Food preservatives play a crucial role in extending the shelf life of various products, maintaining nutritional value, and ensuring food safety. Among these, sodium propionate and calcium propionate are widely recognized for their ability to prevent the growth of mold and bacteria in foods. These compounds are especially pivotal in the baking and dairy industries, where they help to keep products fresh and safe for consumption.
Sodium propionate and calcium propionate differ primarily in their base elements—sodium and calcium. Sodium propionate, a sodium salt of propionic acid, is highly soluble in water and is primarily used in baked goods. Calcium propionate, on the other hand, is the calcium salt of propionic acid, offering similar preservative benefits but with added nutritional contributions of calcium, making it preferable in dietary products.
These preservatives are not only essential for food safety but also influence the nutritional and sensory properties of food. They are chosen based on factors like solubility, impact on taste, and nutritional enhancements, making the choice between them crucial for food manufacturers aiming to meet specific product needs and consumer preferences.

Basic Properties
Sodium Propionate
Chemical Structure and Formula
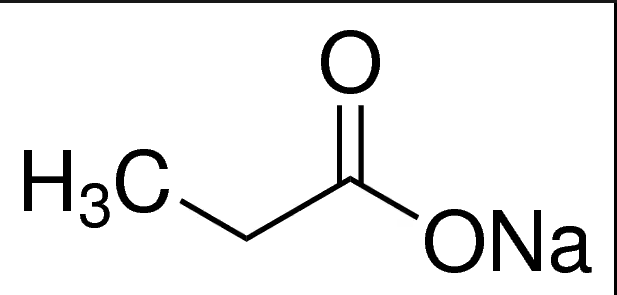
Sodium propionate, chemically known as sodium propanoate, has the formula C3H5NaO2. This compound is the sodium salt of propionic acid and includes three carbon atoms, making it a short-chain fatty acid salt. Its molecular structure features a carboxylate anion (C2H5COO-) and a sodium ion (Na+), which interact through ionic bonds.
Physical Characteristics
Sodium propionate appears as a white, crystalline powder or granules. It is odorless or has a faint acetic-butyric acid smell. The compound is highly soluble in water and moderately soluble in ethanol, making it adaptable for various industrial applications. Its hygroscopic nature allows it to absorb moisture from the environment, which is a crucial property in food preservation.
Calcium Propionate
Chemical Structure and Formula
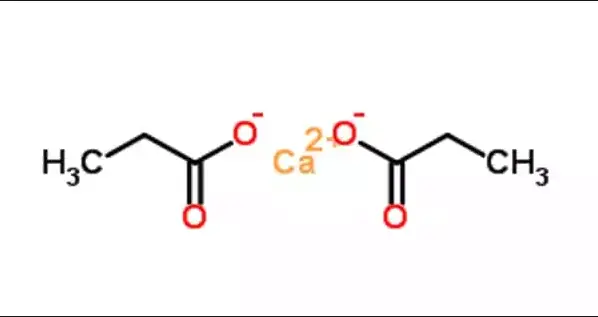
Calcium propionate, or calcium propanoate, has the chemical formula C6H10CaO4. It consists of two propionate groups attached to a calcium ion. This arrangement makes it a doubly charged calcium salt of propionic acid, which enhances its stability and effectiveness as a food additive.
Physical Characteristics
This compound is available as a white powder or crystalline solid. It has a slight odor of propionic acid but is not overpowering. Calcium propionate is sparingly soluble in water and practically insoluble in alcohol. This selective solubility is particularly beneficial in environments where moisture control is necessary.
Production Methods
Sodium Propionate
Key Manufacturing Processes
The production of sodium propionate typically involves the neutralization of propionic acid with sodium hydroxide or sodium carbonate. This process can be outlined in the following steps:
- Reacting propionic acid with sodium carbonate to yield sodium propionate and carbon dioxide.
- Drying the resulting mixture to remove any excess water and achieve the desired purity.
- Milling the dried product to obtain a fine powder suitable for various applications.
Calcium Propionate
Key Manufacturing Processes
Similar to sodium propionate, calcium propionate is produced by reacting propionic acid with calcium hydroxide. Key steps include:
- Mixing propionic acid with calcium hydroxide in a controlled environment.
- Allowing the reaction to complete, forming calcium propionate and water as by-products.
- Filtering and drying the mixture to achieve the crystalline form of the preservative.
Application Areas
In Food
Role in Bakery Products
Sodium and calcium propionate are essential in bakery items to prevent mold and bacterial growth. Their application includes:
- Direct addition to dough and batter to extend the shelf life of baked goods.
- Maintaining freshness in packaged and sliced breads, cakes, and pastries.
Use in Dairy Products
In the dairy sector, calcium propionate serves as a mold inhibitor in:
- Cheeses: Particularly in sliced and shredded varieties where surface mold is a concern.
- Milk powders and condensed milk: Where it prevents spoilage during storage.
In Pharmaceuticals
Applications in Medication Preservation
Propionates are used in pharmaceuticals to:
- Prevent fungal growth in topical creams and ointments.
- Stabilize formulations by inhibiting microbial contamination.
Benefits in Topical Formulations
Calcium propionate is beneficial in topical medications due to its:
- Anti-inflammatory properties, reducing redness and irritation.
- Ability to enhance skin barrier function, which helps maintain skin health.

