Isotopes play a pivotal role in the tapestry of scientific understanding, weaving through disciplines from archaeology to medicine. These variants of elements, distinguished by their number of neutrons, offer clues to the age of the earth, the timing of geological events, and even the diagnosis of diseases. The distinction between parent and daughter isotopes serves as a cornerstone in the field of radiometric dating, enabling scientists to unlock the chronicles of natural history and technological advancement.
Parent and daughter isotopes are integral to the science of radiometric dating, providing a clock by which time is measured in the natural world. Parent isotopes decay into daughter isotopes at a predictable rate, known as the half-life. By measuring the ratio of parent to daughter isotopes in a sample, scientists can determine the age of the material with remarkable accuracy, offering insights into the timing of geological and biological events.
The narrative of isotopic transformation from parent to daughter encapsulates the essence of atomic decay and the transitory nature of matter. This transition not only marks the passage of time but also fuels the processes that shape our planet and life itself. From the depths of the earth to the frontiers of space, the study of parent and daughter isotopes illuminates the intricate dance of particles that constructs the universe.
Isotope Basics
What Are Isotopes?
Isotopes are variations of elements with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. This slight difference does not alter the chemical properties of an element significantly but does have profound implications on its physical properties and stability. Hydrogen, for example, exists as three isotopes: protium (no neutron), deuterium (one neutron), and tritium (two neutrons). While all three forms behave similarly in chemical reactions, their physical properties, such as mass and stability, vary considerably.
Examples of Isotopes
- Carbon-12 and Carbon-14: Both are isotopes of carbon but differ in their neutron count. Carbon-12 is stable, while Carbon-14 is radioactive and is used in radiocarbon dating.
- Uranium-238 and Uranium-235: These isotopes of uranium differ in their ability to sustain nuclear fission, with Uranium-235 being used as fuel in nuclear reactors and bombs.
Isotopes in Nature
Isotopes occur naturally and play critical roles in various environmental and geological processes. For instance, the ratio of oxygen isotopes in ice cores is used to infer past temperatures on Earth. Similarly, isotopes of nitrogen and carbon help scientists study ecological systems and trace nutrient cycles.
Role in Environmental and Geological Processes
The natural abundance of isotopes, like Carbon-14 and Uranium-Series isotopes, enables researchers to date archaeological finds and understand earth formation processes. Their decay rates act as a clock that provides insights into the timing of geological events, such as volcanic eruptions and the formation of mineral deposits.
Parent Isotopes
Definition and Characteristics
Parent isotopes are the unstable, radioactive isotopes that undergo decay to form stable isotopes, known as daughter isotopes. These isotopes are characterized by their half-lives, the time it takes for half of the isotopes in a sample to decay. Uranium-238, with a half-life of about 4.5 billion years, is a prime example of a parent isotope.
Explanation of Parent Isotopes
Parent isotopes are the source of daughter isotopes. Their decay is a natural process that occurs at a predictable rate, providing a powerful tool for dating and studying natural processes.
Key Features
- Radioactivity: The key feature of parent isotopes.
- Half-life: Defines the rate at which they decay.
Formation and Sources
Parent isotopes are formed in supernova explosions and during the formation of the solar system. They are found in rocks, minerals, and in the atmosphere.
Common Sources in Nature
- Rocks and Minerals: Uranium and thorium are commonly found in zircon and apatite.
- Atmosphere: Carbon-14 is formed in the atmosphere through the interaction of nitrogen with cosmic rays.
Daughter Isotopes
Definition and Characteristics
Daughter isotopes are the stable or more stable isotopes resulting from the decay of parent isotopes. Unlike their parents, daughter isotopes do not undergo significant radioactive decay and thus accumulate over time in materials.
Explanation of Daughter Isotopes
Daughter isotopes provide evidence of the decay process and are essential for dating materials and understanding the Earth’s and universe’s history.
Distinctive Features
- Stability: They are more stable compared to parent isotopes.
- Accumulation: Accumulate over time as parent isotopes decay.
Formation Process
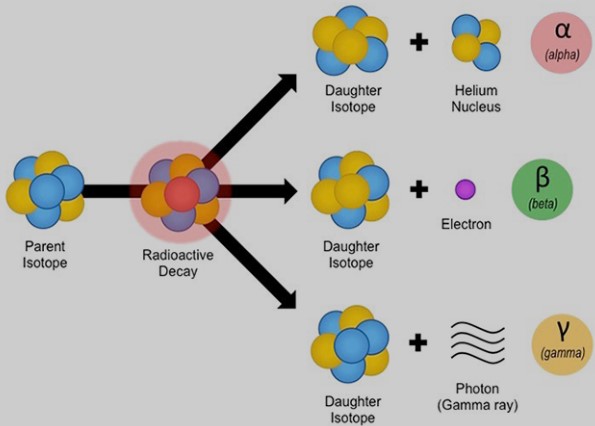
The transformation from parent to daughter isotopes involves various types of radioactive decay, including alpha decay, beta decay, and gamma decay. Each type involves the emission of particles or energy, leading to the formation of new isotopes.
