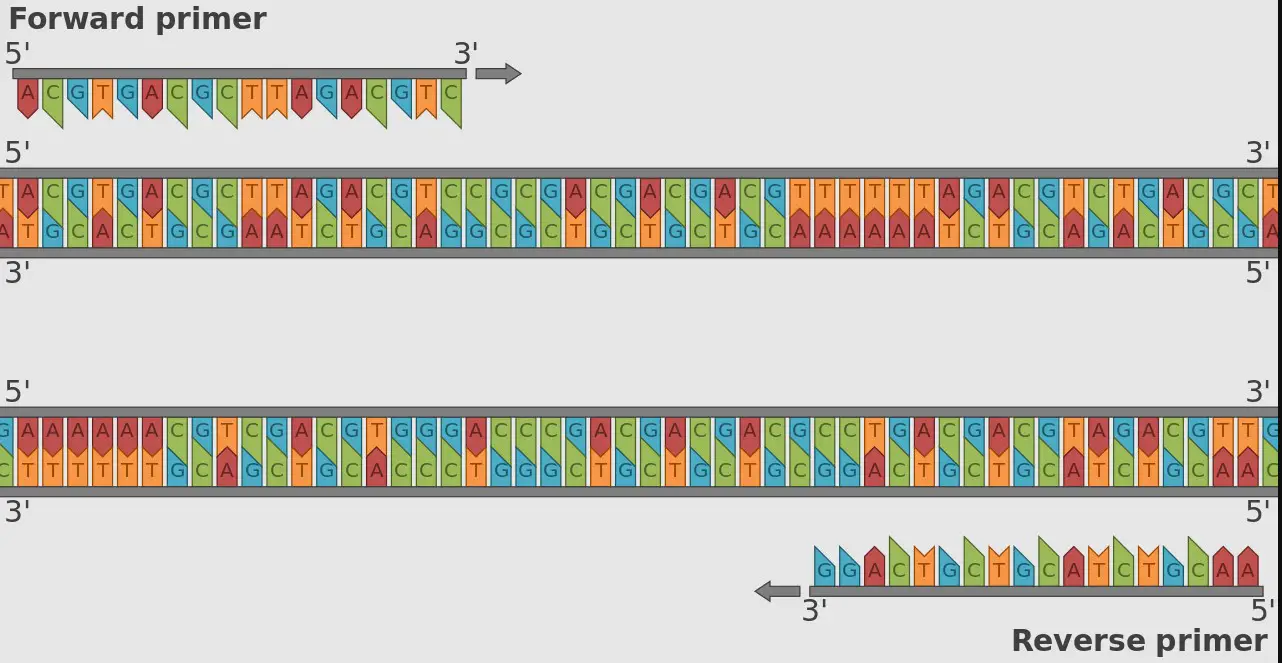
Molecular biology, with its complex mechanisms and terminologies, often introduces tools and concepts that are foundational yet intricate. Among these are primers, specific sequences of nucleotides that play a crucial role in DNA and RNA synthesis. The focus of this discussion zeroes in on two types of primers: random primers and oligo dT, each serving unique purposes in the realm of genetic analysis and experimentation.
Random primers and oligo dT are two distinct tools used in molecular biology for synthesizing DNA from RNA templates. Random primers, short sequences of nucleotides, are utilized for generating a comprehensive representation of an RNA sample. Oligo dT primers, on the other hand, are tailored to target and initiate synthesis specifically from the poly(A) tail of mRNA, facilitating the study of gene expression.
These primers are not merely chemical compounds but tools that guide the accuracy and specificity of molecular biology experiments. They have been ingeniously designed to attach to specific starting points on the RNA or DNA sequences, which allows for the synthesis of new strands of DNA in a controlled manner. Understanding their differences is crucial for researchers to select the appropriate primer that aligns with their experimental goals, be it for cloning, sequencing, or analyzing gene expressions.
