Polymers are fundamental to numerous industries, from packaging and textiles to aerospace and biomedicine. Their broad utility derives from their diverse structural characteristics, which allow for extensive customization of their physical properties. The distinction between homochain and heterochain polymers lies at the core of this variability, impacting everything from mechanical strength to chemical resistance.
Homochain polymers consist exclusively of identical monomer units linked together, whereas heterochain polymers are composed of two or more different kinds of monomer units. This fundamental difference in molecular structure dictates not only the physical and chemical properties of the polymers but also their suitability for specific applications. The distinction influences everything from a polymer’s durability to its biodegradability.
Recognizing these differences is crucial for scientists and engineers designing materials for specific purposes. Homochain and heterochain polymers each offer unique advantages and limitations, dictated by their molecular structures. These properties are pivotal in their application across various sectors, making the understanding of their differences essential for innovation in material science.
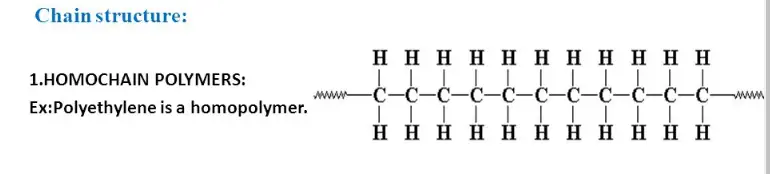
Homochain Polymer
Definition and Characteristics
Homochain polymers, also known as homopolymers, are made from a single type of monomer that repeats throughout the entire molecular chain. These polymers are characterized by their uniformity and simplicity, which contribute to consistent mechanical and chemical properties. This uniformity arises because each monomer unit within the polymer chain interacts with its neighbors in a predictable manner, leading to a material that behaves consistently under given conditions.
Common Examples
Some common examples of homochain polymers include polyethylene and polystyrene. Polyethylene, used widely in the production of plastic bags and containers, is renowned for its strength and flexibility. Polystyrene, on the other hand, is often found in packaging materials and disposable coffee cups due to its excellent insulation properties and light weight.
Applications in Industry
Homochain polymers have broad applications across various industries due to their predictable properties. For instance:
- Packaging: Polyethylene films are extensively used in packaging because of their durability and resistance to moisture.
- Construction: Polystyrene foam serves as effective insulation in buildings.
- Textiles: Polyester fibers, another form of homopolymer, are essential in the textile industry for making durable and resistant fabrics.
Heterochain Polymer
Definition and Characteristics
In contrast, heterochain polymers, or copolymers, consist of two or more different types of monomers linked in the same polymer chain. This diversity allows the polymers to exhibit properties not found in homopolymers, such as increased flexibility, enhanced chemical resistance, and improved strength. The variation in monomer types can significantly alter how the polymer chains interact with each other and with their environment.
Common Examples
Examples of heterochain polymers include nylon and polyester. Nylon is known for its strength and elasticity, making it ideal for use in textiles like hosiery and upholstery. Polyester, used in everything from clothing to industrial applications, is appreciated for its durability and resistance to environmental factors.
Applications in Industry
Heterochain polymers’ versatility makes them valuable in more specialized applications:
- Automotive: Nylons are used in car parts for their durability and heat resistance.
- Electronics: Polyesters provide insulation in electrical components due to their thermal stability.
- Medical: Certain copolymers are utilized in medical devices and implants for their biocompatibility and strength.
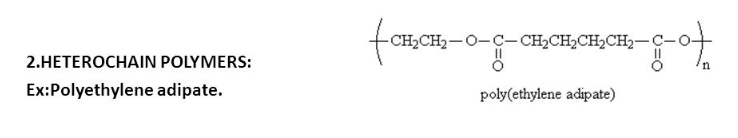
Structural Differences
Chain Composition
The fundamental difference between homochain and heterochain polymers lies in their chain composition. Homochain polymers have a simpler structure with repeating single monomer types, while heterochain polymers incorporate a variety of monomers, each bringing different properties to the polymer.
Molecular Bonding
Molecular bonding also differs significantly between the two types of polymers. In homochain polymers, bonding interactions are generally uniform, contributing to predictable properties. In contrast, heterochain polymers may exhibit varied bonding types and strengths across the chain, which can lead to complex behaviors under different conditions.
Impact on Properties
These structural and molecular differences critically impact the physical properties of the polymers. For example, heterochain polymers can be engineered to have higher impact resistance or lower melting points compared to their homochain counterparts due to the presence of different monomer units within the chain.
Physical Properties
Durability and Strength
The durability and strength of a polymer are heavily influenced by its molecular structure. Homochain polymers typically show high strength and durability under consistent conditions, whereas heterochain polymers can be tailored to exhibit these properties under a broader range of conditions by mixing monomers that contribute positively to these traits.
