Blood is a vital fluid in the human body, but not all blood is the same. The blood that flows through veins during injury or medical tests, commonly referred to as regular blood, serves multiple physiological purposes. However, menstrual blood, which is part of a woman’s monthly menstrual cycle, carries unique characteristics and functions that distinguish it significantly from the regular blood.
Menstrual blood differs from regular blood primarily in composition and function. While regular blood is composed of plasma, red cells, white cells, and platelets and serves the purpose of transporting oxygen, nutrients, and hormones throughout the body, menstrual blood includes these components along with decidual cells, endometrial particles, cervical mucus, and vaginal secretions. This makes menstrual blood not only thicker but also more varied in its composition than regular blood.
Understanding the differences between these two types of blood is crucial for both medical professionals and individuals looking to manage or diagnose conditions related to either type of blood. Menstrual blood’s unique composition can impact a variety of conditions, from menstrual irregularities to more complex reproductive issues, making its study and understanding essential for women’s health.

Blood Basics
Composition
Cells and Plasma
Blood is composed primarily of plasma and cells. Plasma, the liquid component, makes up about 55% of blood’s volume and is mostly water. It serves as a transport medium for glucose, hormones, proteins, and waste products. Within plasma, there are three main types of cells: red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
- Red blood cells (erythrocytes) carry oxygen from the lungs to the body and bring carbon dioxide back to the lungs for expulsion.
- White blood cells (leukocytes) are crucial for immune function, fighting infections and orchestrating healing processes.
- Platelets (thrombocytes) are essential for blood clotting and wound repair.
Common Elements in All Blood
Both types of blood contain the same fundamental elements:
- Water
- Salts (electrolytes)
- Proteins
- Nutrients
- Gases
- Waste products
Functions
Role in Body Regulation
Blood plays several critical roles in body regulation including:
- Temperature regulation by redistributing heat throughout the body.
- pH balance maintenance, crucial for cellular function.
- Fluid volume control, influencing blood pressure and cellular health.
Healing and Immune Responses
Blood’s components are vital in healing and the immune response:
- White blood cells detect and attack foreign pathogens.
- Platelets and plasma proteins facilitate clot formation to stop bleeding and begin tissue repair.
Menstrual Blood Explained
Definition
Menstrual blood is the blood and tissue shed from the lining of the uterus during a woman’s menstrual cycle.
What Constitutes Menstrual Blood?
Menstrual blood consists of:
- Shed endometrial cells: the lining of the uterus.
- Cervical mucus: which helps the passage of menstrual blood out of the body.
- Vaginal secretions: which provide lubrication and protect against infection.
- Blood cells: both red and white cells involved in the menstrual process.
Composition
Unique Components in Menstrual Blood
Menstrual blood has several components not typically found in regular blood:
- Decidual cells: specialized cells that form the uterine lining.
- Endometrial particles: tissue fragments from the uterus lining.
- Enzymes and cytokines: which aid in the breakdown of the lining and regulate the process.
Regular Blood Details
Definition
Regular blood, also known as systemic or peripheral blood, is involved in the ongoing maintenance and functioning of the body.
Overview of Regular Blood Functions
Functions include:
- Transportation: of oxygen, nutrients, and waste products.
- Regulation: of body systems through hormones and enzymes.
- Protection: through immune surveillance and clotting mechanisms.
Composition
Key Differences from Menstrual Blood
While sharing some basic elements with menstrual blood, regular blood differs in:
- Absence of tissue particles: no endometrial or decidual cells.
- Lower viscosity: due to a consistent composition, less cellular debris.
- Different cellular composition: mainly focused on transport and immune function rather than tissue breakdown and renewal.
Biological Processes
Menstrual Cycle
Phases and Hormonal Influences
The menstrual cycle is a complex biological process regulated by hormones, which can be divided into four main phases:
- Menstrual phase: This begins on day one of the cycle, marked by the shedding of the endometrial lining. Hormone levels, particularly progesterone and estrogen, are low.
- Follicular phase: Rising levels of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) stimulate the growth of ovarian follicles. The dominant follicle produces more estrogen.
- Ovulation phase: Triggered by a peak in luteinizing hormone (LH), this phase sees the release of an egg from the dominant follicle.
- Luteal phase: The ruptured follicle forms the corpus luteum, which secretes progesterone to prepare the endometrium for a potential pregnancy. If pregnancy does not occur, progesterone levels fall, and a new cycle begins.
These hormonal changes are essential for the regulation of reproductive health and influence other systemic functions, including mood, bone density, and cardiovascular health.
