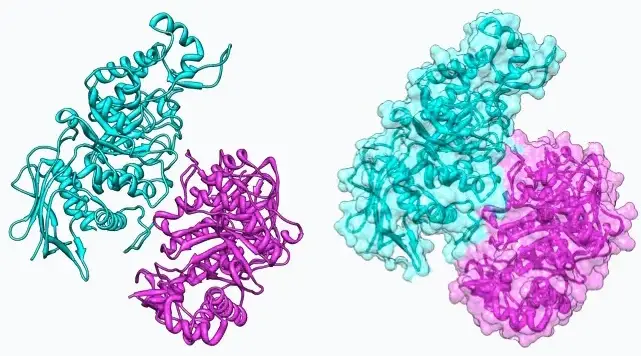
Proteins, the building blocks of life, often function not as individual units but as complex structures formed by the binding of multiple subunits. Among these structures, dimers stand out due to their critical roles in various biological processes. Dimers are molecular complexes consisting of two protein subunits, which can either be identical or different, leading to the formation of homodimers and heterodimers, respectively.
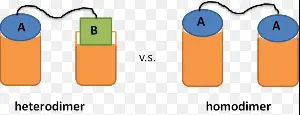
The primary difference between homodimers and heterodimers lies in their subunit composition. Homodimers are formed when two identical protein molecules bind together, while heterodimers are composed of two different protein molecules. This distinction is crucial as it influences their structure, function, and role in cellular activities, making them vital in many physiological and pathological contexts.
In biology, the study of homodimers and heterodimers extends beyond mere curiosity. These interactions are fundamental to understanding cellular mechanisms, signaling pathways, and the development of therapeutic interventions. The formation, structure, and function of these protein complexes have significant implications for the development of drugs and the treatment of diseases, highlighting their importance in biomedical research.
Protein Dimers Defined
What is a Dimer?
In the realm of molecular biology, a dimer refers to a complex structure formed when two proteins bind together. These bindings can be either covalent, involving stable chemical bonds, or non-covalent, involving weaker interactions such as hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, and hydrophobic interactions. The formation of dimers is a critical step in many cellular processes, including signal transduction, DNA replication, and enzyme catalysis.
Types of Dimers
There are two primary types of dimers:
- Homodimers: These are formed by two identical protein molecules.
- Heterodimers: These consist of two different protein molecules.
Each type plays a unique role in cellular functions and offers different advantages in biological processes, making the distinction between them crucial for understanding protein function at a molecular level.
Homodimer Basics
Definition of Homodimer
A homodimer is a protein complex formed when two identical protein molecules associate. This association can be integral to the protein’s function, stability, and regulatory mechanisms within the cell.
Key Characteristics
Homodimers share several defining characteristics:
- Symmetry: Homodimers typically exhibit symmetrical structures, which can affect their interaction with other molecules and their overall stability.
- Specificity: Due to their identical nature, the subunits in a homodimer often interact with high specificity, leading to enhanced functional performance.
- Regulatory function: In many cases, homodimerization is a regulatory mechanism that activates or inhibits the function of the protein.
Biological Functions
Homodimers are pivotal in numerous biological functions:
- Enzyme activity: Many enzymes function as homodimers, where the dimerization is essential for their catalytic activity.
- Signal transduction: Homodimeric receptors play critical roles in the transmission of signals across cell membranes.
- Structural roles: Some structural proteins form homodimers to maintain cell shape and integrity.
Heterodimer Fundamentals
Definition of Heterodimer
A heterodimer consists of two different protein subunits. This diversity allows for complex and versatile functionality within the cell, often complementing the roles of homodimers.
Distinct Features
Heterodimers are characterized by:
- Complementarity: The different subunits often complement each other’s functions, leading to a more versatile and adaptable molecular tool.
- Complex regulation: The regulation of heterodimers can be more complex, as it involves multiple regulatory mechanisms.
- Diverse functionality: The combination of different proteins allows heterodimers to participate in a wider range of biological processes.
Role in Cellular Processes
Heterodimers are involved in various crucial cellular processes:
- Signal diversification: They can transmit a variety of signals, thus contributing to the complexity of cellular signaling networks.
- Gene regulation: Heterodimers can regulate gene expression by interacting with different transcription factors and other regulatory proteins.
- Cellular differentiation: They play roles in differentiating cells into various types during development.
Structural Differences
Amino Acid Composition
The amino acid composition of homodimers and heterodimers significantly influences their structure and function. Homodimers, being made of identical subunits, have a uniform amino acid composition throughout, while heterodimers, composed of different subunits, exhibit a varied amino acid landscape, which can affect their interaction sites and stability.
Molecular Bonds
The types of molecular bonds that form between the protein subunits in dimers also differ:
- Homodimers often rely on similar types of bonds between identical sites.
- Heterodimers may involve complementary bonding, where different parts of the subunits interact to form stable complexes.