Thermal and Chemical Resistance
Thermal and chemical resistance are crucial for applications involving harsh environments. Homochain polymers, like polyethylene, generally exhibit good chemical resistance but may lack in thermal stability compared to some heterochain polymers like polyesters, which can withstand higher temperatures without degrading.
Applications and Uses
Industry-specific Applications
Polymers, both homochain and heterochain, play essential roles across various industries due to their adaptable properties. For instance, in the automotive industry, polymers are used to manufacture lightweight parts that contribute to fuel efficiency. In electronics, polymers are vital for insulating and protecting components due to their electrical resistivity and durability.
Comparative Advantages
Comparing homochain and heterochain polymers highlights their tailored advantages for specific applications. Homochain polymers often provide superior consistency and predictability, which are critical in high-volume manufacturing processes. Heterochain polymers, with their customizable properties, are better suited for applications requiring materials that can withstand diverse environmental stresses.
Synthesis and Production
Homochain Polymerization
The production of homochain polymers involves polymerization processes where identical monomers link to form long chains. This can occur through various mechanisms:
- Addition polymerization: Common in making polyethylene and polystyrene, this process involves the reaction of monomers with a double bond, which opens up and links together.
- Condensation polymerization: Used for creating polymers like nylon, where each monomer contributes a part of the polymer chain, releasing small molecules like water as a byproduct.
Heterochain Polymerization
Heterochain polymerization involves more complex procedures as it requires the co-polymerization of different monomers. This process allows for the incorporation of monomers with different chemical functionalities, resulting in copolymers with properties that are not achievable with homopolymers.
Challenges in Manufacturing
Manufacturing polymers, especially heterochain polymers, presents several challenges:
- Purity of raw materials: Ensuring the monomers are pure is crucial as impurities can significantly affect the properties of the polymer.
- Control over molecular weight: Achieving the desired molecular weight requires precise control over the polymerization process, which can be difficult.
- Reproducibility: Producing consistent results in heterochain polymerization can be challenging due to the complexity of the monomer mixtures.
Environmental Impact
Biodegradability
The environmental impact of polymers is significant, particularly concerning their biodegradability. Homochain polymers, such as polyethylene, are notoriously difficult to degrade, leading to long-term environmental pollution. Heterochain polymers can be engineered to be more biodegradable through the incorporation of monomers that break down more easily under natural conditions.
Recycling Challenges
Recycling is another critical aspect of polymers’ environmental impact. While homochain polymers are generally easier to recycle due to their uniform structure, heterochain polymers can be problematic because their varied monomer content requires more sophisticated sorting and processing techniques.
Future Trends
Innovations in Polymer Technology
The future of polymer science holds promising innovations, particularly in developing materials that are both performance-oriented and environmentally friendly. Advances in catalyst and polymer design are leading to more efficient synthesis methods that produce less waste and consume less energy.
Emerging Applications
Emerging applications of polymers include:
- Biomedical applications: Biocompatible polymers are being developed for use in drug delivery systems and tissue engineering.
- Smart materials: Polymers that respond to environmental stimuli such as temperature, light, and pH are being integrated into sensors and other electronic devices.
- Sustainable materials: Efforts are increasing to create polymers from renewable resources or those that are inherently more recyclable.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are Homochain Polymers?
Homochain polymers, also known as homopolymers, are polymers that consist of only one type of monomer repeated throughout the chain. This simplicity often leads to uniform physical properties, making them ideal for applications requiring consistent performance under predictable conditions.
What are Heterochain Polymers?
Heterochain polymers, or copolymers, are made from two or more different monomers. The incorporation of varied monomers allows for enhanced and tailored properties such as improved temperature resistance or mechanical strength, catering to more demanding or specialized applications.
How do Homochain and Heterochain Polymers Differ?
The primary difference between homochain and heterochain polymers lies in their monomeric composition. Homochain polymers offer predictability and simplicity, while heterochain polymers provide versatility and adaptability, allowing them to meet specific performance criteria across diverse industries.
Why is the Monomer Variety Important in Polymers?
Monomer variety is crucial because it determines the physical and chemical properties of the polymer. By varying the monomer types, manufacturers can design polymers that are more resistant to chemicals, heat, or stress, thereby extending the utility of these materials in various applications.
Conclusion
In sum, the distinction between homochain and heterochain polymers serves as a foundation for material science, influencing the development of new materials and technologies. These classifications help dictate the applications and innovations possible within industries reliant on polymer materials.
Understanding the structural differences and applications of homochain and heterochain polymers is more than academic—it’s a practical necessity for advancing material science and engineering. As the demand for specialized materials grows, the role of these polymers will only expand, underscoring the importance of mastering this area of study.