Health Impacts
Sodium Propionate
Safety Profile
Sodium propionate is recognized as safe by health authorities like the FDA. It is non-toxic and generally causes no harm when used within prescribed limits.
Potential Side Effects
Although rare, excessive consumption can lead to:
- Metabolic disturbances in sensitive individuals.
- Mild skin irritation when used in topical products.
Calcium Propionate
Safety Profile
Similarly, calcium propionate is considered safe for consumption and has a GRAS (Generally Recognized As Safe) status from the FDA.
Potential Side Effects
Its side effects are minimal but may include:
- Gastrointestinal disturbances if consumed in large quantities.
- Allergic reactions in rare cases, manifesting as skin rashes.

Regulatory Status
Sodium Propionate
FDA Guidelines
Sodium propionate is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as a food additive. Classified under the Generally Recognized As Safe (GRAS) category, it is permitted in various food products including baked goods, cheeses, and confections. The FDA specifies acceptable concentrations and usage conditions to ensure consumer safety.
Global Regulatory Landscape
Globally, sodium propionate is recognized and regulated by food safety authorities in many countries. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) and Health Canada also classify it as safe, allowing its use under similar conditions as the FDA. In Asia, agencies like the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) follow comparable regulations, ensuring a consistent approach to food safety.
Calcium Propionate
FDA Guidelines
Like sodium propionate, calcium propionate also holds GRAS status from the FDA. It is commonly used as a preservative in bakery products, preventing mold and bacterial growth. FDA regulations ensure that its application does not compromise food taste or quality while maintaining safety.
Global Regulatory Landscape
In the international arena, calcium propionate is approved by the EFSA and is included in the Codex Alimentarius, which sets global food safety standards. This broad acceptance helps maintain uniform food safety standards across borders, facilitating international trade and compliance.
Market Insights
Demand Trends
The demand for sodium and calcium propionate has been steadily increasing, driven by rising consumer demand for fresh and longer-lasting food products. The trend towards natural preservatives and clean labels has somewhat moderated their growth, but their effectiveness, especially in preventing fungal growth, keeps them relevant in the preservative market.
Key Suppliers and Market Leaders
Major chemical companies such as BASF, Kemira, and Niacet are key players in the propionate market. These companies not only supply large quantities worldwide but also invest in research and development to improve the efficiency and applications of propionates.
Consumer Perceptions
Public Knowledge and Acceptance
While there is a general awareness of propionates being used as food preservatives, public knowledge is often limited to their roles without a deep understanding of their benefits and safety. Educational campaigns and transparent labeling can help improve consumer understanding and acceptance.
Misunderstandings and Correct Facts
Common misconceptions include fears about the safety and health effects of food preservatives like sodium and calcium propionate. It is important to note that both compounds are tested and proven safe for consumption within the regulatory limits. They do not accumulate in the body and are metabolized and excreted, minimizing health risks.
Future Prospects
Innovative Uses in the Pipeline
Research is ongoing to expand the applications of sodium and calcium propionate beyond food preservation. Innovations include their use in agricultural feed to prevent spoilage and in packaging materials where they could help extend the shelf life of packaged foods.
Research and Development Directions
Future R&D is focusing on enhancing the efficiency of propionates in lower concentrations and in synergy with other natural preservatives. This is particularly relevant in the context of the clean label trend, where consumers prefer products with fewer synthetic additives. Advances in biotechnology might soon enable the production of propionates through fermentation processes, offering a more natural and sustainable production method.

FAQs
What is Sodium Propionate?
Sodium propionate is a sodium salt of propionic acid, commonly used as a food preservative. It effectively inhibits the growth of mold and some bacteria, making it a popular choice in bakery products where these issues are prevalent.
What is Calcium Propionate?
Calcium propionate, the calcium salt of propionic acid, serves a dual purpose as a food preservative and a source of calcium. It prevents mold and bacterial growth in food, particularly in baked goods and dairy products, while also contributing to calcium content, beneficial for bone health.
How do Sodium and Calcium Propionate Differ?
The primary difference between sodium and calcium propionate lies in their base elements and solubility. Sodium propionate is more water-soluble, influencing its use in products requiring high solubility. Calcium propionate provides calcium, making it suitable for nutritionally enhanced foods.
Are Sodium and Calcium Propionate Safe?
Both sodium and calcium propionate are recognized as safe by major food safety authorities, including the FDA. They are used within regulated limits to prevent food spoilage without posing health risks when consumed in typical dietary amounts.
Conclusion
Choosing between sodium propionate and calcium propionate involves understanding their chemical differences and the specific needs they meet in food preservation. While both preservatives are effective in combating spoilage, their unique properties make them suitable for different applications. Sodium propionate is preferred for its solubility and mild flavor in baked goods, whereas calcium propionate is valued in products requiring a nutritional boost of calcium.
The decision to use either of these compounds should be guided by product requirements, consumer dietary needs, and regulatory standards, ensuring that food remains safe, nutritious, and enjoyable. By selecting the appropriate preservative, manufacturers can significantly enhance the shelf life and quality of their products, meeting consumer expectations and industry standards.
