Chemical reactions are the backbone of scientific exploration and industrial innovation, serving as the basis for everything from the creation of new materials to the energy that powers our world. At the heart of this vast expanse of chemistry lies two pivotal types of reactions: metathesis and redox reactions. Each plays a unique role in both the natural and engineered worlds, yet their differences are often a source of confusion.
Metathesis reactions involve the exchange of ions between two compounds without a change in the oxidation state of any atoms. In contrast, redox reactions are characterized by the transfer of electrons between two entities, resulting in changes in their oxidation states. Understanding the distinction between these processes is crucial for anyone looking to grasp the fundamentals of chemical reactions.
These reactions not only illustrate basic chemical principles but also underscore the diversity of chemical processes. Metathesis and redox reactions influence a broad range of applications, from the synthesis of pharmaceuticals to the mechanisms of batteries. This highlights the importance of recognizing their differences, as well as their individual contributions to chemistry and technology.
Reaction Basics
Chemical Reactions
Definition and Significance
At its core, a chemical reaction is a process where reactants transform into products through the breaking and forming of chemical bonds. This fundamental process is crucial for life, supporting everything from our metabolism to the technology we rely on daily. Chemical reactions are everywhere, from the food we digest to the fuels that power our vehicles.
Reaction Types
Chemical reactions can be classified into several types based on their nature and the changes they induce in reactant molecules. These categories include synthesis, decomposition, single displacement, double displacement (metathesis), and redox (oxidation-reduction) reactions. Each type has unique characteristics and plays a vital role in both natural processes and technological applications.
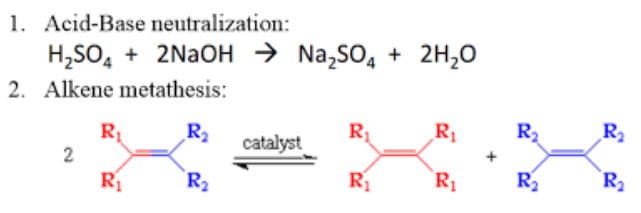
Metathesis Reactions
Definition
A metathesis reaction, also known as a double displacement or exchange reaction, involves the swapping of ions between two compounds to form two new compounds. It’s like a dance between molecules where partners exchange hands.
Key Characteristics
- Exchange of ions: This is the hallmark of metathesis reactions, where cations and anions from different molecules switch places.
- No change in oxidation state: Unlike redox reactions, metathesis reactions do not involve changes in the oxidation states of atoms.
Examples in Daily Life
- Precipitation reactions: The formation of an insoluble salt when two solutions are mixed is a common example.
- Neutralization reactions: When an acid and a base react to form water and a salt, it’s a metathesis reaction in action.
Mechanism
The step-by-step process of a metathesis reaction typically involves:
- Reactants collide, providing the energy needed for the reaction.
- Ionic bonds in the reactants break, allowing the ions to freely move and exchange.
- New ionic bonds form between the exchanged ions, creating the products.
Applications
- Industrial: Used in the manufacture of various salts and compounds.
- Scientific importance: Fundamental in the study of ionic compounds and their behaviors.
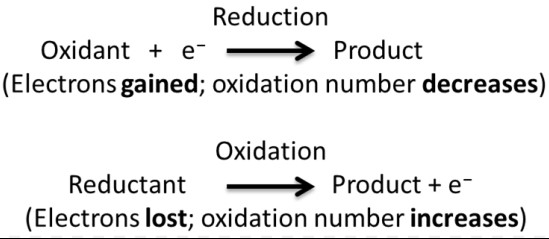
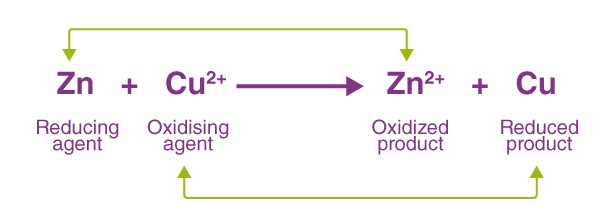
Redox Reactions
Definition
Redox reactions are chemical processes where electrons are transferred between molecules, resulting in changes in their oxidation states. These reactions are the driving force behind many natural and technological processes.
Key Characteristics
- Transfer of electrons: The essence of redox reactions, defining the oxidation and reduction process.
- Oxidation and reduction: Oxidation involves the loss of electrons, while reduction involves the gain of electrons.
Mechanism
The mechanism of a redox reaction involves:
- The oxidizing agent gains electrons (is reduced) from the reducing agent, which loses electrons (is oxidized).
- The transfer of electrons can occur directly or through a series of steps in complex reactions.
Applications
- Energy: Central to the operation of batteries and fuel cells.
- Synthesis: Important in the production of chemicals and materials.
- Environmental relevance: Plays a role in processes like corrosion, biodegradation, and water treatment.