Decay Process from Parent to Daughter
- Alpha Decay: Emission of an alpha particle, leading to a decrease in atomic number and mass.
- Beta Decay: Conversion of a neutron into a proton, increasing the atomic number.
- Gamma Decay: Emission of gamma radiation, resulting in no change in atomic number or mass but a decrease in energy.
Types of Radioactive Decay Involved
These decay processes are fundamental to changing the composition of isotopes and play a crucial role in the natural isotopic evolution and technological applications, such as nuclear medicine and radiometric dating.

Comparative Analysis
Physical Properties
Isotopes, both parent and daughter, have unique physical properties that distinguish one from the other. The most notable difference lies in their mass. Due to the varying number of neutrons, isotopes of the same element have different atomic masses. For example, Carbon-14 is heavier than Carbon-12 because it has two more neutrons. This difference in mass affects how isotopes interact with their environment and with other particles.
Charge and other physical properties remain consistent among isotopes of the same element, as these characteristics are determined by the number of protons and electrons, which do not change during decay. However, the nuclear stability and radioactivity vary significantly, impacting everything from radioactive dating to medical applications.
Half-Life
The half-life of an isotope is the time required for half of a sample of the isotope to decay. This concept is crucial in understanding the differences between parent and daughter isotopes. Parent isotopes, being unstable, have half-lives that can range from fractions of a second to billions of years. Daughter isotopes, on the other hand, may be stable or have much longer half-lives, indicating a slower rate of decay, if they decay at all.
Comparing the half-lives of parent and daughter isotopes offers insights into the age of rocks and organic materials. The longer the half-life, the older the sample can be dated.
Role in Radiometric Dating
Radiometric dating relies on the decay of radioactive isotopes from parent to daughter forms. The ratio of parent to daughter isotopes in a sample allows scientists to calculate the sample’s age with remarkable accuracy. This method is foundational in fields such as archaeology and geology, providing a timeline for the Earth’s history and human civilization.
Applications
Archaeology
In archaeology, radiometric dating, especially carbon dating, is a tool for determining the age of artifacts made from organic materials. This application has revolutionized our understanding of human history, allowing for the dating of objects up to 50,000 years old. By measuring the Carbon-14 content, archaeologists can pinpoint when a tree was cut down to make a tool or when a clay pot was fired.
Earth Sciences
Geologists use isotopic dating to map the Earth’s age and the timing of geological events like volcanic eruptions and the formation of mountain ranges. Isotopes like Uranium-238 are instrumental in dating rocks and minerals, providing a window into the planet’s formative processes.
Medical Applications
In the medical field, isotopes are used both in diagnostics and treatment. Radioactive isotopes like Iodine-131 are used in small doses to treat thyroid conditions, while others, such as Technetium-99m, are used in radiography to image internal organs.
Environmental Studies
Isotopes play a crucial role in environmental studies, tracing the sources of pollution and studying climate change. For instance, the ratio of Oxygen-18 to Oxygen-16 in ice cores helps scientists understand past temperatures and climate conditions.
Safety and Environmental Concerns
Radioactive Waste
The management of radioactive waste from medical, industrial, and nuclear power applications poses significant challenges. This waste, if not properly handled, can remain hazardous for thousands of years. Safe disposal methods are essential to protect human health and the environment.
Environmental Impact
The decay of isotopes, while a natural process, can have profound effects on ecosystems, especially when accelerated by human activities such as nuclear tests and reactor accidents. Monitoring and managing the isotopic composition of the environment is crucial to maintaining ecological balance and public health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are parent isotopes?
Parent isotopes are the original, unstable radioactive isotopes that undergo decay to form stable daughter isotopes over time. This transformation is a natural process and is fundamental to the principles of radiometric dating, providing a means to measure the age of various materials.
How does radioactive decay work?
Radioactive decay is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by emitting radiation, resulting in the transformation of the parent isotope into a more stable daughter isotope. This decay occurs at a predictable rate for each isotope, known as its half-life.
Why is the parent-daughter ratio important in radiometric dating?
The parent-daughter ratio is crucial in radiometric dating as it helps determine the age of a sample. By measuring the proportion of parent isotopes to daughter isotopes, and knowing the half-life of the parent, scientists can calculate how long the decay process has been occurring, thereby estimating the age of the sample.
Can parent and daughter isotopes be the same element?
Yes, in some cases, parent and daughter isotopes can be the same element but with different numbers of neutrons, resulting in isotopes of the same element. This occurs in processes like beta decay, where the identity of the element remains the same, but its atomic mass changes.
Conclusion
The journey from parent to daughter isotopes encapsulates the fundamental principles of nuclear chemistry and physics, offering a window into the past and a tool for understanding the natural world. Through the meticulous study of these isotopic transformations, scientists have developed methods to date ancient artifacts, explore the dynamics of the earth’s crust, and diagnose diseases, showcasing the versatility and importance of this scientific concept.
As we continue to explore the nuances of isotopic decay, we not only unlock the secrets of the universe but also pave the way for innovations in science and technology. The understanding of parent and daughter isotopes goes beyond academic curiosity, serving as a testament to humanity’s quest for knowledge and its application for the betterment of society.

