The human body operates through an incredibly intricate network of cellular components, each playing a vital role in maintaining health and fighting off disease. Among these, phagolysosomes and phagosomes stand out for their critical functions within the cells. These structures are essential in the process of ingesting and digesting foreign particles, such as bacteria and viruses, a process that is fundamental to the immune response and overall cellular health.
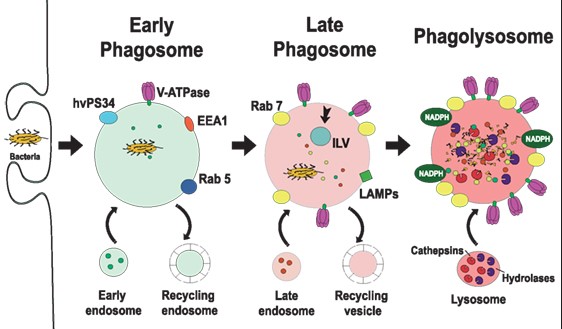
The difference between phagolysosomes and phagosomes lies primarily in their formation and function within a cell. Phagosomes are vesicles formed around a particle ingested by a cell, serving as the initial step in the degradation of foreign material. Phagolysosomes, on the other hand, are the result of the fusion between phagosomes and lysosomes, creating a more potent structure equipped with enzymes capable of breaking down ingested materials more effectively.
This topic is not just a matter of academic interest but has significant implications for understanding how our immune system works to protect us from diseases. The efficient operation of phagolysosomes and phagosomes is crucial for the clearance of pathogens and the prevention of infections. Any dysfunction in these processes can lead to a weakened immune response and increased vulnerability to diseases. Thus, exploring the differences between these cellular structures provides insights into their importance in cellular biology and immune system function.
Cell Biology Basics
Cellular Components
Definition and Function of Cells
Cells are the basic building blocks of all living organisms, from the simplest bacteria to complex human beings. They perform vital functions such as energy production, nutrient processing, and waste elimination, making life as we know it possible. Each cell operates as a self-contained unit, capable of converting food into energy, replicating itself, and responding to external stimuli.
Overview of Organelles
Organelles are specialized structures within cells that carry out specific tasks. Think of them as miniature organs within the cell. Key organelles include the nucleus, which stores genetic information; the mitochondria, known as the powerhouse of the cell for energy production; the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus for protein and lipid processing; and lysosomes and peroxisomes for waste breakdown and detoxification.
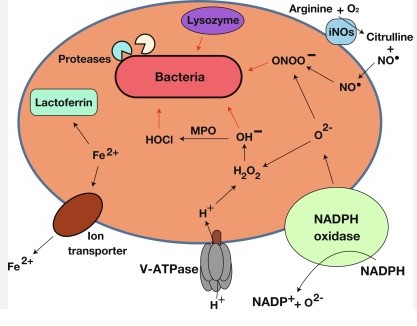
Immune System Role
Cells in the Immune System
The immune system is made up of various cell types, each with a specific role in defending the body against pathogens. White blood cells (WBCs), such as lymphocytes and phagocytes, are front-line defenders. Lymphocytes, including T-cells and B-cells, recognize specific pathogens and remember them for faster response in the future. Phagocytes, like macrophages and neutrophils, engulf and destroy invaders.
Mechanism of Pathogen Clearance
Pathogen clearance by the immune system is a complex process involving multiple steps:
- Recognition: Immune cells identify foreign invaders through specific markers.
- Response: Once recognized, a series of immune responses is triggered to neutralize the threat.
- Elimination: Immune cells, particularly phagocytes, ingest and break down pathogens.