Comparing Metathesis and Redox Reactions
Core Differences
Exchange vs. Transfer
Metathesis and redox reactions differ fundamentally in their process. Metathesis involves the exchange of ions between compounds without altering the oxidation state of the atoms involved. In contrast, redox reactions are characterized by the transfer of electrons between substances, leading to changes in their oxidation states.
Ionic vs. Electronic Changes
The distinction extends to the type of changes that occur during these reactions. Metathesis reactions focus on ionic changes, where compounds swap ions to form new products. Redox reactions, however, are centered around electronic changes, specifically the movement of electrons that dictate the oxidation and reduction processes.
Impact on Chemistry
Theoretical and Practical Implications
Understanding these differences is crucial, not just academically but for practical applications in various fields including pharmaceuticals, environmental science, and energy production. The principles of metathesis and redox reactions guide scientists in predicting reaction outcomes, synthesizing new compounds, and innovating in material science and energy solutions.
Visual Diagrams
Schematic representations of metathesis and redox reactions help visualize their distinct processes. Diagrams illustrating ion exchange in metathesis and electron transfer in redox reactions can simplify complex concepts, making them accessible to students and professionals alike.
Identifying Reactions
Indicators of Metathesis
- Solubility rules: These rules can predict whether a precipitate will form in a reaction, indicating a possible metathesis.
- Precipitate formation: The appearance of a solid from a solution signifies an exchange has occurred, a hallmark of metathesis reactions.
Indicators of Redox
- Color changes: A change in color can indicate a change in oxidation state, signaling a redox reaction.
- Gas evolution: The production of gas during a reaction often results from a redox process.
- Electrode potential: Measuring the potential difference in an electrochemical cell can help identify redox reactions.
Practical Examples
Everyday Examples
Metathesis: Water Softening and Precipitation Reactions
Water softening systems often use metathesis reactions to remove calcium and magnesium ions, replacing them with sodium or potassium ions. This process prevents the buildup of scale, extending the life of plumbing and improving water quality.
Redox: Batteries and Combustion
Batteries operate on redox reactions, with electrons flowing from the anode to the cathode through an external circuit. Combustion, such as the burning of fuel in an engine, is another example of a redox reaction, where oxygen reduces the fuel, releasing energy.
Laboratory Analysis
Techniques for identifying metathesis and redox reactions in the laboratory include:
- Conductivity tests: To detect ion exchange in metathesis reactions.
- Redox titrations: To determine the oxidizing or reducing strength of a solution.
- Spectrophotometry: To observe color changes indicative of redox processes.
Importance in Research and Industry
Current Trends
The ongoing research in chemical reactions, including metathesis and redox, drives innovation across many sectors. Recent advancements in green chemistry seek to make chemical processes more environmentally friendly by using metathesis reactions to minimize waste. In energy, redox flow batteries offer promising solutions for storing renewable energy efficiently.
Innovations and Advancements
Noteworthy developments include the Nobel Prize-winning work in metathesis that has revolutionized organic synthesis, allowing for more efficient and selective reactions. In redox chemistry, the exploration of new materials for better battery technologies continues to be a hotbed of innovation, addressing global energy storage challenges.
Future Prospects
The potential for new discoveries in both metathesis and redox reactions is vast. Researchers are exploring the use of metathesis in polymerization to create new materials with unique properties. Redox reactions are at the forefront of developing sustainable energy solutions, such as solar fuels and more efficient batteries, which could transform our energy landscape.
FAQs
What defines a metathesis reaction?
A metathesis reaction is characterized by the exchange of ions between two reacting chemicals, leading to the formation of two new products. This type of reaction often occurs in solutions where ions can freely move and swap partners, resulting in the precipitation of a new compound or the formation of a gas.
How do redox reactions work?
Redox reactions function through the transfer of electrons from one molecule (the reductant) to another (the oxidant). This electron transfer results in a change in the oxidation states of both molecules, which is fundamental to processes like combustion, rusting, and photosynthesis.
Why are metathesis and redox reactions important?
Metathesis and redox reactions are crucial for numerous chemical processes and industrial applications. They are fundamental to understanding chemical kinetics, reaction mechanisms, and the synthesis of various compounds. Additionally, they play a key role in energy production, environmental chemistry, and material science.
Can a reaction be both metathesis and redox?
While it’s rare, some reactions can exhibit characteristics of both metathesis and redox processes. However, for a reaction to be classified as both, it must involve the exchange of ions as well as a change in the oxidation state of the involved elements, which is not commonly observed.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between metathesis and redox reactions is more than an academic exercise; it’s a window into the vast and varied world of chemistry that impacts our daily lives. These reactions are the silent workhorses behind many of the modern world’s conveniences and necessities, from the clean water we drink to the energy that powers our devices.
In closing, a deep appreciation and knowledge of these chemical processes enrich our understanding of the natural and engineered worlds. They not only pave the way for advancements in science and technology but also help us to conceptualize and appreciate the complexity and beauty of the chemical interactions that sustain life and drive innovation.