Basics of Priming
Primer Function
Primers are short strands of nucleotides that serve a fundamental role in DNA and RNA synthesis. They act as starting points for DNA polymerases, the enzymes that synthesize DNA strands by adding nucleotides to the primer. This process is essential in various laboratory techniques, including polymerase chain reaction (PCR), DNA sequencing, and cDNA synthesis, to replicate or amplify specific DNA or RNA sequences.
Types of Primers
Primers can be broadly classified into several types based on their application and the specificity of the sequences they are designed to bind. The main categories include:
- Random Primers: Short, nonspecific sequences that can bind anywhere along the DNA or RNA template.
- Specific Primers: Designed to bind at specific sites on the DNA or RNA template, used in PCR to amplify specific sequences.
- Oligo dT Primers: Tailored to bind to the poly(A) tail of mRNA, used in reverse transcription for cDNA synthesis.
- Degenerate Primers: Contain a mixture of sequences at specific positions in their structure to amplify genetically similar sequences from different organisms or genes.
Random Primers
Definition and Use
Random primers are short DNA oligonucleotides, typically 6-12 nucleotides long, with sequences that do not specifically target any particular segment of DNA or RNA. They are used in molecular biology for various applications, notably in PCR and cDNA synthesis. Their primary function is to initiate DNA synthesis across multiple regions of the template, making them ideal for generating a comprehensive overview of the genome or transcriptome.
Advantages
The use of random primers offers several key benefits in molecular biology research:
- Comprehensive Coverage: Random primers can bind to multiple sites across the DNA or RNA template, facilitating the amplification or synthesis of a wide range of sequences.
- Flexibility: They are not sequence-specific, making them suitable for a variety of templates and applications.
- Efficiency in cDNA Synthesis: Especially useful in reverse transcription for creating cDNA libraries from RNA, as they ensure coverage of RNA molecules that may not have poly(A) tails.
Limitations
Despite their advantages, random primers also present certain challenges:
- Lower Specificity: Can result in nonspecific binding, leading to the amplification of unintended sequences.
- Complex Data Analysis: The comprehensive nature of amplification may complicate data analysis, especially when specific target identification is required.
- Potential for Primer-Dimer Formation: Their random nature might lead to the formation of primer dimers, which can interfere with the amplification process.
Oligo dT Primers
Definition and Use
Oligo dT primers are designed to specifically anneal to the poly(A) tail found at the 3′ end of most eukaryotic mRNA molecules. This specificity makes them particularly useful in mRNA isolation and cDNA synthesis, as they ensure that only mRNA is transcribed into cDNA, providing a clear focus on gene expression.
Advantages
The specificity of oligo dT primers to mRNA offers distinct advantages:
- High Specificity for mRNA: Enables selective amplification of mRNA, excluding rRNA, tRNA, and other RNA species, which is crucial for gene expression studies.
- Cleaner cDNA Libraries: Results in cDNA libraries that represent the coding transcriptome, facilitating the study of gene function and expression.
- Efficiency: Ideal for use in experiments where the interest lies specifically in coding sequences, streamlining the research process.
Limitations
However, oligo dT primers also come with limitations:
- Restricted to Poly(A) mRNA: They will not transcribe RNA species without a poly(A) tail, potentially missing important non-polyadenylated transcripts.
- Risk of Incomplete Reverse Transcription: Particularly for long mRNA molecules, as synthesis may not proceed all the way to the 5′ end.
- Not Suitable for All Applications: Their specificity for mRNA means they are not ideal for studies requiring a broader overview of the transcriptome or for use with prokaryotic RNA.
Comparative Analysis
Selection Criteria
Choosing between random primers and oligo dT depends on several key factors:
- Research Objective: The specific goals of the experiment guide primer choice. For comprehensive analysis, random primers are preferred, whereas oligo dT primers are selected for mRNA-related studies.
- Template Type: The nature of the RNA or DNA template, including its complexity and the presence of modifications, influences primer selection.
- Sensitivity and Specificity Needs: Depending on the need for sensitivity to detect low-abundance transcripts or specificity to target particular mRNA, the choice of primer varies.
Application Differences
The application significantly affects experimental outcomes. For instance:
- Gene Expression Studies: Oligo dT primers are superior due to their specificity to mRNA.
