Plants, like all living organisms, adapt and respond to their environment in remarkable ways to survive and thrive. Two of the most fascinating processes through which plants interact with their surroundings are photoperiodism and vernalization. These mechanisms enable plants to sense time and seasonal changes, guiding their growth, flowering, and dormancy patterns based on external cues such as light and temperature.
Photoperiodism refers to the plant’s ability to respond to the length of day or night, which in turn influences its flowering and growth cycles. Vernalization, on the other hand, involves the induction of a plant’s flowering process through exposure to prolonged cold temperatures. Both processes are crucial for the successful reproduction and survival of many plant species, affecting everything from the timing of flowering to seed germination.
While photoperiodism relies on light to signal plants when to enter a new phase of their life cycle, vernalization uses temperature as its cue. This distinction is vital for plants to align their growth cycles with the most favorable environmental conditions, ensuring they can reproduce and spread their genes. By understanding these processes, scientists and farmers can better predict plant behavior and improve agricultural practices, making our food supply more sustainable and resilient.

What is Photoperiodism?
Definition and Basics
Photoperiodism is a biological response in plants to the length of day or night they experience. It’s a process that allows plants to sense and react to seasonal changes in day length, enabling them to time critical events such as flowering, seed germination, and leaf fall. This adaptation is crucial for their survival, reproduction, and efficient energy use.
Types of Photoperiodism
There are three main types of photoperiodism, each defining how different plants respond to changes in daylight:
- Short-day plants (SDPs): These plants flower when the night is longer than a certain critical length. Examples include rice and chrysanthemums.
- Long-day plants (LDPs): These plants flower when the night is shorter than a critical length. Spinach and lettuce are examples.
- Day-neutral plants (DNPs): The flowering of these plants is not affected by day length. Tomatoes and cucumbers fall into this category.
Role in Flowering and Plant Behavior
Photoperiodism is vital for timing the flowering in many plants, ensuring that reproduction occurs at the optimal time for seed development and dispersal. It also influences vegetative growth and dormancy, helping plants prepare for adverse conditions like winter.
Key Aspects of Photoperiodism
Light Quality and Plant Response
The quality of light, particularly the ratio of red to far-red light, significantly impacts photoperiodic responses. Plants use this ratio to gauge the density of vegetation around them, which in turn influences flowering time and growth patterns to avoid shading.
Photoreceptors and Signaling Pathways
Plants have specialized photoreceptors, such as phytochromes and cryptochromes, that detect changes in light quality and quantity. These receptors activate signaling pathways that alter gene expression, leading to physiological changes aligned with the plant’s developmental needs.
Examples in Nature
- SDPs like soybeans initiate flowering as days get shorter, aligning seed production with the end of the growing season.
- LDPs such as wheat flower in late spring or early summer when days are longer, ensuring seeds mature during the warmest months.
- DNPs exhibit flowering independent of day length, allowing for flexible cultivation in various environmental conditions.
What is Vernalization?
Definition and Basics
Vernalization is the process by which exposure to prolonged cold induces flowering in some plants. This requirement prevents plants from flowering before winter, ensuring that seed production occurs under favorable conditions. It’s a crucial adaptation for winter annuals and biennials, which must survive cold before they can flower.
Mechanism of Action
During vernalization, cold temperatures modify the methylation patterns of certain genes, leading to their activation or repression. This genetic change primes the plant to flower once it experiences sufficient warmth and light, aligning reproductive activities with optimal environmental conditions.
Importance for Germination and Flowering
Vernalization is essential for the germination of many seeds, which may only sprout after experiencing cold. For flowering, it ensures that plants only reproduce after escaping the harsh winter conditions, timing seed development with the spring and summer months when conditions for growth and dispersal are ideal.
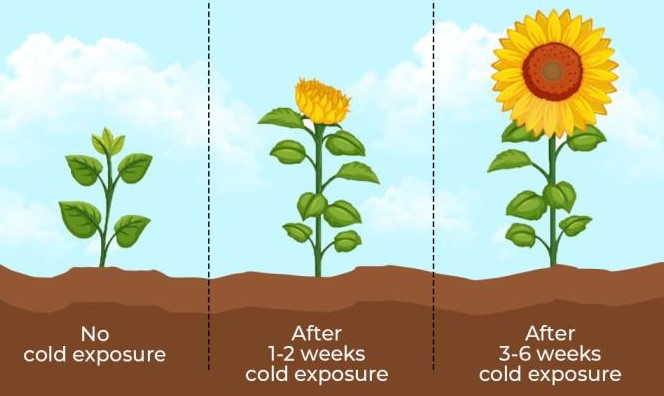
Key Aspects of Vernalization
Temperature Requirements
For vernalization to occur effectively, plants must be exposed to low temperatures for a specific period, typically between 0°C and 10°C. The necessary duration can range from a few weeks to several months, depending on the species and its adaptation to its native climate. This exposure to cold doesn’t just prevent premature flowering; it also ensures that the plant’s development aligns with optimal environmental conditions for survival and reproduction.
