Magnesium is a crucial mineral that plays a pivotal role in over 300 biochemical reactions in the human body. From supporting muscle and nerve function to maintaining a healthy immune system, its impact on overall health cannot be overstated. However, not all magnesium supplements are created equal, with Magnesium Orotate and Magnesium Citrate being two popular forms that often confuse consumers due to their differing benefits and uses.
Magnesium Orotate and Magnesium Citrate are both effective supplements but serve different purposes based on their absorption rates and overall health impacts. Magnesium Orotate is often used for its potential to support heart health and enhance athletic performance due to its better cellular uptake. On the other hand, Magnesium Citrate is favored for its laxative properties and effectiveness in treating constipation and improving digestion.
These magnesium compounds vary not only in their health benefits but also in their biochemical makeup and suitability for different health conditions. While both are essential for those looking to supplement their magnesium intake, the choice between them should be informed by individual health goals and medical advice.
Magnesium Essentials
Types of Magnesium
Magnesium, an essential mineral, is vital for numerous physiological functions. It is available in several forms, each with specific properties and uses that make it more or less suited to different health needs. Common types of magnesium include:
- Magnesium Orotate: Often used for cardiovascular health.
- Magnesium Citrate: Known for its laxative effect.
- Magnesium Oxide: Typically used for relief from acid reflux and as a laxative.
- Magnesium Chloride: Absorbed well by the body, it can be used to increase magnesium levels.
- Magnesium Sulfate: Also known as Epsom salt, used in baths to soothe muscle aches.
- Magnesium Glycinate: Highly absorbable, this form is frequently used for its calming effects.
Each type binds magnesium to different compounds to enhance its absorption and effectiveness for specific health conditions.
Magnesium’s Role in Health
Magnesium is a cornerstone of health, influencing various critical bodily functions:
- Energy production: Contributes to converting food into energy.
- Protein synthesis: Aids in the creation and repair of DNA and RNA.
- Muscle movements: Regulates neuromuscular signals and muscle contractions.
- Nervous system regulation: Helps manage neurotransmitter activities that send messages throughout your brain and nervous system.
Adequate magnesium levels can prevent complications related to heart health, diabetes, and migraine headaches. Despite its importance, many people do not meet their daily magnesium needs, which can lead to deficiencies.
Magnesium Orotate
Definition and Properties
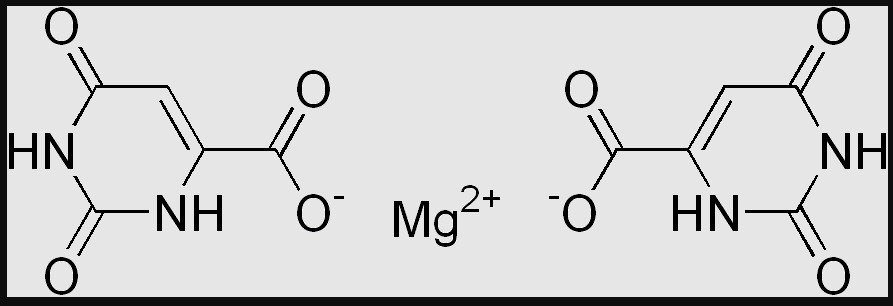
Magnesium Orotate is a compound where magnesium is bound to orotic acid, a natural substance involved in the body’s genetic material production. This form is notable for its excellent bioavailability and its role in supporting intracellular processes.
Health Benefits
The combination of magnesium and orotic acid makes Magnesium Orotate particularly effective for supporting heart health. It helps in:
- Improving heart efficiency: Enhances the energy production of heart cells.
- Reducing cardiovascular risk: Potentially lowers the risk of common heart diseases.
- Enhancing recovery: Beneficial for athletes and those recovering from cardiac events.
Common Uses
Magnesium Orotate is commonly used by individuals interested in:
- Enhancing athletic performance due to its ability to support energy production.
- Supporting heart health, especially among those with cardiovascular concerns.
- Improving overall cellular function, making it popular in holistic health circles.
Magnesium Citrate
Definition and Properties
Magnesium Citrate combines magnesium with citric acid, a natural preservative that also occurs naturally in citrus fruits. This form is well-known for its ability to be efficiently absorbed by the body and its gentle laxative effect.
Health Benefits
Due to its high solubility, Magnesium Citrate is primarily used for:
- Relieving constipation: Helps to attract water into the intestines, which promotes bowel movements.
- Pre-surgical bowel preparation: Often used before certain types of surgical procedures.
- Acid reflux relief: Can neutralize stomach acid.
Common Uses
People turn to Magnesium Citrate for:
- Quick relief from constipation, making it a go-to choice for those with occasional constipation.