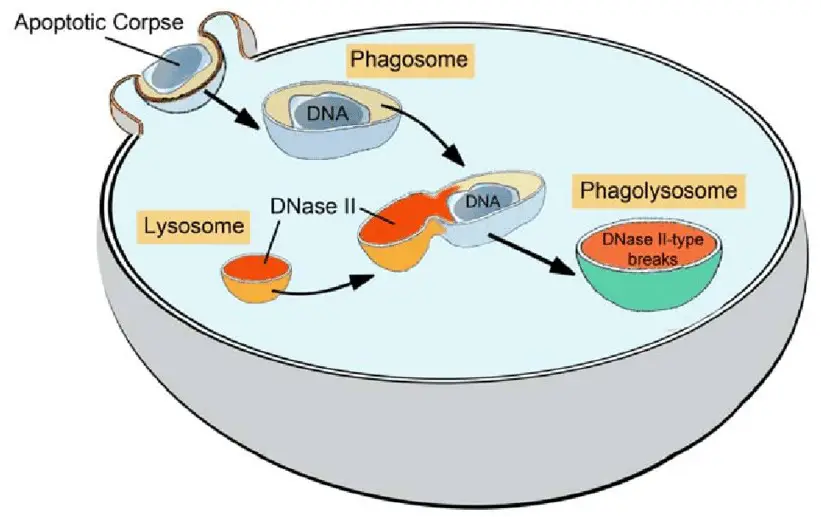
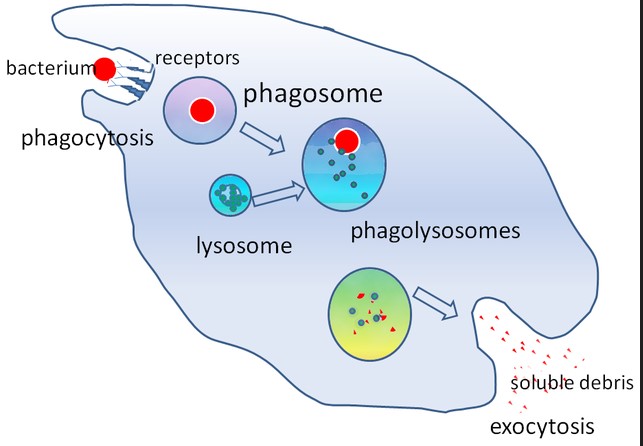
Phagosome Explained
Formation
Origin and Development in the Cell
Phagosomes form when a cell engulfs a foreign particle or microorganism. This process, known as phagocytosis, begins when the cell’s membrane wraps around the particle, eventually enclosing it in a membrane-bound vesicle—the phagosome.
Involvement in the Immune Response
Phagosomes are crucial for the immune response, serving as the cell’s first line of defense. By isolating and targeting pathogens for destruction, phagosomes prevent the spread of infection and signal other immune cells to the site of infection.
Function
Role in Cellular Defense
The primary role of phagosomes is to neutralize threats to the cell. After engulfing a pathogen, the phagosome transports it to a lysosome, where it will be destroyed. This process ensures that the pathogen is contained and eliminated before it can harm the cell or replicate.
Interaction with Pathogens
Phagosomes directly interact with pathogens by:
- Encapsulating them to prevent them from reaching other parts of the cell.
- Transporting them to lysosomes for degradation.
- Presenting pieces of the pathogen on the cell surface to alert the immune system.
Phagolysosome Overview
Creation
Phagosome and Lysosome Fusion
A phagolysosome forms when a phagosome fuses with a lysosome, a process facilitated by cellular signals triggered by the presence of a pathogen. The lysosome contributes digestive enzymes to the phagosome, creating a more potent structure capable of breaking down complex materials.
Triggering Factors
The fusion is triggered by factors such as:
- The chemical nature of the engulfed material.
- Cellular signals that indicate the presence of foreign particles.
- Environmental cues like pH changes within the phagosome.
Role
Enhanced Enzymatic Breakdown
Within the phagolysosome, enzymes from the lysosome work to dismantle the captured material. This process is highly efficient, ensuring that pathogens are rapidly broken down into harmless substances that the cell can either use or expel.
