Are you confused about the differences between isosmotic, hyperosmotic, and hypoosmotic solutions? In this blog, we’ll explore the differences between these three solutions and look at examples of each. We’ll also discuss why these solutions are important and how they interact with cells.
We’ll also discuss why these solutions are important and how they interact with cells. By the end of this blog, you’ll have a better understanding of the differences between isosmotic, hyperosmotic, and hypoosmotic solutions and why they are important.
Characteristics of isosmotic solutions
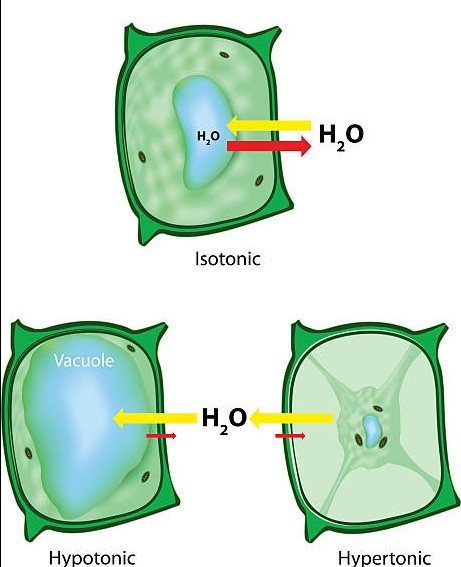
Isosmotic solutions contain the same number of solute molecules and water molecules as the surrounding environment, making them ideal for maintaining the balance of fluids in the body. However, this is not the only type of osmotic solution.
Hyperosmotic and hypoosmotic solutions have their own unique characteristics, making them distinct from isosmotic solutions. Hyperosmotic solutions have higher concentrations of solute molecules than the surrounding environment, while hypoosmotic solutions have lower concentrations of solute molecules than the surrounding environment. This difference in solute concentration makes hyperosmotic and hypoosmotic solutions excellent for transporting materials across membranes, which can be beneficial in a variety of medical treatments.
Characteristics of hyperosmotic solutions
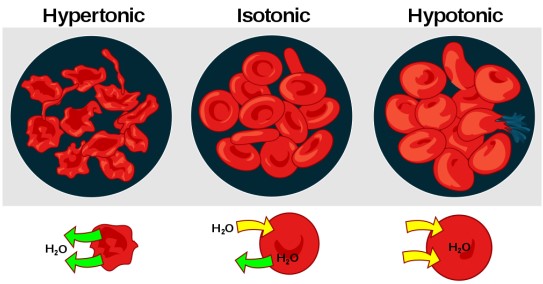
Hyperosmotic solutions are solutions that have a higher osmolarity than other solutions. They are characterized by having a higher concentration of dissolved solutes than other solutions. This can be compared to isosmotic solutions which have the same osmolarity as another solution, and hypoosmotic solutions which have a lower osmolarity than other solutions.
This can be compared to isosmotic solutions which have the same osmolarity as another solution, and hypoosmotic solutions which have a lower osmolarity than other solutions. The difference between hyperosmotic and isosmotic solutions is that hyperosmotic solutions have more solutes and therefore higher osmolarity. Hypoosmotic solutions have less solutes and therefore lower osmolarity.
The characteristics of hyperosmotic solutions play an important role in a variety of biological processes.
Characteristics of hypoosmotic solutions
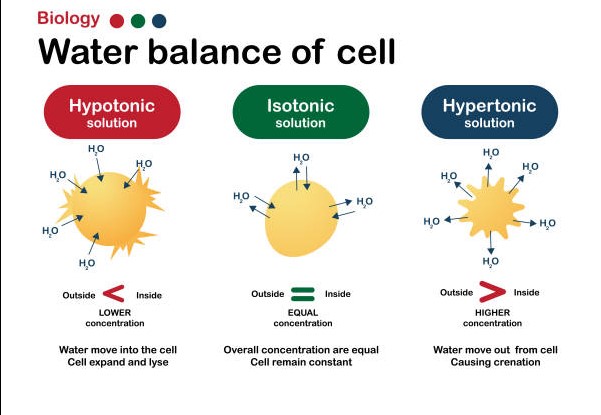
The difference between isosmotic, hyperosmotic and hypoosmotic solutions can be summed up in one word: osmolarity. Osmolarity is the measure of the number of osmoles per liter of solution. An isosmotic solution has an osmolarity equal to that of the surrounding environment; a hyperosmotic solution has an osmolarity greater than the surrounding environment; and a hypoosmotic solution has an osmolarity lower than the surrounding environment.
An isosmotic solution has an osmolarity equal to that of the surrounding environment; a hyperosmotic solution has an osmolarity greater than the surrounding environment; and a hypoosmotic solution has an osmolarity lower than the surrounding environment. Hypoosmotic solutions are characterized by their ability to draw water into the cell, and are commonly used to treat dehydration and other medical conditions. In addition, hypoosmotic solutions may be used as a medium for cell cultures, or to provide a favorable environment for the growth of microorganisms.
How to calculate the osmotic pressure of a solution
Osmotic Pressure is the force with which a solution tries to equalize its concentration of dissolved particles with its surroundings. It is an important concept for understanding the behavior of cells and solutions.
The terms isosmotic, hyperosmotic, and hypoosmotic refer to the relative concentrations of solutes in two solutions. An isosmotic solution has equal concentrations of solutes on either side of the membrane.
A hyperosmotic solution has a higher concentration of solutes on one side of the membrane than the other, whereas a hypoosmotic solution has a lower concentration of solutes on one side than the other. To calculate the osmotic pressure of a solution, one must first determine the difference in solute concentration between the two solutions, then multiply this difference by the osmotic coefficient. This will yield the osmotic pressure of the solution.
Examples of isosmotic, hyperosmotic and hypoosmotic solutions
When studying the differences between isosmotic, hyperosmotic and hypoosmotic solutions, it’s important to understand the key differences between each. Isosmotic solutions are those in which the amount of solute particles is equal to the amount of solvent particles, meaning that the solute and solvent concentrations are equal. Hyperosmotic solutions, on the other hand, contain a higher concentration of solute particles than the solvent particles.
Hyperosmotic solutions, on the other hand, contain a higher concentration of solute particles than the solvent particles. Finally, hypoosmotic solutions contain a lower concentration of solute particles than the solvent particles. In each type of solution, osmolarity, or the amount of solute particles per liter of solution, plays an important role.
Understanding the differences between these three solutions is essential for anyone working in a lab or other scientific field.