The human body is a complex system equipped with a variety of sensory receptors that allow us to interact with our environment. Among these, mechanoreceptors and proprioceptors play crucial roles in processing information related to touch, pressure, position, and movement. These receptors are fundamental to our daily activities, enabling us to perform tasks seamlessly and efficiently.
Mechanoreceptors are specialized sensory receptors that respond to mechanical pressure or distortion, playing a pivotal role in touch, pressure sensation, and even hearing. Proprioceptors, on the other hand, are sensors that provide information about body position, movement, and the orientation of one’s body in space, critical for maintaining balance and coordinated movement. Despite their distinct functions, both receptor types are indispensable for the intricate interplay of sensory perception and motor control.
The significance of mechanoreceptors and proprioceptors extends beyond mere sensation; they are integral to our understanding of the body’s interaction with its environment. Through the relay of mechanical and positional information to the brain, they enable a nuanced perception of the external world and our body’s position within it, facilitating a coordinated response to varying stimuli. This complex system underscores the marvel of human physiology and its capacity to adapt and interact with the surrounding environment.
Sensory Receptors Basics
Types of Sensory Receptors
Our bodies are equipped with an intricate sensory system, a network designed to detect and respond to various stimuli from our environment. This system is our interface with the world, allowing us to experience touch, temperature, pain, and more. At the heart of this system are sensory receptors, specialized cells that translate external stimuli into nerve impulses understood by the brain.
Overview of the Sensory System
The sensory system is categorized into two primary types: the somatic sensory system, which senses external stimuli like touch and temperature, and the visceral sensory system, which perceives internal body conditions. These systems help maintain homeostasis, enabling our bodies to respond adaptively to external and internal changes.
Classification Based on Stimulus Type
Sensory receptors are classified based on the type of stimulus they detect:
- Mechanoreceptors: Respond to mechanical pressure or distortion.
- Thermoreceptors: Detect changes in temperature.
- Nociceptors: Sense pain from tissue damage.
- Photoreceptors: Found in the eyes, these respond to light.
- Chemoreceptors: Detect chemical stimuli, including tastes and smells.
Mechanoreceptors at a Glance
Definition and Function
Mechanoreceptors are sensory receptors that respond to mechanical forces, such as pressure, vibration, and stretch. These receptors play a critical role in our sense of touch, as well as in proprioception — the awareness of the position and movement of our body parts.
Key Characteristics