- Genome Mapping and Sequencing: Random primers offer a more comprehensive approach, beneficial for exploratory studies where coverage is crucial.
Efficiency and Specificity
Random primers provide high efficiency in applications requiring a broad overview of genetic material, but oligo dT primers outperform in specificity for targeting mRNA transcripts, crucial for precise gene expression analysis.
Technical Considerations
Reaction Conditions
Reaction conditions, including temperature, ion concentration, and enzyme choice, have a significant impact:
- Random Primers: Require optimal conditions for nonspecific binding, which might involve adjusting temperatures to balance coverage and specificity.
- Oligo dT Primers: The conditions are tailored to promote binding to the poly(A) tails, often requiring lower temperatures to prevent secondary structures that hinder primer binding.
Sample Type
The nature of the sample—whether it’s total RNA, mRNA, environmental samples, or clinical specimens—determines primer appropriateness:
- Total RNA Samples: Random primers are advantageous for covering all transcript types.
- mRNA Samples: Oligo dT primers are ideal for focusing on coding RNA.
Experimental Goals
Experimental objectives guide primer selection:
- Broad Analysis: Random primers are chosen for a comprehensive view.
- Specific Targeting: Oligo dT primers are used when the focus is on mRNA.
Industry Applications
Clinical Research
In clinical research, primers play critical roles:
- Random Primers: Used in pathogen detection from diverse samples, ensuring wide-ranging coverage.
- Oligo dT Primers: Essential in cancer research for studying gene expression patterns in tumors.
Biotechnology
Primers are pivotal in biotechnology:
- Random Primers: Facilitate the development of genetic modifications by allowing for the broad analysis of genetic material.
- Oligo dT Primers: Used in the production of recombinant proteins, targeting mRNA to understand and manipulate gene expression.
Future Perspectives
Technological Advancements
Emerging technologies, such as next-generation sequencing (NGS) and CRISPR-Cas9, influence primer choice, steering towards more specific and efficient primers for targeted research and therapeutic applications.
Challenges and Opportunities
The future holds challenges like the need for higher specificity and efficiency in primer design, and opportunities in the development of new materials and methods for primer synthesis, enhancing molecular biology research and applications.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are Random Primers?
Random primers are short, synthetic strands of DNA that bind non-specifically across an RNA or DNA template. Their primary use is in creating cDNA libraries and facilitating the synthesis of the first strand of cDNA, allowing for a comprehensive overview of the genetic material present in a sample.
How do Oligo dT Primers Work?
Oligo dT primers are designed to anneal specifically to the polyadenylated tail of messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules. This specificity allows for the selective reverse transcription of mRNA into cDNA, making oligo dT primers invaluable in studying gene expression and identifying coding sequences within a genome.
When to Use Random Primers vs. Oligo dT?
The choice between random primers and oligo dT depends on the research objective. Random primers are preferred when a complete representation of the RNA sample is required, including various RNA species. Oligo dT primers are chosen for experiments focused on mRNA and gene expression analysis, due to their specificity for the poly(A) tail of mRNA.
Can Random Primers and Oligo dT be Used Together?
Yes, random primers and oligo dT can be used together in certain protocols to maximize the diversity of cDNA synthesis. This approach combines the comprehensive coverage of random primers with the mRNA specificity of oligo dT, offering a more complete snapshot of an organism’s transcriptome.
Conclusion
The choice between random primers and oligo dT encapsulates a fundamental decision-making process in molecular biology research. It reflects a balance between the need for comprehensive genomic representation and the desire for targeted, specific gene expression analysis. This article has shed light on the distinct features, applications, and considerations associated with each primer type, offering a guide for researchers to make informed decisions tailored to their experimental needs.
Understanding the intricate details of these primers not only equips researchers with the knowledge to select the appropriate tool for their experiments but also underscores the meticulous nature of scientific inquiry. As molecular biology continues to evolve, the thoughtful application of these primers will remain a cornerstone of genetic analysis, propelling discoveries that deepen our understanding of the living world.