- Managing symptoms of indigestion, like acid reflux or upset stomach.
- Ensuring proper bowel cleansing before medical tests or surgeries.
Comparative Analysis
Chemical Structure
Magnesium Orotate and Magnesium Citrate differ significantly in their chemical composition. Magnesium Orotate consists of magnesium bound to orotic acid. This complex is thought to facilitate the entry of magnesium into cells, enhancing its effectiveness. Magnesium Citrate, however, is formed when magnesium is combined with citric acid, resulting in a salt that has a laxative effect due to its osmotic activity in the intestines.
Absorption Rates
The body absorbs these two forms of magnesium differently:
- Magnesium Orotate: Due to the presence of orotic acid, which plays a role in the body’s natural synthesis of DNA and RNA, Magnesium Orotate is believed to penetrate cell membranes more efficiently, making it highly bioavailable.
- Magnesium Citrate: This form is also well absorbed by the gastrointestinal tract, but its primary function tends to lean more towards increasing water content in the intestines, which helps with bowel movement.
Side Effects
While both forms of magnesium are generally safe for most people, they can cause side effects, especially when taken in high doses:
- Magnesium Orotate: Rarely causes side effects but may lead to digestive upset if consumed in excess.
- Magnesium Citrate: Commonly causes loose stools or diarrhea, which is why it’s often used as a laxative.
Suitable Applications
When to Use Magnesium Orotate
Magnesium Orotate is best used in situations where improving heart health and cellular energy is needed:
- Cardiovascular support: Especially beneficial for those recovering from cardiac conditions or those who need support for cardiovascular health.
- Athletic performance: Helps in the synthesis of ATP, thus enhancing energy and endurance.
When to Use Magnesium Citrate
Magnesium Citrate is suitable for:
- Constipation relief: Quickly relieves constipation by attracting water into the intestines.
- Pre-operative bowel preparation: Ensures the bowel is clean before surgeries or diagnostic procedures like colonoscopies.
Consumer Insights
Purchasing Decisions
Consumers choose between these magnesium forms based on several factors:
- Health goals: Whether the goal is to improve heart health or relieve constipation influences the choice.
- Recommendations: Advice from healthcare providers plays a critical role.
- Personal experiences: Individual reactions or benefits previously noted also guide decisions.
Product Availability
Both Magnesium Orotate and Citrate are widely available in various forms:
- Pharmacies and health stores: Commonly found in the supplement aisles.
- Online: Both types are readily available through numerous online health retailers and marketplaces.
Expert Opinions
Medical Recommendations
Doctors and healthcare professionals often recommend:
- Magnesium Orotate for patients with specific cardiovascular needs or those seeking to enhance cellular function and performance.
- Magnesium Citrate for patients who need effective and immediate relief from constipation or require a bowel cleanse before medical procedures.
Research Findings
Scientific studies highlight:
- Magnesium Orotate: Studies suggest its potential benefits in improving the function of heart muscle and overall cellular health.
- Magnesium Citrate: Research confirms its efficacy as a laxative, making it a reliable choice for treating gastrointestinal issues related to bowel movement.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Magnesium Orotate?
Magnesium Orotate comprises magnesium bound to orotic acid, which is believed to enhance magnesium’s bioavailability and support cellular functions more effectively than other forms.
How does Magnesium Citrate differ?
Magnesium Citrate combines magnesium with citric acid, a formulation that increases water in the intestines and can be used effectively as a laxative or for bowel preparation before medical procedures.
Which is better for heart health?
Magnesium Orotate is often recommended for heart health due to its potential to facilitate the synthesis of ATP in heart cells, thus supporting heart muscle function and cardiovascular health.
Can I use Magnesium Citrate for sleep issues?
Yes, Magnesium Citrate can help improve sleep quality due to its muscle-relaxing properties, making it a popular choice for those looking to enhance sleep and reduce insomnia.
Are there any side effects?
Both supplements can cause digestive side effects if taken in high doses. Magnesium Citrate is more likely to cause diarrhea, whereas Magnesium Orotate is typically better tolerated.
Conclusion
In concluding, Magnesium Orotate and Magnesium Citrate serve distinct purposes and are suited to different health needs. Whether one opts for Magnesium Orotate to support cellular health and cardiovascular function or Magnesium Citrate for its effective relief of constipation, understanding their unique properties and effects can guide users to make informed decisions tailored to their health requirements.
By choosing the right type of magnesium supplement, individuals can effectively address specific health concerns, enhancing their overall well-being and maintaining optimal health. Consulting with a healthcare provider is recommended to determine the most beneficial form of magnesium based on individual health profiles and goals.