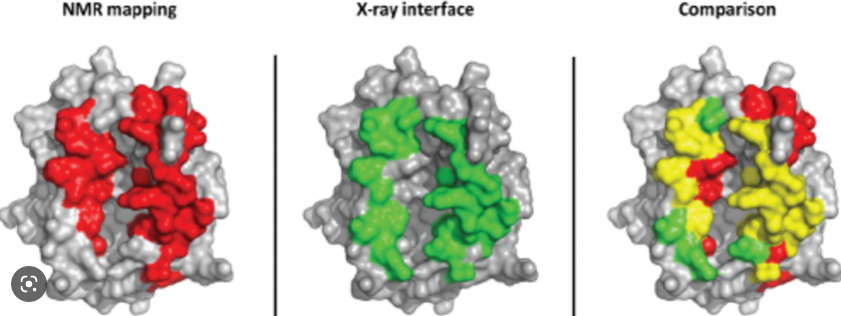
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) and X-ray crystallography are two pivotal techniques widely utilized in the fields of chemistry, biology, and materials science for determining the structures of molecules. Both methods offer unique insights, yet they operate on entirely different principles and serve diverse scientific needs. NMR spectroscopy analyzes the magnetic properties of atomic nuclei to reveal molecular identity, structure, and dynamics, whereas X-ray crystallography examines the diffraction patterns of X-rays passing through a crystal to depict the arrangement of atoms within a molecule.
The primary distinction between NMR and X-ray crystallography lies in their methodological approaches and the type of information they provide. NMR is renowned for its ability to analyze molecules in a solution, capturing dynamic changes and providing detailed information about molecular environments and interactions. On the other hand, X-ray crystallography offers unparalleled precision in visualizing the arrangement of atoms within a crystal structure, making it invaluable for detailed structural analysis of complex molecules.
Both techniques have shaped countless scientific advancements and continue to be integral in the development of new materials, the understanding of biological processes, and the creation of various drugs. Each method’s unique capabilities ensure that they complement rather than replace one another, offering expansive coverage across multiple scientific disciplines.
Core Principles
NMR Basics
Fundamental Concepts
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) is a spectroscopic technique that relies on the magnetic properties of atomic nuclei. When nuclei that possess a spin are placed in a magnetic field, they can absorb radio frequency energy, which then can be measured and used to deduce structural information about molecules.
How NMR Works
The process of NMR involves several key steps:
- Alignment of Nuclear Spins: In a strong magnetic field, the nuclei of atoms like hydrogen or carbon align their spins in two energy states.
- Radio Frequency Pulse: A pulse of radio frequency energy is applied, causing some of the aligned nuclear spins to flip to a higher energy state.
- Relaxation and Detection: As the nuclei return to their original state, they emit energy detectable as an NMR signal, which is unique for different types of atoms in various chemical environments.
X-ray Crystallography Basics
Fundamental Concepts
X-ray crystallography is a technique used to determine the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal. The crystalline atoms cause a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions. By measuring the angles and intensities of these diffracted beams, a three-dimensional picture of electron density can be generated.
How X-ray Crystallography Works
The operation of X-ray crystallography can be outlined as follows:
- Crystal Preparation: A crystal of the substance is prepared, which must be perfectly structured and large enough to diffract X-rays.
- X-ray Diffraction: X-rays are directed at the crystal, and the scattered X-rays are observed creating a diffraction pattern.
- Data Analysis: The pattern is analyzed to reveal the structure of the crystal, providing detailed insights into the arrangement of molecules.
Key Differences
Sample Preparation
NMR Requirements
- Solubility: The sample must dissolve in a suitable solvent, often deuterated versions to avoid background hydrogen signals.
- Concentration: Sufficient concentration to yield detectable signals, typically in the mM range.
X-ray Crystallography Requirements
- Crystallization: Samples must form a stable, defect-free crystal.
- Size and Quality: Larger and more perfect crystals yield better diffraction patterns and thus more precise data.
Data Collection
NMR Process
- Sample Insertion: The sample is placed in a magnetic coil within a strong magnetic field.
- Pulse Sequence: Specific sequences of radio frequency pulses are applied to manipulate the spins.
- Signal Acquisition: The emitted signals are collected over time, providing data on the environment of the nuclei.
X-ray Process
- Mounting the Crystal: The crystal is mounted on a goniometer in the path of an X-ray beam.
- Rotation and Detection: The crystal is rotated, and the diffraction pattern is recorded from different angles to construct a comprehensive image of the crystal.
Information Yield
Types of Data from NMR
- Chemical Shifts: Indicate electronic environments of nuclei.
- Coupling Constants: Offer information about the number of bonds separating interacting nuclei.
- Relaxation Times: Provide insights into dynamics and molecular size.
Types of Data from X-ray
- Electron Density Maps: Show the distribution of electrons within the crystal.
- Molecular Geometry: Details about bond lengths, angles, and absolute configuration.
Technical Comparison
Resolution and Accuracy
Comparing Resolution Capabilities
NMR generally offers lower resolution compared to X-ray crystallography but provides valuable information about dynamic states and interactions in solution. X-ray crystallography provides high-resolution images of static structures, critical for detailed molecular modeling.
Accuracy in Structural Details
X-ray crystallography can pinpoint atom positions to within a fraction of an angstrom, much more precise than NMR, which is better suited for larger scale structural themes and dynamic studies.