3D Structure Analysis
The three-dimensional structures of homodimers and heterodimers reveal much about their functionality and interaction with other molecules. Advances in technologies such as X-ray crystallography and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy have provided detailed views of these structures, highlighting the precise manner in which dimers operate within the cell.
Functional Disparities
Biological Pathways
Homodimers and heterodimers play critical roles in diverse biological pathways, each modulating different cellular responses and mechanisms. For example, homodimers in receptor tyrosine kinases are essential for the activation of many intracellular signaling cascades, which influence cell growth and differentiation. Conversely, heterodimers like those formed between the retinoid X receptor and various other nuclear receptors expand the repertoire of genetic responses to hormonal and environmental stimuli, enabling fine-tuned genetic control.
Interaction with Other Molecules
The ability of dimers to interact with other molecules is pivotal for their function. Homodimers often have a symmetrical interaction site, which allows for the selective pairing with other identical molecules, enhancing the specificity of biological reactions. Heterodimers, with their asymmetrical binding sites, can bridge molecular interactions across different pathways, introducing versatility and adaptability in cellular responses.
Impact on Cellular Health
The formation of both homodimers and heterodimers is vital for maintaining cellular health. Misregulated dimer formation can lead to diseases such as cancer, where altered dimerization patterns disrupt normal cell signaling and control. For instance, the overexpression of certain homodimers in growth factor receptors can lead to unchecked cellular proliferation, while defective heterodimer formation might result in impaired DNA repair mechanisms.
Detection Techniques
Laboratory Methods for Identification
To study protein dimers, scientists employ various laboratory techniques:
- Immunoprecipitation is used to pull down protein complexes from cell extracts, which can then be analyzed by Western blotting.
- Gel-filtration chromatography separates proteins based on size, allowing researchers to identify potential dimers.
- Cross-linking stabilizes protein interactions, facilitating the identification of dimers through mass spectrometry.
Comparative Analysis
Comparative analysis of homodimers and heterodimers involves assessing their structural and functional attributes to understand their distinct roles in cells. Techniques like differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) help in determining the thermal stability of protein complexes, while analytical ultracentrifugation provides insights into the shape and size of these molecules.
Applications in Medicine
Therapeutic Uses of Homodimers
Homodimers have been exploited for therapeutic purposes, particularly in enzyme-targeted drug design and antibody development. Drugs that can specifically inhibit or stabilize homodimers are being developed to treat diseases where these dimers play a significant role. For example, drugs targeting the HIV-1 protease, a homodimer, are crucial in the fight against HIV/AIDS.
Heterodimers in Drug Design
Heterodimers offer a unique advantage in drug design due to their ability to modulate multiple pathways. By designing drugs that specifically affect heterodimer formation or activity, it is possible to achieve more targeted therapeutic effects with potentially reduced side effects. This approach is particularly valuable in cancer therapy, where heterodimeric receptors are often key targets.
Future Research Directions
Emerging Studies
The ongoing research into protein dimers is unveiling more about their mechanisms and applications. Emerging studies focus on the dynamic nature of dimer formation and its implications for cellular adaptability and signaling diversity. The use of cutting-edge techniques like cryo-electron microscopy is revealing unprecedented details of dimer structures at atomic resolutions.
Potential Breakthroughs
Potential breakthroughs in dimer research may revolutionize our approach to understanding and treating diseases. For example, insights into the selective inhibition of specific dimer forms could lead to more precise cancer treatments that minimize damage to healthy cells. Furthermore, understanding how environmental factors influence dimer stability and function could lead to breakthroughs in biomaterials and synthetic biology.
FAQs
What is a Protein Dimer?
A protein dimer is a type of molecular complex that consists of two protein subunits joined by either non-covalent or covalent bonds. These structures play essential roles in cellular functions and are crucial in many biological processes, including cellular signaling and metabolic regulation.
How Do Homodimers Differ from Heterodimers?
Homodimers consist of two identical protein subunits, while heterodimers are formed by the pairing of two different protein subunits. This variation affects their functionality and interaction with other cellular components, influencing numerous biological pathways.
Why Are Dimers Important in Biology?
Dimers are critical in biology because they enable intricate control over cellular processes. By forming dimers, proteins can alter their structural configuration and functional capabilities, facilitating precise responses to environmental changes and signaling cues.
Can Dimers Influence Disease Development?
Yes, protein dimers can influence disease development. Abnormal dimer formation has been linked to various diseases, including cancer and neurodegenerative disorders. Understanding how dimers interact and function could lead to new therapeutic strategies for these conditions.
Conclusion
In sum, the distinction between homodimers and heterodimers is a fundamental aspect of protein science with broad implications across biology and medicine. Their study not only deepens our understanding of cellular structure and function but also enhances our ability to design targeted therapies for a range of diseases.
As research continues to unveil the intricate details of these protein complexes, it becomes increasingly clear that homodimers and heterodimers are more than just small parts of cellular machinery. They are pivotal elements that drive the dynamism and versatility necessary for life. Understanding their differences and interactions remains a key focus in the quest to harness their potential in medicine.