X chromosome inactivation is a vital genetic process that ensures balanced gene expression between males and females. Both sexes inherit an X chromosome from their mother, but females inherit an additional X from their father. To balance this genetic inequality, one of the X chromosomes in female cells is inactivated during early development.
The difference between random and imprinted X inactivation lies in the selection of the X chromosome that undergoes silencing. Random X inactivation means any X chromosome can be silenced in a cell, regardless of its parental origin. In contrast, imprinted X inactivation systematically silences the X chromosome inherited from a specific parent, usually the paternal X.
The phenomenon of X inactivation is not just a curiosity of genetics; it has profound implications for development, disease, and genetic inheritance. This process is intricately regulated and varies widely not only between different species but also among individuals, impacting their health and susceptibility to various genetic conditions.

Basics of X Inactivation
Definition and Purpose
X inactivation is a critical genetic mechanism in female mammals that serves to balance the expression of genes from X chromosomes. Since females possess two X chromosomes and males only one, without this balancing act, females would produce double the amount of X chromosome gene products compared to males—a situation that could lead to developmental disorders and other health issues.
The purpose of X inactivation is straightforward: to equalize the genetic activity of X chromosomes between males and females. This process ensures that one of the two X chromosomes in each cell of a female is largely inactive, making the effective gene dosage comparable to that in males, who have only one X chromosome.
Role in Development and Disease
X inactivation is vital for healthy development. Errors in this process can lead to a variety of genetic disorders, including but not limited to:
- Turner Syndrome: Where females have one X chromosome instead of two.
- Triple X Syndrome: Where females have three X chromosomes.
These conditions illustrate the crucial role of precise X chromosome inactivation in normal development and health maintenance. Disruptions can affect everything from height and skeletal development to fertility and cognitive function.
Random X Inactivation
Explanation of the Process
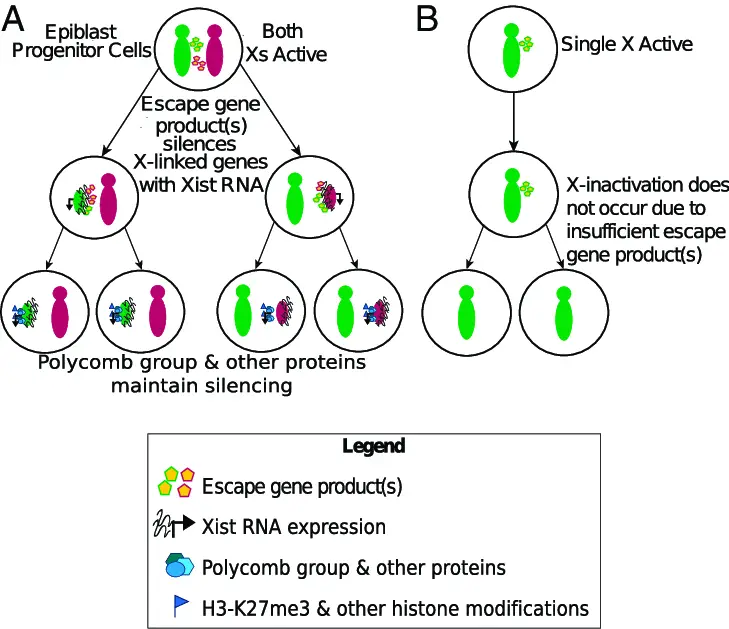
Random X inactivation occurs when each cell in a developing female embryo randomly chooses one X chromosome to silence. This decision is made early in embryonic development and once an X chromosome is inactivated, all daughter cells will also inactivate the same X chromosome. The process involves:
- Coating: The chosen X chromosome is coated with the XIST RNA, which prevents transcription of genes.
- Modification: DNA methylation and histone modification further silence the chromosome.
Occurrence and Significance
This form of inactivation is significant because it leads to a mosaic of cells expressing either the maternal or paternal X chromosome. This genetic diversity within the tissues can be beneficial, providing a form of natural protection against X-linked diseases—if one X chromosome carries a harmful mutation, some cells will express the healthy chromosome from the other parent.
Genetic Mechanisms Involved
Several genetic mechanisms underlie random X inactivation, including:
- XIST gene expression: This gene is crucial for initiating the inactivation process.
- DNA methylation: Adds a methyl group to DNA, thereby modifying the expression of genes.
- Histone modification: Changes to histones that help DNA wrap more tightly, reducing gene expression.
Imprinted X Inactivation
Definition and Characteristics
Imprinted X inactivation differs from the random type by always silencing the X chromosome inherited from one specific parent, usually the paternal one. This type of inactivation is less common and typically observed in certain marsupials and in extraembryonic tissues of mice, where it plays a role in development.
How It Differs from Random Inactivation
Unlike random X inactivation, imprinted inactivation does not involve a choice between two chromosomes. Instead, it systematically targets the X chromosome from one parent:
- Paternal X inactivation: Typically seen in marsupials, where the paternal X chromosome is always inactivated.
- Maternal X inactivation: Rarely observed, but can occur under specific genetic conditions.
Key Biological Processes
The processes driving imprinted X inactivation include:
- Genetic imprinting: Specific genes are marked by DNA methylation to be silenced depending on their parental origin.
- Regulatory RNAs: Play a role in maintaining the silence of the imprinted X chromosome.
Comparative Analysis
Side-by-Side Comparison of Random and Imprinted
When comparing random and imprinted X inactivation, key differences arise in:
- Choice of chromosome: Random allows any X to be inactivated; imprinted always chooses the paternal X.