Blood Production
How Regular Blood is Generated
Regular blood is produced through a process called hematopoiesis. This occurs primarily in the bone marrow and involves the maturation of hematopoietic stem cells into mature blood cells. The steps include:
- Stem cell differentiation: Pluripotent stem cells in the marrow differentiate into myeloid or lymphoid progenitors.
- Lineage commitment: These progenitors then commit to specific lineages, becoming precursors to red cells, white cells, or platelets.
- Maturation and release: These cells mature and are eventually released into the bloodstream.
Key Differences Highlighted
Physical Properties
Color, Consistency, and Volume Differences
Menstrual blood and regular blood exhibit distinct physical characteristics:
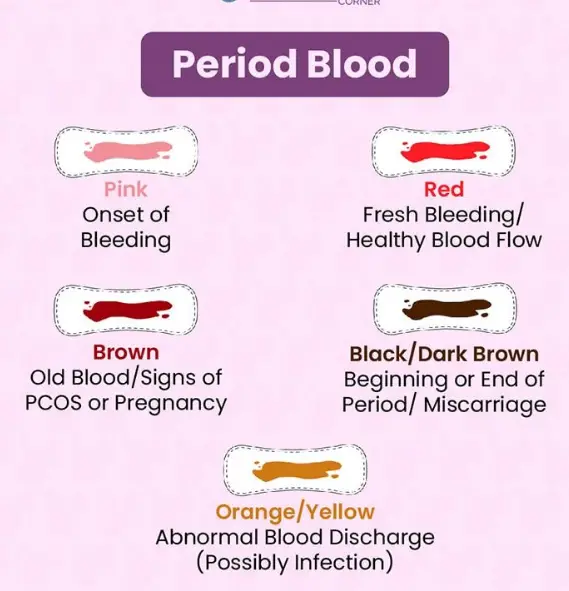
- Color: Menstrual blood is generally darker due to the longer oxidation time and presence of decomposed tissue.
- Consistency: Menstrual blood can appear thicker and more variable due to the mixture of blood, tissue fragments, and cervical mucus.
- Volume: Menstrual flow varies but can be heavier than the average blood loss through minor cuts or injuries.
Chemical Properties
Hormonal and Protein Content Differences
The chemical makeup of menstrual blood differs significantly from that of regular blood, notably in:
- Hormones: Menstrual blood contains hormones like progesterone and estrogen that are not as prevalent in regular blood.
- Proteins: Unique proteins involved in the menstrual cycle, such as fibrinogen (which aids in clotting during menstruation), differ from those commonly found in regular blood.
Health Implications
Menstrual Health
Common Disorders and Their Symptoms
Several conditions can affect menstrual health, including:
- Premenstrual Syndrome (PMS): Symptoms include mood swings, bloating, and irritability.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): Characterized by irregular menstrual cycles, excess androgen levels, and polycystic ovaries.
- Endometriosis: Where endometrial-like tissue grows outside the uterus, causing pain and potentially affecting fertility.
- Menorrhagia: Excessive menstrual bleeding that can lead to anemia and fatigue.
Blood Health
Disorders Affecting Regular Blood
Regular blood can also be impacted by various disorders, which include:
- Anemia: A deficiency of red cells or hemoglobin, leading to fatigue and weakness.
- Leukemia: A type of cancer affecting white blood cells, impairing the immune system and overall health.
- Hemophilia: A genetic disorder where blood does not clot normally, leading to excessive bleeding.
FAQs
What defines menstrual blood?
Menstrual blood is primarily composed of blood and tissue shed from the inner lining of the uterus during the menstrual cycle. It also contains cervical mucus, vaginal secretions, and the remains of the endometrial lining, making it distinct from regular blood.
How does menstrual blood differ in color from regular blood?
Menstrual blood typically appears darker than regular blood. This is due to its longer exposure to the body’s enzymes and its slower exit from the body, which causes more oxidation.
Is menstrual blood as sterile as regular blood?
Menstrual blood is not as sterile as regular blood. It can contain bacteria from the vagina’s natural flora, which does not usually pose a health risk unless there is an underlying condition affecting the vaginal microbiome.
Can menstrual blood be used for medical tests like regular blood?
Menstrual blood is generally not used for medical testing in the same way that regular blood is. Its composition, which includes additional biological matter and cells, makes it unsuitable for standard blood tests that measure things like blood sugar levels or cholesterol.
Conclusion
The distinctions between menstrual blood and regular blood highlight significant aspects of human biology that affect health, particularly women’s health. Each type of blood has unique properties and roles within the body, emphasizing the importance of targeted medical understanding and treatments.
Grasping these differences not only aids in better healthcare but also deepens the general understanding of the human body’s complexities. As research continues to evolve, the knowledge of how distinct types of blood function can lead to improved health outcomes and more personalized approaches in medicine and healthcare.

