Valency is an important concept in chemistry that describes the ability of an atom or molecule to form chemical bonds. Primary and secondary valency are two types of valency and they have distinct differences. In this blog post, we will discuss the differences between primary and secondary valency, how they are used in chemistry, and their importance in the study of chemical reactions.
History of valency theory
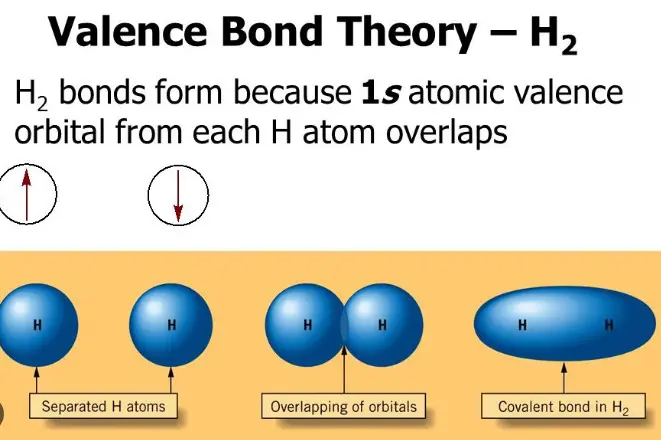
The history of valency theory can be traced back to the 18th century, when chemists first began to observe patterns in the chemical behavior of different elements. This led to the development of the concept of valency, which is the number of chemical bonds an atom can form with other atoms.
Valency is an important factor in understanding the structure and reactivity of molecules. Valency theory is divided into two categories – primary and secondary valency. Primary valency is the number of bonds that an atom can form directly with other atoms, while secondary valency is the number of bonds that an atom can form indirectly with other atoms, usually through a third atom.
The ability of an atom to form both primary and secondary valencies is what allows for the formation of complex molecules.
Types of valencies: primary and secondary
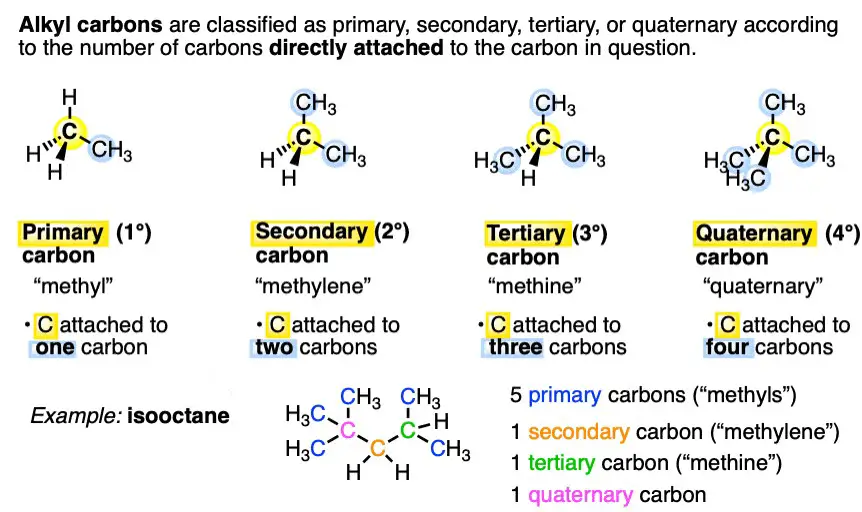
Valency is a measure of the ability of an atom or a molecule to combine with other atoms or molecules. It is the number of bonds that an atom can form with other atoms. There are two types of valency: primary and secondary.
Primary valency is the number of bonds an atom can form without rearrangement of its electrons. Secondary valency is the number of bonds an atom can form after rearranging its electrons.
Primary valency is a fixed number for a given atom, whereas secondary valency is variable and can be changed depending on the nature of the atoms it bonds with. Primary valency is usually determined by the number of electrons in the outermost shell of the atom, whereas secondary valency is determined by the number of electrons that can be donated or accepted by the atom.
Primary valency is usually considered to be more stable than secondary valency, since it does not require rearrangement of electrons.
Factors that impact primary and secondary valency
Understanding the difference between primary and secondary valency is key to understanding why certain chemicals react the way they do. Primary valency is the number of electrons an atom needs to reach its ideal electron configuration, while secondary valency is the number of electrons an atom gives away or shares in a chemical reaction. Factors such as ionic radius, electronegativity, and electron affinity can all influence the primary and secondary valency of a given atom.
Ionic radius is the distance between the nucleus and the outermost electrons of an atom, and it can impact the primary valency of a given atom as the farther away the outermost electrons are, the easier it is for the atom to gain or lose electrons. Electronegativity is the degree to which an atom tends to attract electrons, and it can be a factor in determining the secondary valency of an atom as it determines the ability of the atom to hold onto electrons.
Lastly, electron affinity is the amount of energy released when an atom gains an electron, and it can influence the primary and secondary valency of an atom as the more energy it releases, the easier it is for the atom to gain or lose an electron.
Examples of primary and secondary valency in everyday life
Understanding the difference between primary and secondary valency in everyday life can help us make more informed decisions in our daily lives. Primary valency refers to the number of connections or bonds that an atom can form with other atoms. It describes the number of atoms, ions, or molecules that an atom can bind to.
It describes the number of atoms, ions, or molecules that an atom can bind to. Secondary valency, on the other hand, is the number of bonds that an atom can form with other atoms of the same type. This is the type of valency that can determine the strength and stability of a compound.
For example, carbon has a primary valency of four, meaning it can form four bonds with other atoms. However, carbon also has a secondary valency of two, meaning it can form two strong bonds with other carbons.
Applications of primary and secondary valency
Valency is a concept which refers to the number of bonds that an atom or molecule can form with other atoms or molecules. Primary valency is the number of bonds an atom can form due to its electrons in the outermost shell. On the other hand, secondary valency is the number of bonds an atom can form due to electrons in its inner shells.
On the other hand, secondary valency is the number of bonds an atom can form due to electrons in its inner shells. The main difference between primary and secondary valency is that primary valency is the number of bonds an atom can form due to its electrons in the outermost shell whereas secondary valency is the number of bonds an atom can form due to electrons in its inner shells. Primary valency is often determined by the number of electrons in the outermost shell of the atom, while secondary valency is determined by the electron configuration of the inner shells.
Primary valency is more stable and stronger than secondary valency due to the more stable electron configuration of the outermost shell. The applications of primary and secondary valency can be found in a variety of fields, including chemistry, biology, medicine, and engineering. For example, in chemistry, primary and secondary valency are used to determine the properties and reactivity of compounds.
In biology, primary and secondary valency are used to understand the structure and function of proteins and other biological molecules. In medicine, primary and secondary valency are used to design drugs and other therapeutic agents.
Finally, in engineering, primary and secondary valency are used to design and synthesize new materials.
Conclusion
In conclusion, primary and secondary valency are two different types of valency, each with its own unique characteristics. Primary valency is based on the number of bonds a particular atom can form, while secondary valency is based on the number of atoms that can be attached to a particular atom.
Primary valency can be thought of as a measure of the atom’s ability to form strong bonds, whereas secondary valency refers to the number of connection points an atom has to other atoms. Both primary and secondary valency are important when considering the properties of a molecule and its interactions with other molecules.