- Developmental timing and tissues affected: Random occurs in all somatic cells; imprinted is usually restricted to certain tissues and stages.
Genetic and Epigenetic Factors
Both forms of X inactivation are influenced by a mix of genetic and epigenetic factors, such as:
- Gene regulation: Both types utilize XIST and other regulatory RNAs.
- Epigenetic changes: Including DNA methylation and histone modifications, though the specific patterns and timings differ.
Impact on Genetic Diseases
Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for addressing X-linked genetic diseases. Differences in inactivation can influence the severity and expression of diseases like hemophilia and Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Depending on which X chromosome is inactivated, a female carrier might show symptoms of these typically male-linked diseases.
Case Studies
Examples in Human Genetics
X inactivation has been pivotal in understanding various genetic conditions affecting humans. Turner Syndrome, where individuals typically have one X chromosome instead of two (45,X instead of 46,XX), offers insight into the developmental and health impacts of X chromosome anomalies. Studies show that the single X chromosome in Turner Syndrome is usually the maternal one, which remains active because there is no counterpart to be inactivated.
Another significant case is Rett Syndrome, a rare genetic disorder affecting brain development in girls. It is linked to mutations in the MECP2 gene on the X chromosome. Because of random X inactivation, some cells have a normal MECP2 gene active while others do not, leading to a mosaic pattern of functional and non-functional cells that affects the severity and symptoms of the disorder.
Research Findings on Abnormalities
Research into X-linked lymphoproliferative disease demonstrates the critical role of X inactivation in immune function. This disease, often fatal in boys, has been observed in some female carriers who exhibit symptoms due to skewed X inactivation favoring the X chromosome with the faulty gene.
Studies on Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD), primarily affecting boys, also underline the role of X inactivation. Female carriers occasionally manifest mild symptoms if there is skewed inactivation towards the X chromosome carrying the defective dystrophin gene.
FAQs on X Inactivation
Common Questions and Expert Answers
What triggers X inactivation?
X inactivation is triggered by the XIST gene, which produces an RNA molecule coating the X chromosome to be silenced, initiating the inactivation process.
Does X inactivation affect all cells?
X inactivation affects all female somatic cells but is not present in male cells or the germ cells that produce eggs and sperm.
Can X inactivation be reversed?
Under normal circumstances, once an X chromosome is inactivated in a cell, the inactivation is permanent in that cell and all its descendants.
Clarifications on Misconceptions
Is X inactivation always complete?
No, X inactivation is not absolute. About 15% of genes on the inactivated X chromosome can still be expressed, leading to some level of genetic activity.
Do all females have the same X chromosome inactivated?
No, in random X inactivation, the choice of which X chromosome to silence varies from cell to cell across different tissues.
Future Directions
Ongoing Research and Potential Discoveries
Current research is exploring the possibility of reactivating the inactivated X chromosome as a potential therapy for X-linked diseases like Rett Syndrome and DMD. Scientists are investigating ways to silence the XIST RNA on the inactivated X, which could allow genes on that chromosome to be expressed again.
Advancements in CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing technology also hold promise for correcting mutations on the X chromosome in diseases like hemophilia. If researchers can safely apply these techniques in vivo, it could revolutionize treatment for these disorders.
Impact on Medical Genetics and Therapies
The study of X inactivation is advancing our understanding of genetic disorders and is crucial in the development of gene therapies. Insights from X inactivation could lead to breakthroughs in managing conditions traditionally considered untreatable.
For example, knowing which X chromosome is inactivated in carriers of X-linked diseases could improve carrier screening programs and help predict the likelihood of a disease manifesting in offspring. Moreover, therapies that modulate X chromosome inactivation patterns could offer novel treatments for diseases that currently have no cure.
FAQs on X Inactivation
What is X inactivation?
X inactivation is a cellular mechanism used to deactivate one of the two X chromosomes found in female mammals. This process ensures that females, like males, have one functionally active X chromosome per cell, balancing the dosage of X-linked genes.
How does random X inactivation differ from imprinted?
Random X inactivation involves the silencing of one X chromosome in female cells at random, meaning it could be either the maternal or paternal X. Imprinted X inactivation, however, always targets the X chromosome from a specific parent, typically the paternal one.
Why is X inactivation important in genetics?
X inactivation plays a critical role in preventing an overdose of X-linked gene expression in females, which could lead to developmental abnormalities and diseases. Understanding this process helps in diagnosing and treating X-linked genetic disorders.
Can X inactivation affect males?
Typically, males have only one X chromosome and do not undergo X inactivation. However, rare genetic conditions involving additional X chromosomes, such as Klinefelter syndrome (XXY), may lead to X inactivation in males.
Does X inactivation occur in all cells?
X inactivation generally occurs in all female somatic (non-reproductive) cells early in embryonic development. However, the specific X chromosome inactivated can vary from cell to cell in the case of random X inactivation.
Conclusion
X chromosome inactivation is a cornerstone of genetic balance and diversity. By silencing one X chromosome, it ensures that males and females express a similar amount of X-linked genes, crucial for normal development and health. This genetic mechanism is not just a safeguard against imbalance; it is a fascinating example of nature’s precision in maintaining genetic stability across generations.
In light of ongoing research, our understanding of X inactivation, particularly how it influences genetic disorders and treatments, is expected to grow. This evolving knowledge promises to enhance our ability to manage and potentially cure a range of genetic conditions, highlighting the importance of genetics in medical science.

