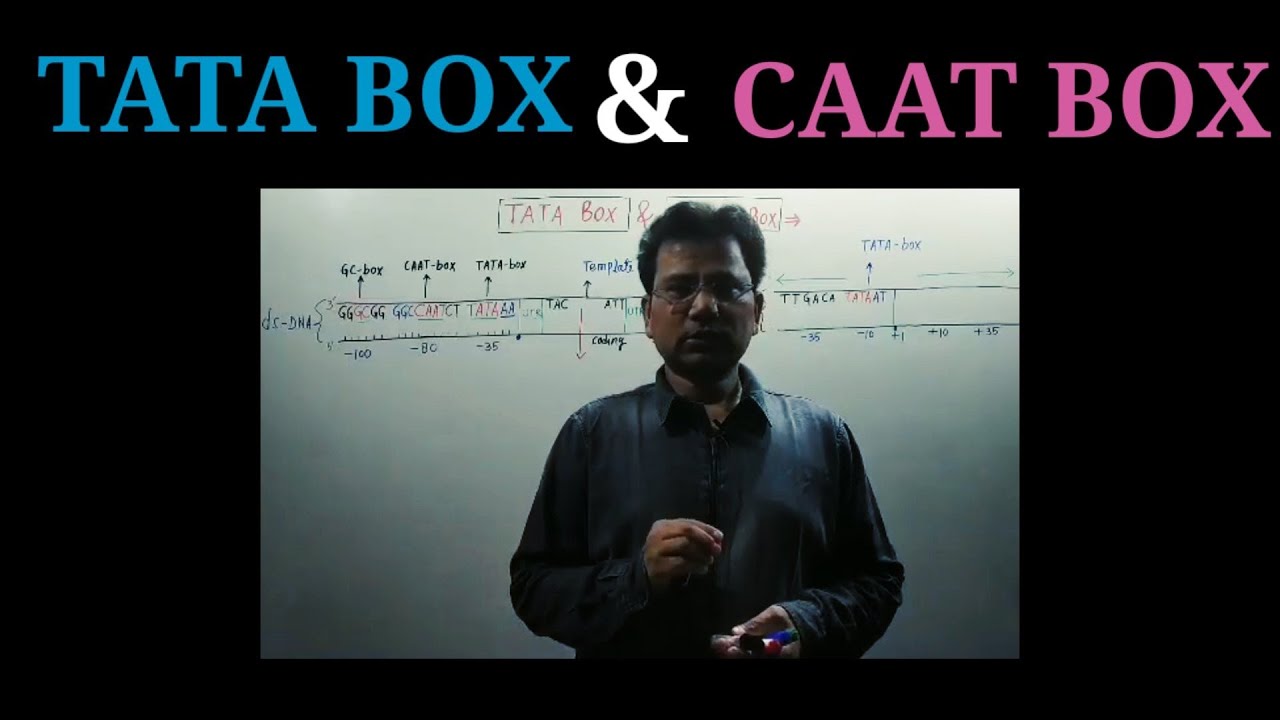
The genetic landscape is intricately detailed, revealing components like the Tata Box and Caat Box, which play crucial roles in gene expression and regulation. These elements are often mentioned in genetic studies but seldom explained in layman’s terms. Both serve as binding sites for transcription factors but differ in structure and function, making them essential for the correct expression of genes.
The Tata Box and Caat Box are short sequences found in the promoter regions of genes, essential for initiating transcription. The Tata Box is typically located around 25-35 base pairs upstream of the transcription start site and is crucial for precise transcription initiation. In contrast, the Caat Box, usually found about 80 base pairs upstream, helps in the assembly of the transcription machinery and enhances the binding of RNA polymerase to DNA.
Despite their small size, these elements are vital for the accurate transcription of genetic information into RNA, subsequently dictating the synthesis of proteins necessary for various biological functions. Understanding these boxes not only unravels part of the complex DNA transcription puzzle but also highlights their potential implications in genetic diseases and biotechnological applications.
