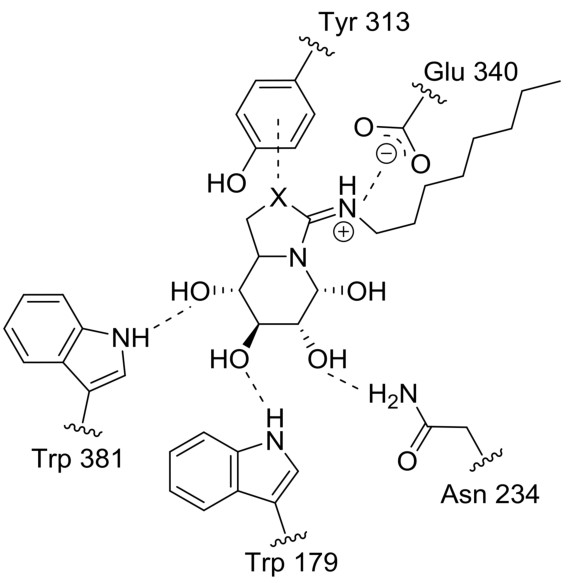
In the intricate world of molecular interactions, understanding the various types of bonds that govern the behavior and stability of compounds is essential. Among these, salt bridges and hydrogen bonds stand out for their critical roles in both biological mechanisms and chemical processes. Their distinct characteristics and functions highlight the complexity of molecular structures and their interactions.
Salt bridges and hydrogen bonds are fundamentally different in their formation, structure, and impact on molecular behavior. A salt bridge is typically formed between an anion and a cation, creating a strong electrostatic interaction that plays a crucial role in stabilizing protein structures and enzyme activities. Hydrogen bonds, on the other hand, occur when a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to an electronegative atom like oxygen or nitrogen, is attracted to another electronegative atom, facilitating interactions critical in DNA base pairing and protein folding.
The importance of these interactions cannot be overstated, as they are pivotal in dictating the three-dimensional structures of macromolecules, influencing solubility, boiling points, and the overall behavior of molecules. Through a deeper exploration of their differences, we gain insights into their unique contributions to the fundamental processes that drive biological life and chemical reactions.
Basic Concepts
Chemical Bonds Overview
Definition and Significance
Chemical bonds form the foundation of matter in the universe, holding atoms together to create molecules and compounds. These bonds are vital for the structure and function of everything from simple gases like oxygen to complex biological molecules such as DNA.
Types of Chemical Bonds
- Covalent Bonds: Atoms share electron pairs, forming a strong bond. This type is crucial for the structure of molecules like water and organic compounds.
- Ionic Bonds: Electrons are transferred from one atom to another, creating ions that attract each other. This bond is essential for salts and many minerals.
- Metallic Bonds: Electrons float freely among a lattice of metal atoms, providing metals their unique properties like conductivity.
- Van der Waals Forces: Weak attractions between molecules or parts of molecules that contribute to the physical properties of substances.
Salt Bridges
Definition
A salt bridge is an interaction between oppositely charged ions within a molecule or between molecules. They are not actual physical bridges but electrostatic interactions critical for the structure and stability of many compounds.
Formation
Salt bridges form when:
- An anionic site on one molecule attracts a cationic site on another molecule, or within the same molecule, forming a stabilizing bond.
Characteristics
- Electrostatic in nature: Unlike covalent bonds, salt bridges result from the attraction between charged groups.
- Contribute to structural stability: Especially important in large molecules like proteins.
Role in Biology
- Enzymes and Proteins: Salt bridges are crucial for maintaining the 3D structure of enzymes and proteins, affecting their function and interaction with other molecules.
- Muscle Contraction: They play a role in the contraction of muscle fibers through the interaction between amino acids.
Role in Chemistry
- Synthesis: Salt bridges can influence the outcome of chemical reactions by stabilizing certain reactants or intermediates.
- Stability: They are used in the design of more stable compounds in pharmaceuticals and materials science.
Hydrogen Bonds
Definition
A hydrogen bond is a type of weak bond that forms when a hydrogen atom, covalently bonded to a highly electronegative atom like oxygen or nitrogen, is attracted to another electronegative atom.
Formation
Hydrogen bonds form through:
- The attraction between a hydrogen atom bonded to an electronegative atom and another electronegative atom.
Characteristics
- Directional: Hydrogen bonds have a specific orientation relative to the involved atoms.
- Strength: They are stronger than van der Waals forces but weaker than covalent or ionic bonds.
- Influences physical properties: Such as boiling point and solubility.
Role in Biology
- DNA: Hydrogen bonds hold together the two strands of the DNA double helix.
- Proteins: They help maintain the structure of proteins, affecting their function and interaction with other molecules.
Role in Chemistry
- Solubility: Hydrogen bonding affects the solubility of compounds in water and other solvents.
- Boiling Points: Compounds capable of hydrogen bonding often have higher boiling points due to the extra energy required to break these bonds.