Mechanoreceptors are characterized by their rapid response to physical changes. Their sensitivity varies, enabling the detection of both light touches and deep pressures. They are broadly distributed throughout the body, including in the skin, around hair follicles, and within internal organs.
Proprioceptors Explained
Definition and Role in the Body
Proprioceptors are a type of mechanoreceptor specifically involved in proprioception. They monitor the position and movement of the body, providing continuous feedback to the brain. This information is crucial for coordinating voluntary movements and maintaining balance and posture.
How They Differ from Other Receptors
Unlike other mechanoreceptors that primarily detect external stimuli, proprioceptors are focused on internal body states. They are located in muscles, tendons, and joints, making them integral to our sense of body awareness and spatial orientation.
Mechanoreceptors in Detail
Location and Types
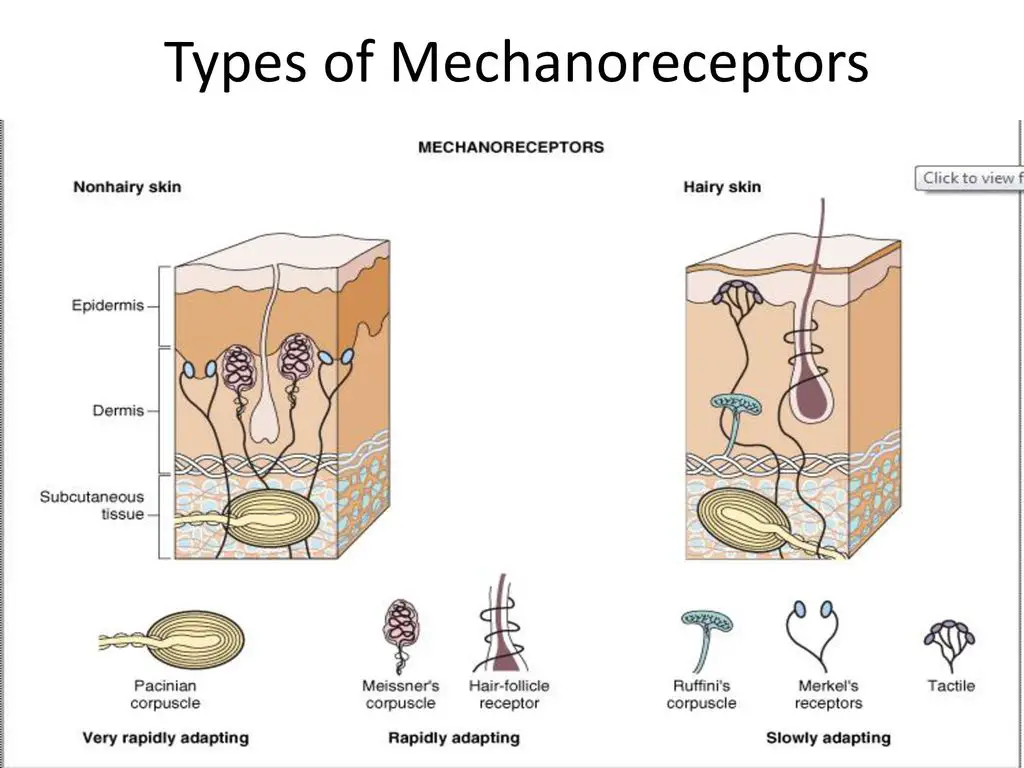
Cutaneous Mechanoreceptors
Located in the skin, cutaneous mechanoreceptors are responsible for our sense of touch and texture. They include:
- Merkel cells: Detect steady pressure and texture.
- Meissner’s corpuscles: Sensitive to light touch and vibration.
- Pacinian corpuscles: Respond to deep pressure and vibration.
- Ruffini endings: Detect stretch and sustained pressure.
Baroreceptors and Others
Baroreceptors, found in blood vessels, monitor blood pressure by sensing changes in vessel walls. Other mechanoreceptors, such as those in the inner ear, play a pivotal role in balance and hearing by detecting sound vibrations and head movements.
Functionality and Importance
Role in Touch and Pressure Detection
Mechanoreceptors are fundamental to our sense of touch. They allow us to feel textures, perceive pressure, and even detect environmental hazards, such as sharp objects. This sensory input is essential for performing everyday tasks and interacting with our surroundings.
Contribution to Hearing and Balance
In addition to touch, mechanoreceptors in the ear, specifically the hair cells, are vital for our ability to hear and maintain balance. These receptors convert sound vibrations into electrical signals that the brain interprets as sound. They also help us detect changes in head position, crucial for balance and spatial orientation.
Proprioceptors in Focus
Location in the Body
The body houses proprioceptors in several key areas, each serving a unique function in our sensory and motor systems. These specialized receptors are primarily found in muscles, tendons, and joints, where they continuously monitor the body’s position and movement.
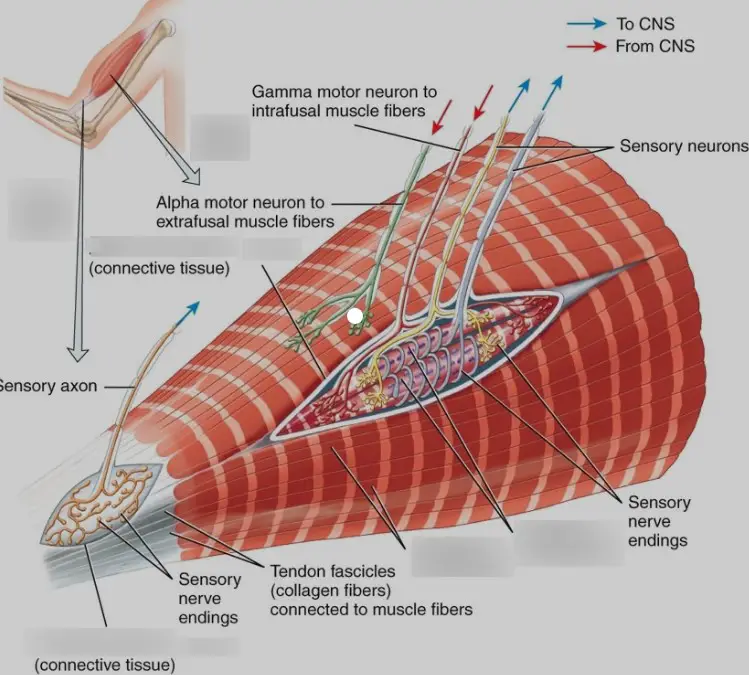
Muscle Spindles
Muscle spindles are sensory receptors located within the belly of muscles. They are particularly sensitive to changes in muscle length, playing a crucial role in stretch reflexes. When a muscle stretches, the muscle spindles are activated, sending signals to the brain to contract the muscle, thereby preventing overstretching and injury.