Tata Box Basics
Definition and Function
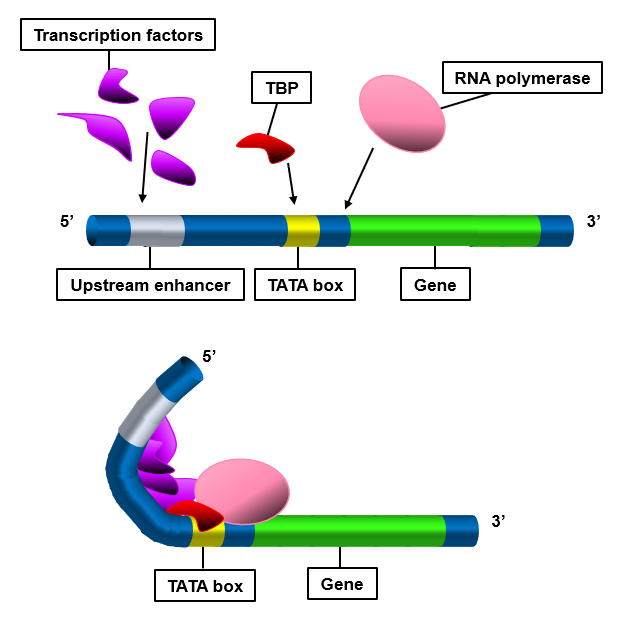
The Tata Box is a DNA sequence crucial in the process of transcription, where genetic information from DNA is copied into RNA. This sequence acts primarily as a binding site for several proteins, including the TATA-binding protein (TBP), which is part of the larger transcription factor IID (TFIID). The presence of the Tata Box helps to initiate transcription by positioning the transcription machinery accurately at the start site of genes.
Location in DNA
Located typically around 25-35 base pairs upstream of the transcription start site, the Tata Box is found in the promoter region of many genes. Its strategic positioning is key to its function, facilitating the assembly of the transcription factors and RNA polymerase at the correct location on the DNA strand.
Role in Genetics
The Tata Box’s role extends beyond mere initiation of transcription. It is fundamental in regulating the expression of genes necessary for various biological processes. Its influence on genetic expression makes it a focal point in studies related to gene regulation, development, and differentiation.
Caat Box Essentials
Definition and Purpose
The Caat Box is another important DNA sequence located in the promoter regions of genes. It serves to enhance the assembly of the transcription complex by facilitating the binding of additional transcription factors. Unlike the Tata Box, the Caat Box is more often involved in the regulation and increased efficiency of transcription, rather than the direct initiation.
Comparison with Tata Box
While both the Tata and Caat Boxes are located in promoter regions and are essential for transcription, they have distinct roles. The Tata Box is crucial for the initiation of transcription, directly influencing where RNA polymerase begins synthesizing RNA. The Caat Box, however, primarily enhances the binding efficiency and stability of the transcription complex, indirectly supporting the initiation process initiated by the Tata Box.
Functionality in Transcription
In transcription, the Caat Box’s functionality can be seen as supporting the Tata Box. It helps gather necessary transcription factors that increase the RNA polymerase’s affinity to the DNA, thus enhancing the transcription rate and ensuring robust gene expression.
Structural Differences
Core Elements Analysis
Both the Tata and Caat Boxes contain specific nucleotide sequences that are crucial for their function. The Tata Box sequence is typically characterized by a consensus sequence TATA(A/T)A(A/T), whereas the Caat Box generally follows the consensus sequence GGCCAATCT. These core elements define their binding capabilities with specific transcription factors.
Sequence Variations
Despite having consensus sequences, variations exist within these sequences that can affect their functionality. For instance, slight changes in the nucleotide composition of the Tata Box can alter its binding efficiency with the TATA-binding protein, which can lead to variations in gene expression levels among different organisms or even different cells within the same organism.
Interaction with Transcription Factors
The interaction of these boxes with transcription factors is a finely tuned process. The Tata Box’s interaction with TBP is well understood, where TBP binds to the minor groove of the DNA double helix, causing a significant bend. This bending is critical as it facilitates the recruitment of other transcription factors. On the other hand, the Caat Box interacts with the CAAT-binding factor (CBF), among others, which helps to stabilize the binding of RNA polymerase II to the promoter.
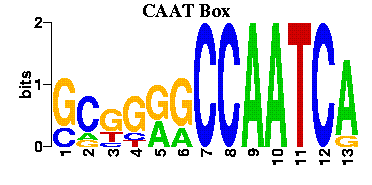
Functional Implications
Impact on Gene Expression
The presence of Tata Boxes and Caat Boxes in the promoter regions of genes critically impacts gene expression. These elements are not merely placeholders; they actively dictate the timing and volume of gene transcription. Variations in these sequences can lead to differences in how genes are expressed, which can have cascading effects on cellular functions and organismal traits. For example, mutations in the Tata Box may lead to a reduced affinity for transcription factors, thus lowering the gene’s expression.