Genetic and Molecular Basis
Vernalization triggers changes at the genetic and molecular levels, altering the expression of certain genes critical for flowering. One well-studied pathway involves the FLC gene, which suppresses flowering. Cold exposure gradually reduces FLC expression, removing the block and allowing flowering to proceed. This process is mediated by complex interactions between histone modifications, DNA methylation, and non-coding RNAs, illustrating the sophisticated control plants have over their reproductive timing.
Examples in Agriculture
- Winter Wheat: Requires cold exposure to flower and produce grain, making it suitable for regions with cold winters.
- Brassicas: Many vegetables in this family, including broccoli and cauliflower, benefit from cold periods for optimal growth and flowering.
Photoperiodism vs. Vernalization
Core Differences
While both photoperiodism and vernalization are crucial for plant development, they rely on different environmental cues: light and temperature, respectively. Photoperiodism regulates growth based on day length, whereas vernalization depends on exposure to cold. These processes often work together to ensure that flowering and reproduction occur at the best possible time.
Impact on Plant Development
Photoperiodism and vernalization have profound impacts on the timing of flowering, seed germination, and dormancy. They enable plants to synchronize their life cycles with favorable environmental conditions, enhancing survival and reproductive success.
Practical Implications in Farming
Understanding these processes allows farmers to manipulate plant growth for better yields. For example, farmers can use artificial lighting or refrigeration to mimic natural conditions, inducing plants to flower or enter dormancy at specific times.
Role in Agriculture
Crop Breeding Strategies
Breeding programs often select for plants with desirable photoperiodic and vernalization responses, aiming to extend the growing season or adapt crops to different climates. For instance, breeding wheat varieties that require less cold to vernalize allows their cultivation in warmer regions.
Manipulation for Yield Optimization
Farmers and horticulturists manipulate light and temperature to optimize yields. Greenhouses, for example, control these factors to produce vegetables year-round, irrespective of natural seasons.
Climate Change Challenges
As climate change alters temperature patterns and seasonal timings, plants’ photoperiodic and vernalization responses may no longer align with optimal conditions. Breeders are now working to develop new varieties that can adapt to changing climates, ensuring food security.
Advances in Research
Recent Findings in Photoperiodism
Recent studies have unveiled new photoreceptors and signaling molecules involved in photoperiodism, offering insights into how plants perceive and respond to light. These discoveries are helping scientists understand plant behaviors in greater detail, from flowering to stress responses.
Breakthroughs in Vernalization Studies
Advances in genomic and molecular biology tools have illuminated the vernalization pathway in various plants, identifying key genes and mechanisms that control this complex process. Such knowledge is crucial for manipulating flowering times and improving crop resilience.
Future Directions in Plant Biology
Future research will likely focus on integrating knowledge of photoperiodism and vernalization with other environmental responses, such as drought and heat tolerance. This holistic understanding will enable the development of crops that can withstand the multifaceted challenges of a changing global climate, ensuring sustainable agricultural practices and food security for future generations.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does photoperiodism affect plant growth?
Photoperiodism plays a critical role in determining when a plant will flower, based on the length of day and night. This adaptation allows plants to synchronize their flowering time with the most favorable seasonal conditions, optimizing their chances for successful pollination and seed production.
What is the purpose of vernalization in plants?
Vernalization ensures that plants only flower after being exposed to a period of cold, preventing premature flowering during unseasonably warm winter days. This process is crucial for winter annuals and biennials, which require a cold period to complete their life cycle and flower in spring.
Can photoperiodism and vernalization be manipulated for agricultural benefit?
Yes, by manipulating photoperiodism and vernalization, farmers and horticulturists can optimize plant growth and flowering times to increase yields and extend growing seasons. This manipulation involves controlling light exposure and temperature conditions to induce or delay flowering, allowing for more efficient food production and ornamental plant cultivation.
Are all plants affected by photoperiodism and vernalization?
Not all plants are equally affected by photoperiodism and vernalization. While many species rely on these processes to trigger key life cycle events, some plants are less sensitive to day length or temperature changes and may use other environmental cues for their developmental processes.
Conclusion
The intricate dance between plants and their environmental cues, governed by processes like photoperiodism and vernalization, underscores the complexity of life on Earth. These mechanisms not only allow plants to thrive in diverse ecosystems but also offer insights into how life adapts to the ever-changing planet. By understanding these natural processes, humanity can better harness the potential of plants for food, medicine, and ecological stability.
As we continue to study and apply our knowledge of photoperiodism and vernalization, the potential for innovative agricultural practices and ecological conservation efforts becomes even more pronounced. These processes remind us of the delicate balance required to sustain life and the importance of respecting and preserving our natural world for future generations.