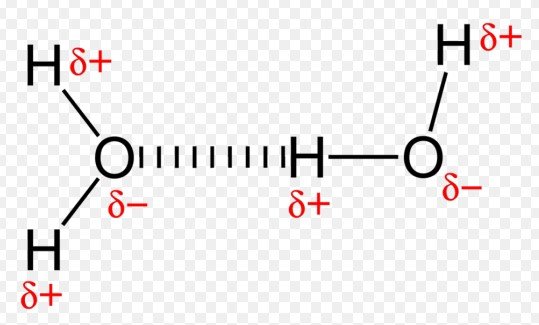
Differences Highlighted
Structural Differences
Salt bridges and hydrogen bonds, though both pivotal in molecular interactions, exhibit key structural differences. Salt bridges occur due to the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions, often seen in the side chains of amino acids within proteins. In contrast, hydrogen bonds form when a hydrogen atom, covalently attached to an electronegative atom like oxygen or nitrogen, is attracted to another electronegative atom. This distinction is crucial for visualizing the spatial arrangements and 3D structures of molecules.
Formation Mechanism
The formation mechanisms of these bonds are fundamentally distinct. Salt bridges result from the ionic bonding between anions and cations, which can either be within the same molecule or between different molecules. Hydrogen bonds, however, arise due to the partial positive charge of hydrogen atoms being attracted to the partial negative charge on electronegative atoms. These mechanisms highlight the diversity of interactions that can occur at the molecular level.
Strength and Stability
In terms of strength and stability, hydrogen bonds are generally weaker than salt bridges due to their reliance on partial charges rather than full ionic charges. However, the strength of a hydrogen bond can significantly influence the boiling points and solubility of compounds, whereas the stability offered by salt bridges is critical in maintaining the tertiary and quaternary structures of proteins.
Biological and Chemical Implications
Both bond types play distinct roles in biological systems and chemical reactions. Salt bridges are vital for the structural integrity of proteins and enzymatic functions, affecting biological pathways and reactions. Hydrogen bonds, on the other hand, are crucial for the properties of water, DNA structure, and protein folding, influencing a wide range of biological and chemical processes.
Common Misunderstandings
Not All Electrostatic Interactions Are Salt Bridges
It’s important to clarify that not all electrostatic interactions qualify as salt bridges. Electrostatic interactions can occur between any two charged groups, whereas salt bridges specifically involve the attraction between positively and negatively charged ions. This distinction is crucial for correctly identifying and understanding the nature of molecular interactions.
Not All Weak Bonds Are Hydrogen Bonds
Similarly, not all weak bonds are hydrogen bonds. There are various types of weak interactions, including van der Waals forces and dipole-dipole interactions. Hydrogen bonds are a specific kind of dipole-dipole interaction with distinct characteristics, such as the involvement of a hydrogen atom bonded to an electronegative atom.
Real-world Applications
In Pharmaceuticals
In the pharmaceutical industry, understanding salt bridges and hydrogen bonds is essential for drug design and function. Salt bridges can influence the stability and solubility of drugs, affecting their bioavailability and efficacy. Hydrogen bonding, on the other hand, plays a crucial role in drug-receptor interactions, dictating the binding affinity and specificity of drugs to their targets.
In Material Science
Polymers and nanomaterials rely heavily on the principles of salt bridges and hydrogen bonds for their properties and applications. Hydrogen bonding can affect the mechanical strength, elasticity, and thermal stability of polymers. Salt bridges, within polymeric chains or between different molecules, can enhance the strength and durability of materials, leading to innovations in biodegradable materials, nanocomposites, and high-performance polymers.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a salt bridge?
A salt bridge is an electrostatic interaction between oppositely charged ions, typically found within proteins or between molecules in solution. This interaction is crucial for maintaining the stability of protein structures, enabling the proper function of enzymes and receptors.
How is a hydrogen bond formed?
Hydrogen bonds form when a hydrogen atom, which is covalently bonded to a strongly electronegative atom such as oxygen or nitrogen, experiences an attractive force towards another electronegative atom. This bond is weaker than covalent or ionic bonds but plays a significant role in determining the physical properties of water, the structure of DNA, and the secondary and tertiary structures of proteins.
Why are salt bridges important in proteins?
Salt bridges are vital in proteins because they contribute significantly to the stability of a protein’s three-dimensional structure. They help maintain the proper folding of proteins, which is essential for their function. The disruption of these bridges often leads to loss of function or misfolding, which can cause diseases.
Can hydrogen bonds exist between different molecules?
Yes, hydrogen bonds can form between different molecules, a phenomenon known as intermolecular hydrogen bonding. This type of bonding is critical in determining the boiling and melting points of substances, as well as in the formation of complex structures like those seen in DNA and proteins.
Conclusion
The distinction between salt bridges and hydrogen bonds is not just a matter of academic interest but has profound implications for understanding biological systems and chemical properties. These interactions underpin the structural integrity of proteins, the intricacies of DNA architecture, and the myriad behaviors of molecules in different environments. Recognizing their differences helps elucidate the delicate balance and intricate dance of atoms and molecules that constitute the fabric of life and the material world.
The exploration of salt bridges and hydrogen bonds illustrates the beauty and complexity of molecular interactions. As we continue to unravel the mysteries of these bonds, we deepen our appreciation for the elegant mechanisms of nature and the sophisticated strategies employed in the design of drugs and materials. Their study not only enriches our knowledge of chemistry and biology but also opens new avenues for innovation in science and technology.