Final Steps in Pathogen Digestion
The final steps involve:
- Enzymatic degradation of the pathogen into smaller components.
- Recycling of useful materials back into the cell.
- Excretion of waste products out of the cell.
Key Differences
Structural Variations
Composition and Structural Differences
Phagosomes and phagolysosomes, while related, display distinct structural variations that define their roles within the cell. Phagosomes are primarily enclosed vesicles formed by the cell membrane engulfing a particle. Their structure is relatively simple, designed to transport the ingested material to lysosomes. In contrast, phagolysosomes are complex entities, the result of a phagosome fusing with a lysosome. This fusion introduces enzymatic machinery into the vesicle, enabling the breakdown of materials.
Membrane Properties
The membrane properties of phagosomes and phagolysosomes differ significantly, reflecting their distinct functions. Phagosome membranes are designed to be fusion-compatible with lysosomes, a feature that is crucial for the formation of phagolysosomes. On the other hand, phagolysosome membranes exhibit adaptations that maintain an acidic environment optimal for enzymatic activity, crucial for the degradation of ingested materials.
Functional Disparities
Enzymatic Activity Comparison
The enzymatic activity within phagosomes and phagolysosomes is markedly different. Phagosomes, being preliminary structures, contain little to no enzymes. Their main role is to sequester and transport. Phagolysosomes, however, are enzymatic powerhouses, packed with lysosomal enzymes that can break down almost any type of biological material, from bacteria to damaged cell parts.
Efficiency in Pathogen Degradation
The efficiency of pathogen degradation also sets phagosomes and phagolysosomes apart. Phagosomes can contain and transport pathogens but cannot degrade them. Phagolysosomes, with their arsenal of digestive enzymes, not only contain but also efficiently break down pathogens, rendering them harmless. This distinction is crucial in the cell’s ability to defend itself against infectious agents.
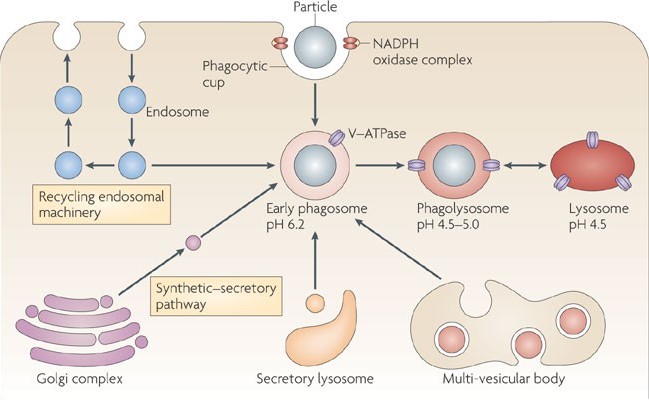
Significance in Disease
Phagosome in Disease
Implications of Dysfunction
Dysfunction in phagosome formation or transport can lead to impaired immune responses. Without effective phagosome function, pathogens may evade initial containment, leading to uncontrolled infections. This dysfunction can contribute to the severity of diseases, particularly those caused by bacteria and viruses that evade the immune system.
Examples of Diseases
Specific diseases, such as tuberculosis and leprosy, caused by bacteria that can resist or manipulate phagosome functions, illustrate the critical role of these structures. These pathogens can prevent the fusion of phagosomes with lysosomes, allowing them to survive and multiply within host cells.
Phagolysosome in Pathology
Role in Disease Progression
The role of phagolysosomes in disease progression is dual. On one hand, efficient phagolysosome function is essential for eliminating pathogens and preventing disease. On the other, certain pathogens have evolved mechanisms to survive or even thrive within phagolysosomes, using them as niches for replication. This ability can exacerbate disease progression and complicate treatment strategies.
Impact on Cellular Health
Phagolysosomes are also involved in cellular homeostasis by removing cell debris and damaged organelles. Dysfunction in phagolysosome formation or activity can lead to the accumulation of cellular waste, contributing to cell death and tissue damage, which are hallmarks of various degenerative diseases.