Limitations and Challenges
NMR Limitations
- Sensitivity: Requires relatively large amounts of sample.
- Size Limitations: Less effective with very large molecules.
X-ray Crystallography Limitations
- Crystallization: Not all substances can be crystallized easily.
- Static Picture: Only provides a snapshot of the molecule in a solid state, potentially overlooking dynamic aspects.
Applications
NMR Applications
Common Uses in Research
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) is fundamental in organic chemistry for identifying the structure of organic molecules. It is equally pivotal in biochemistry for examining interactions and dynamics within proteins, nucleic acids, and other biomolecules. Researchers employ NMR to study complex biological processes, such as enzyme kinetics and drug interactions, providing insights that are critical for drug discovery and development.
Real-world Examples
- Drug Design: NMR spectroscopy is instrumental in the pharmaceutical industry for studying drug-target interactions. For instance, it was crucial in the development of HIV protease inhibitors, enhancing drug efficacy and selectivity.
- Material Science: NMR helps in understanding the composition and behavior of materials, including polymers and ceramics, which is essential for developing new materials with optimized properties.
X-ray Crystallography Applications
Common Uses in Research
X-ray crystallography is a mainstay in structural biology, crucial for elucidating the three-dimensional structure of biomolecules. It aids in revealing the precise arrangement of atoms within a molecule, which is vital for understanding function and interaction. This method is also extensively used in geology and materials science to analyze mineral structures and properties.
Real-world Examples
- Protein Structure Determination: The structure of the ribosome, an essential cellular component, was determined using X-ray crystallography, a breakthrough that won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 2009.
- Small Molecule Analysis: X-ray crystallography is essential in the pharmaceutical industry for obtaining the detailed molecular structure of drug candidates, which guides chemical modifications to improve efficacy and safety.
Advances and Innovations
Recent Advances in NMR
Technological Improvements
Recent advancements in NMR technology include the development of higher field magnets, which significantly improve sensitivity and resolution. Cryoprobes, which cool the detector to very low temperatures, are another innovation that enhances signal strength and data quality.
Impact on Research
These technological advances have expanded the scope of NMR spectroscopy, allowing for the analysis of larger, more complex molecules. As a result, NMR has become indispensable in studying biological macromolecules and complex multi-atomic structures in solution, providing a deeper understanding of biological functions and interactions.
Recent Advances in X-ray Crystallography
Technological Improvements
Innovations in X-ray crystallography include the use of synchrotron radiation sources, which produce X-rays of much greater brightness than conventional sources. This development has dramatically increased the resolution and decreased the time required for data collection.
Impact on Research
The enhanced capabilities provided by synchrotrons have allowed researchers to study structures that were previously too small or too complex to analyze effectively. This has led to significant discoveries in the structural basis of diseases and the development of new therapeutic strategies.
Choosing the Right Technique
Factors to Consider
Selecting between NMR and X-ray crystallography depends on several factors:
- Nature of the Sample: Soluble molecules and those in dynamic states are typically better suited for NMR, while stable, crystallizable compounds are ideal for X-ray crystallography.
- Information Required: If detailed atomic-level structure is needed, X-ray crystallography is preferable. For dynamic information and understanding molecular environments, NMR is the choice.
Comparative Analysis
While X-ray crystallography provides unmatched detail about static structures, NMR offers unique insights into the dynamics and environments of molecules in their natural states. The choice between these two methods should be guided by the specific requirements of the research question and the nature of the sample under investigation. Often, combining both techniques can yield complementary information that is more valuable than either method alone.
FAQs
What is NMR used for?
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) is primarily used to identify the structure of organic compounds, study molecular dynamics, and understand chemical environments of molecules. It is indispensable in medicinal chemistry for drug design and in biochemistry for studying protein-ligand interactions.
How does X-ray crystallography work?
X-ray crystallography works by directing X-rays towards a crystallized sample. When these rays hit the crystal, they diffract in many specific directions. By measuring the angles and intensities of these diffracted beams, scientists can produce a three-dimensional picture of the electron density within the crystal, from which the positions of the atoms in the crystal can be inferred.
Can NMR analyze solid materials?
Yes, while NMR is widely known for its application in solution studies, solid-state NMR can also analyze solid materials. It provides detailed insights into the structure, dynamics, and chemical environment of molecules in solids, crucial for materials science and engineering.
Is X-ray crystallography limited to crystals only?
Yes, X-ray crystallography requires a crystalline sample to function effectively. This is because the technique relies on the diffraction of X-rays through a periodic lattice of atoms, which only a crystal can provide. Without a crystal structure, the diffraction pattern would not be interpretable.
Conclusion
In summary, both NMR and X-ray crystallography offer essential yet distinct insights into the molecular world. Their continued development and application drive innovation in various scientific fields, enhancing our understanding of complex biological mechanisms and fostering advancements in pharmaceutical research. While NMR provides valuable information about molecular dynamics and environments, X-ray crystallography excels in detailed structural analysis of crystallized molecules.
Looking forward, the integration of these techniques with emerging technologies promises to further extend their capabilities. As research continues to evolve, the synergy between NMR and X-ray crystallography will undoubtedly uncover new dimensions in science, from material engineering to the exploration of life’s molecular machinery.