yields.
- Purification: The product is purified through distillation, removing water and other impurities.
Physical Characteristics
Boiling and Melting Points
Triethylamine has a relatively low boiling point of about 89°C, which reflects its volatility. Its melting point is around -115°C, indicating its stability at lower temperatures. Triethanolamine, with its higher molecular weight and polarity, boils at around 335°C and has a melting point of 21°C. This higher boiling point and solid state at room temperature are due to the presence of hydrogen bonding among molecules.
Solubility and Density
Triethylamine is soluble in water and most organic solvents due to its small, non-polar nature. It has a density slightly less than water, at about 0.725 g/cm³. Triethanolamine’s solubility is enhanced by its hydroxyl groups, making it highly soluble in water and capable of dissolving many organic compounds. It is denser than water, with a density of approximately 1.124 g/cm³.
Key Applications
Triethylamine in Industry
Triethylamine is a valuable chemical in the production of:
- Pharmaceuticals: Synthesis of active pharmaceutical ingredients.
- Rubber: As a catalyst in the curing process.
- Agriculture: Ingredient in pesticides and herbicides.
Its volatility and reactivity make it suitable for processes requiring a strong base that can easily be removed by evaporation.
Triethanolamine Uses
Triethanolamine is extensively used in various industries, including:
- Cosmetics: As a pH balancer and emulsifier in lotions and creams.
- Cement: Improver for the workability and strength of cement mixtures.
- Textiles: Helps in the adjustment of pH of dye solutions.
Its ability to mix oil and water phases and stabilize emulsions is critical for products requiring homogeneous mixtures.
Health and Safety
Exposure Risks
Both triethylamine and triethanolamine pose distinct health risks upon exposure, necessitating strict adherence to safety guidelines. Triethylamine is particularly notable for its strong, unpleasant odor and volatility, which make it a risk for inhalation exposure. It can cause irritation to the respiratory system, eyes, and skin. Prolonged or repeated exposure may lead to more severe health issues, including respiratory distress or dermatitis.
Triethanolamine, while less volatile, can still cause significant irritation upon direct contact with the skin or eyes. Its use in cosmetic products has been scrutinized due to potential sensitization and allergic reactions, particularly in individuals with sensitive skin.
Handling and Storage Guidelines
Proper handling and storage of these chemicals are critical to minimize health risks:
- Use protective gear: Gloves, goggles, and face shields should be used when handling both chemicals.
- Ventilation: Ensure adequate ventilation in areas where these chemicals are stored or handled to avoid inhalation.
- Storage conditions: Store triethylamine in cool, well-ventilated areas away from sources of ignition due to its flammability. Triethanolamine should be stored in airtight containers to prevent contamination.
Environmental Impact
Biodegradability
Triethylamine and triethanolamine differ significantly in their environmental persistence. Triethylamine, due to its volatile nature, does not tend to accumulate in the environment and is relatively rapidly degraded by microbial action in both soil and water. Conversely, triethanolamine is less biodegradable. It can persist in the environment, particularly in water bodies, where it degrades slowly and can accumulate over time, potentially leading to environmental toxicity.
Toxicity to Aquatic Life
The environmental concerns associated with triethylamine and triethanolamine extend to their effects on aquatic life. Triethylamine is moderately toxic to fish and other aquatic organisms, mainly due to its ability to change water pH and chemical makeup rapidly. Triethanolamine poses a higher risk to aquatic environments; it is toxic to aquatic organisms, with long-term exposure potentially leading to serious ecological damage. Its degradation products can also contribute to environmental toxicity.
Economic Aspects
Market Trends
The market for both triethylamine and triethanolamine has seen consistent growth, driven by expanding applications across various industries. Triethylamine’s market is bolstered by the increasing demand in the pharmaceutical and agricultural sectors, where it is used in the synthesis of active ingredients and herbicides, respectively.
Triethanolamine has witnessed a steady demand in the personal care and construction industries. Its role as an emulsifier in cosmetics and as an additive in cement formulations has made it indispensable in these sectors.
Cost Comparisons
Economically, the cost of triethylamine and triethanolamine can vary based on production methods, availability of raw materials, and market demand. Generally, triethanolamine tends to be more expensive than triethylamine due to the more complex synthesis process and the higher purity required for its use in cosmetics and personal care products.
Cost efficiency in production is a significant factor influencing the price of these chemicals. Advances in manufacturing technologies that allow for more efficient production processes could help reduce costs. Additionally, fluctuations in the prices of ethanol and ethylene oxide, primary raw materials for triethylamine and triethanolamine, respectively, also significantly impact the overall cost structure.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Triethylamine?
Triethylamine, often abbreviated as TEA, is a volatile organic compound used primarily as a base and a catalyst in organic synthesis. It is recognized by its strong, fishy odor and is essential in the production of herbicides, rubber chemicals, and dyes.
What is Triethanolamine?
Triethanolamine, also known as TEA, is a viscous organic chemical compound that plays a crucial role in the manufacture of surfactants and emulsifiers. It is widely used in cosmetic formulations to adjust pH levels and facilitate the blending of oil and water-based components.
How are Triethylamine and Triethanolamine different?
While both compounds are used in industrial processes, triethylamine acts primarily as a solvent and catalyst in chemical reactions, whereas triethanolamine is utilized for its properties as a surfactant and emulsifier in cosmetics and skin care products.
Are Triethylamine and Triethanolamine safe?
Both chemicals can be hazardous under certain conditions. Triethylamine is flammable and can be irritating to the skin and eyes, while triethanolamine can cause allergic reactions when used in high concentrations. Proper handling and adherence to safety guidelines are essential.
How do Triethylamine and Triethanolamine impact the environment?
Triethylamine does not persist in the environment due to its volatile nature. However, triethanolamine can be toxic to aquatic life and requires careful management to prevent environmental contamination.
Conclusion
Triethylamine and triethanolamine are pivotal in their respective applications across a variety of industries, each playing a unique role due to their distinct chemical properties. Their importance extends beyond simple usage as chemicals; they are integral to advancements in safety, efficiency, and environmental sustainability in the chemical industry.
As the demand for both compounds continues to grow, driven by their versatility and broad applicational range, it is vital for industries to remain cognizant of their environmental and health impacts. Ensuring the safe and responsible use of these amines will be crucial as their roles expand in developing innovative and sustainable industrial solutions.
You