Influence on Transcription Efficiency
Transcription efficiency, the rate at which RNA is synthesized from DNA, is significantly influenced by these promoter sequences. The Tata Box enhances the precise initiation of transcription, ensuring that RNA polymerase begins synthesis exactly where needed. On the other hand, the Caat Box boosts the overall efficiency of the process by facilitating the assembly of the necessary transcription machinery, leading to a more robust transcription response.
Relevance to Biological Processes
Both boxes play essential roles in numerous biological processes, including growth, development, and response to environmental stimuli. For instance, genes involved in stress responses often contain these elements in their promoters, allowing quick and efficient transcriptional activation in response to environmental changes. This adaptability highlights the critical nature of Tata and Caat Boxes in the survival and functionality of cells.
Practical Applications
Research and Clinical Relevance
The study of Tata and Caat Boxes has profound implications in research and clinical settings. Understanding how these elements control gene expression helps researchers develop better models of genetic diseases, potentially leading to more effective treatments. For instance, targeting specific promoter elements might allow for the downregulation of genes involved in cancerous growth.
Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology
In biotechnology, these promoter sequences are exploited to drive the expression of recombinant proteins. By integrating Tata or Caat Boxes into vectors, scientists can ensure high levels of protein production, which is crucial in manufacturing vaccines, enzymes, or therapeutic proteins.
Therapeutic Potential and Challenges
The therapeutic potential of manipulating these elements is significant but comes with challenges. For example, modifying a Tata Box to enhance gene expression could treat diseases caused by underexpression of a gene. However, the precise control of such modifications is still a major hurdle, as unintended consequences might arise from altering natural gene regulation systems.
Case Studies
Significant Studies on Tata Box
Research on the Tata Box has unveiled its critical role in diseases like cancer and neurodegenerative disorders. Studies have shown that mutations in the Tata Box can alter the expression of genes involved in cell cycle regulation, potentially leading to cancer.
Influential Research on Caat Box
The Caat Box has been central to studies on gene regulation during development and in response to physiological stress. Research has demonstrated how alterations in Caat Box sequences can affect the stress response in plants, providing insights into how plants cope with drought or nutrient deficiencies.
Comparative Analysis of Findings
Comparing the roles of Tata and Caat Boxes in different species has provided valuable insights into their evolutionary importance. Such studies have helped clarify why these sequences have been highly conserved throughout evolution, emphasizing their fundamental role in gene expression.
Common Misunderstandings
Clarifications on Function
A common misunderstanding is that the Tata Box alone is sufficient for initiating transcription. In reality, it must work in conjunction with other elements like the Caat Box and additional transcription factors to initiate and sustain transcription efficiently.
Misinterpretations in Research
Misinterpretations often arise regarding the universality of these boxes in all genes. Not all genes contain a Tata or Caat Box; their presence is highly dependent on the gene’s role and the organism’s specific regulatory needs.
Correcting Popular Assumptions
It’s often assumed that the stronger the presence of these elements, the more active the gene. However, gene expression is a balance of many factors, including enhancers, silencers, and the physical condition of the chromatin structure. Thus, the role of Tata and Caat Boxes, while vital, is part of a larger regulatory network.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a Tata Box?
The Tata Box is a DNA sequence critical for initiating transcription in some genes. It is recognized and bound by a specific set of proteins that help position the RNA polymerase correctly, which is crucial for starting the transcription process effectively.
What is a Caat Box?
A Caat Box is another important DNA sequence located in the promoter region of genes. It plays a significant role in the regulation of gene expression by facilitating the binding of transcription factors, which increases the efficiency of RNA polymerase’s attachment to the DNA.
How do Tata and Caat Boxes differ?
While both Tata and Caat Boxes are involved in gene transcription, they differ primarily in location and function. The Tata Box is generally closer to the transcription start site and is directly involved in the initiation process, whereas the Caat Box, located further upstream, mainly enhances the binding of transcription machinery.
Why are Tata and Caat Boxes important in genetics?
These DNA sequences are essential for the precise regulation of gene expression. Their role in transcription initiation and enhancement makes them critical in developmental biology, gene therapy, and understanding genetic diseases.
Conclusion
This discussion sheds light on the fundamental aspects of the Tata and Caat Boxes, underlining their significance in genetic transcription. Their roles, though distinct, are pivotal in ensuring that genetic information is accurately transcribed, which is essential for proper cellular function and overall organismal health.
As research continues, the understanding of these genetic elements is expected to deepen, potentially leading to breakthroughs in genetic therapy and biotechnology. The ongoing exploration of their mechanisms and interactions promises to reveal more about the intricate workings of genetic control and expression.