Polypeptides and polyamides are two classes of polymers that play critical roles in both biological systems and industrial applications. Despite their shared status as polymers, their structures, properties, and uses exhibit distinct differences. This introduction aims to clarify these differences without overwhelming with technical jargon.
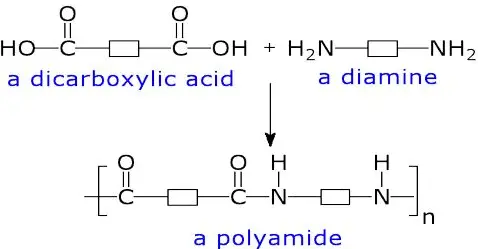
Polypeptides are chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds and are fundamental to biological functions, forming proteins and enzymes that regulate bodily processes. Polyamides, commonly known as nylons, are synthetic polymers formed by the linkage of amide bonds, extensively used in manufacturing due to their robustness and flexibility. The primary difference lies in their building blocks and resultant properties which dictate their applications in various fields.
In exploring these polymers, we’ll examine their molecular structures, properties, biological roles, and industrial uses. This insight not only enhances our understanding of material science but also highlights the innovative potential these materials hold for future applications.
Polypeptide Basics
Definition and Structure
Polypeptides are organic polymers made up of amino acids, which are the fundamental building blocks of proteins. Each amino acid within a polypeptide is connected to another by a peptide bond – a special type of covalent bond. This sequence of amino acids determines the structure and function of the polypeptide. The structure of polypeptides can range from simple linear chains to complex folded shapes, which are critical in determining their function in biological processes.
Production Processes
Polypeptides are typically produced in two main ways: biological synthesis and chemical synthesis.
- Biological synthesis: This natural process occurs in living organisms where ribosomes build polypeptides based on genetic instructions from DNA.
- Chemical synthesis: In the lab, chemists use techniques such as solid-phase peptide synthesis, where amino acids are sequentially added to a growing chain, allowing for the creation of polypeptides with predetermined sequences.
Polyamide Fundamentals
Definition and Characteristics
Polyamides are a type of polymer consisting of monomers linked by amide bonds and are known for their strength, elasticity, and resistance to wear and tear. These characteristics make them ideal for applications requiring durability and flexibility, such as in textiles and automotive parts.
Common Types and Uses
The most well-known polyamides are nylons, with various types tailored to specific uses:
- Nylon 6,6: Renowned for its robustness and is widely used in the manufacture of tire cords, carpets, and apparel.
- Nylon 6: This type is easier to process and is commonly used in food packaging and textiles.
Chemical Properties
Molecular Bonding
The strength of polyamides arises from the amide bonds between monomers, which are extremely strong due to both covalent and hydrogen bonding. This dual bonding nature imparts high thermal and chemical stability to the polymers.
Stability and Reactivity
Polyamides are less reactive compared to other polymers, which makes them resistant to various chemicals. This chemical resistance along with their stability under heat makes polyamides suitable for applications like automotive engine covers, which must withstand high temperatures and aggressive chemicals.
Physical Properties
Density and Solubility
Polyamides typically have a high density, contributing to their toughness and structural integrity. They are generally insoluble in water but can absorb moisture, which may affect their mechanical properties and dimensional stability.
Thermal and Mechanical Behavior
The thermal behavior of polyamides allows them to perform well in a wide range of temperatures, which is essential for applications in environments experiencing extreme heat or cold. Their mechanical properties include high resistance to abrasion and impact, which are beneficial in protective gear and high-performance parts.
Biological Roles of Polypeptides
Functions in Organisms
Polypeptides serve as vital components in virtually all biological systems. They perform a myriad of functions, key among them being:
- Enzymatic activity: Many enzymes are polypeptides that catalyze biochemical reactions, crucial for metabolism and other cellular functions.
- Structural roles: Structural proteins like collagen and keratin are composed of polypeptides and provide support in tissues and cells.
- Signaling: Polypeptides like hormones (insulin and glucagon) play critical roles in signaling pathways that regulate biological processes.
Applications in Medicine
In the medical field, polypeptides have significant applications due to their functionality and specificity:
- Therapeutic agents: Insulin, a polypeptide hormone, is essential for the treatment of diabetes.
- Diagnostic tools: Polypeptide-based markers and antibodies are used in diagnostic assays and medical imaging techniques.
Industrial Uses of Polyamides
Textiles and Plastics
Polyamides, notably nylons, are prevalent in the textile industry due to their durability and flexibility:
- Clothing: Their resistance to abrasion and chemicals makes them ideal for outdoor and performance wear.
- Plastic applications: Polyamides are used in various consumer goods, including robust plastic containers and machine parts due to their strong mechanical properties.
Automotive and Aerospace Applications
In more demanding sectors, polyamides provide critical functionality:
- Automotive: Used in components like gears and bearings that require durability and heat resistance.
- Aerospace: Employed in parts that must withstand extreme conditions, such as high temperatures and mechanical stress.
Environmental Impact
Biodegradability of Polypeptides
Polypeptides are generally biodegradable, making them more environmentally friendly compared to many synthetic polymers. This characteristic is especially important in reducing the impact of biomaterials on the ecosystem.
Recycling and Sustainability of Polyamides
Although polyamides are less biodegradable, efforts are ongoing to enhance their sustainability:
- Recycling processes: Mechanical recycling methods are being developed to reclaim and reuse polyamide materials.
- Bio-based alternatives: Research is focused on developing polyamides from renewable resources to reduce dependency on petroleum-based products.
Future Trends
Innovations in Polymer Science
Advancements in polymer science continue to push the boundaries of what’s possible with both polypeptides and polyamides:
- Smart polymers: Development of stimuli-responsive polymers that change properties in response to environmental variables.
- Biocompatibility: Enhancing the biocompatibility of polymers for use in medical implants and devices.
Emerging Applications
Looking ahead, the application areas for these polymers are set to expand:
- Electronics: Polyamides are being explored for use in flexible electronics due to their insulating properties and durability.
- Biodegradable alternatives: Research into polypeptides that can replace traditional plastics in various applications to improve environmental sustainability.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are Polypeptides?
Polypeptides are organic polymers made up of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. They are essential for various biological functions, forming the structure of proteins and acting as enzymes in biochemical reactions.
How are Polyamides Used?
Polyamides, including the well-known nylons, are utilized extensively in the textile industry for making resilient and durable fabrics. Beyond textiles, they serve in automotive and aerospace industries for manufacturing components that require high mechanical strength and thermal resistance.
What Makes Polypeptides Different from Polyamides?
The main difference between polypeptides and polyamides lies in their molecular structure. Polypeptides are composed of amino acids, while polyamides are made from monomers linked by amide bonds, leading to different physical properties and applications.
Are Polyamides Biodegradable?
Most polyamides are not readily biodegradable, posing environmental challenges. However, recent developments in bio-based polyamides aim to improve their sustainability and reduce environmental impact.
Can Polypeptides be Synthesized?
Yes, polypeptides can be synthesized in the laboratory through techniques like solid-phase peptide synthesis, allowing researchers to design polypeptides with specific properties for medical and biotechnological applications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while polypeptides and polyamides share the common feature of being polymers, their differences are substantial and influential in their respective domains. Polypeptides’ role in biological processes contrasts sharply with polyamides’ extensive industrial applications, demonstrating the versatility and significance of polymers in modern science and technology.
Understanding these materials’ properties and applications not only furthers scientific knowledge but also opens the door to innovative uses in various fields. As research continues, the potential for new and improved polymers holds promising prospects for advancements in medicine, sustainability, and technology.