Golgi Tendon Organs
Golgi tendon organs are located at the junctions between muscles and tendons. Unlike muscle spindles that detect muscle stretch, Golgi tendon organs monitor tension within the muscle. When tension becomes too high, these receptors send inhibitory signals to the brain, which helps prevent muscle damage from excessive force.
Their Unique Function
Proprioceptors, including muscle spindles and Golgi tendon organs, have a unique function in the body. They are instrumental in monitoring position and movement. This feedback mechanism is crucial for the execution of smooth and coordinated movements.
Monitoring Position and Movement
Proprioceptors provide the brain with real-time information about the position of limbs and the degree of muscle contraction. This information is critical for controlling the force and direction of muscle movements, ensuring that actions are carried out with precision.
Importance in Balance and Spatial Awareness
Beyond their role in movement, proprioceptors are essential for balance and spatial awareness. They enable the body to adjust to uneven surfaces, maintain posture, and navigate the environment effectively. Without the continuous feedback from proprioceptors, activities that require coordination, such as walking, running, or even standing, would be significantly impaired.
Comparative Analysis
Functional Differences
While both mechanoreceptors and proprioceptors respond to mechanical stimuli, their functions in the body’s sensory system are distinct.
Response to Stimuli
Mechanoreceptors respond to external mechanical forces like touch, pressure, and vibration. In contrast, proprioceptors are attuned to internal stimuli, specifically the position and movement of the body’s own parts.
Role in the Nervous System
Mechanoreceptors relay information about external stimuli to the brain, enabling the perception of touch and environmental interaction. Proprioceptors, however, provide feedback about internal states, which is integral for motor control and coordination.
Biological and Clinical Significance
The differences between mechanoreceptors and proprioceptors have significant implications for our understanding of human biology and for clinical practice.
Impact on Movement and Coordination
Proprioceptors play a pivotal role in movement and coordination. Their input helps fine-tune motor activities, ensuring that movements are smooth and coordinated. This is not only crucial for complex athletic maneuvers but also for everyday actions like writing, eating, and speaking.
Implications for Therapy and Rehabilitation
Understanding the role of proprioceptors has profound implications for therapy and rehabilitation. For individuals recovering from injuries or dealing with conditions that affect movement, such as stroke or Parkinson’s disease, therapies aimed at enhancing proprioceptive feedback can significantly improve outcomes. Exercises that focus on balance and coordination, for example, can help restore movement and functionality by retraining the proprioceptive system.

FAQs
How do mechanoreceptors and proprioceptors affect daily activities?
Mechanoreceptors and proprioceptors are central to our ability to engage in daily activities with precision and coordination. By sensing touch, pressure, body position, and movement, they allow us to perform complex tasks, from typing on a keyboard to running and jumping, with remarkable accuracy and balance. Their continuous feedback helps the brain adjust our movements in real-time, ensuring smooth and efficient interactions with our environment.
Can these receptors be strengthened or improved?
Yes, through regular physical activity and specific exercises, the sensitivity and functionality of both mechanoreceptors and proprioceptors can be enhanced. Activities that require balance, coordination, and precise movements, such as yoga, Pilates, and martial arts, can effectively train these receptors. Over time, such practices can lead to improved sensory feedback and motor control, enhancing overall physical performance and reducing the risk of injuries.
What happens if mechanoreceptors or proprioceptors malfunction?
Malfunctioning mechanoreceptors can lead to reduced sensitivity to touch and pressure, affecting tasks requiring fine motor skills and altering the perception of pain. If proprioceptors are compromised, it can significantly impact balance and coordination, leading to difficulties in movement and an increased risk of falls. In both cases, therapeutic interventions, including physical therapy and sensory re-education exercises, can help in restoring function to some extent.
Conclusion
The nuanced roles of mechanoreceptors and proprioceptors in our daily lives cannot be overstated. These sensory receptors are the unsung heroes behind our ability to interact with the world around us, facilitating a wide range of activities that define human experience. They enable not just the perception of touch and pressure or the awareness of body position and movement, but also the seamless integration of sensory information that allows for coordinated and graceful interaction with our environment.
Recognizing the importance of these receptors underscores the marvel of the human body and its intricate systems. By understanding how mechanoreceptors and proprioceptors function and contribute to our well-being, we can appreciate the complex interactions that allow us to navigate and interact with the world in an efficient and harmonious manner. This insight not only enriches our understanding of human physiology but also highlights the potential for improving our sensory and motor capabilities through targeted exercises and activities.