Research and Innovations
Current Studies
Latest Findings on Phagosome
Recent research has shed light on the molecular mechanisms underlying phagosome formation and maturation. Studies have identified new proteins and signaling pathways that regulate the engulfment of pathogens and the fusion of phagosomes with lysosomes. These insights open new avenues for targeting infectious diseases that manipulate phagosome functions.
Innovations in Understanding Phagolysosomes
Innovations in microscopy and imaging technologies have provided deeper insights into the dynamic nature of phagolysosomes. Researchers can now observe the real-time interaction between phagolysosomes and their contents, leading to a better understanding of how these structures degrade various materials. This knowledge is crucial for developing strategies to enhance the cell’s ability to combat pathogens.
Future Directions
Potential Therapeutic Targets
The detailed understanding of phagosome and phagolysosome functions offers new therapeutic targets for a wide range of diseases. By manipulating the formation, fusion, or enzymatic activity of these structures, it may be possible to boost the immune response to pathogens or prevent the progression of diseases that exploit these cellular mechanisms.
Advances in Cellular Biology and Disease Treatment
Future research aims to translate these cellular and molecular insights into practical treatments. Potential areas of advancement include gene therapy to correct phagosome and phagolysosome dysfunctions, and the development of drugs that can enhance the immune system’s ability to clear pathogens. The ongoing exploration of these cellular structures holds promise for significant breakthroughs in our ability to treat infectious and degenerative diseases more effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a Phagosome?
A phagosome is a vesicle formed within a cell that encloses a particle to be degraded, such as bacteria or dead cell material. It is created when the cell membrane engulfs a foreign particle, initiating the process of phagocytosis. The phagosome then migrates within the cell, eventually fusing with a lysosome to form a phagolysosome where the enclosed material is degraded.
How Does a Phagolysosome Form?
A phagolysosome forms through the fusion of a phagosome and a lysosome. This process begins when a phagosome, containing ingested foreign material, merges with a lysosome, which is rich in digestive enzymes. The resulting phagolysosome becomes a potent digestive compartment where enzymatic reactions break down the ingested material, leading to the effective elimination of pathogens from the cell.
Why are Phagosomes and Phagolysosomes Important?
Phagosomes and phagolysosomes are critical for the immune system’s ability to fight infections. They help remove pathogens, such as bacteria and viruses, and cellular debris, thus preventing infection and disease. Their efficient operation is essential for maintaining cellular health and ensuring the body’s resilience against infections. Dysfunction in these processes can impair the immune response, leading to increased susceptibility to diseases.
How Do Phagosomes and Phagolysosomes Differ?
The primary difference between phagosomes and phagolysosomes lies in their maturity and functionality. Phagosomes are initial vesicles that form around ingested particles, marking the beginning of the degradation process. Phagolysosomes, however, are more advanced structures formed by the fusion of phagosomes and lysosomes, equipped with digestive enzymes capable of efficiently breaking down the ingested material. This distinction is crucial for the cell’s ability to process and eliminate foreign particles effectively.
Conclusion
The distinction between phagolysosomes and phagosomes is more than just a matter of cellular semantics; it’s a key to understanding how our bodies defend against disease and maintain health. By examining the unique roles and processes of these cellular structures, we gain insights into the complexities of the immune system and the critical importance of efficient pathogen degradation. This knowledge not only enriches our understanding of cellular biology but also underscores the significance of ongoing research in the field.
In essence, the exploration of phagolysosomes and phagosomes highlights the marvels of the cellular machinery at work in our immune system. It serves as a reminder of the sophisticated processes that operate within our bodies, ensuring our health and well-being. Through continued study and understanding of these structures, we can potentially unlock new avenues for treating and preventing diseases, further demonstrating the intricate balance between cellular function and overall health.