Lipids are fundamental components of life, playing critical roles in various biological processes. Among these, glycolipids and phospholipids stand out for their unique structures and functions within cellular membranes. Their significance extends from the microscopic interactions in cells to their broader implications in human health and disease.
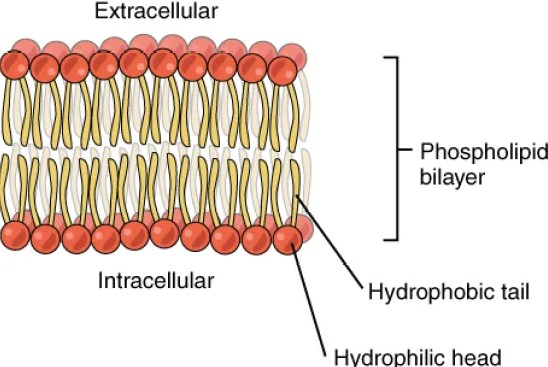
Glycolipids and phospholipids differ primarily in their structure and function. Glycolipids are composed of a carbohydrate attached to a lipid molecule and are crucial in cellular recognition and signaling. On the other hand, phospholipids form the primary structure of the cell membrane, consisting of two fatty acid chains and a phosphate group, providing barrier and pathway functions within and between cells.
While both types of lipids are essential for cellular architecture and function, their distinct roles highlight the diversity of biological molecules and their specific contributions to cellular health and functionality. These differences not only influence how cells operate but also affect various medical and industrial applications, from disease treatment strategies to the development of biotechnological products.
Lipid Basics
What Are Lipids?
Lipids are a diverse group of compounds, universally recognized for their role in biological systems as structural components of cell membranes, energy storage molecules, and signaling molecules. These hydrophobic or amphipathic small molecules are crucial in forming biological membranes, including those of the cell itself.
Types of Lipids
Lipids can be broadly categorized into several types, each serving distinct functions within living organisms:
- Fatty Acids: These are the simplest form of lipids and serve as the building blocks for more complex molecules. They are primarily involved in energy storage.
- Triglycerides: Composed of three fatty acid chains linked to a glycerol molecule, triglycerides are stored in fat cells and are used as a long-term energy reserve.
- Steroids: Including cholesterol and hormones, steroids play significant roles in maintaining cell membrane structure and signaling.
- Phospholipids and Glycolipids: These are key components of the cell membrane, involved in membrane structure and functionality.
Glycolipids Explained
Structure of Glycolipids
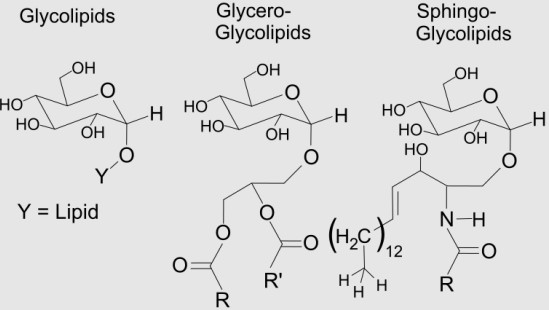
Glycolipids consist of a lipid moiety that is linked to a carbohydrate by a glycosidic bond. The lipid part typically involves a ceramide or sphingolipid, which anchors the molecule within the cellular membranes.
Components and Formation
The formation of glycolipids involves enzymatic processes that attach carbohydrates to lipids. These occur predominantly in the Golgi apparatus of the cell, where sugars are added sequentially to the lipid backbone.
Functions of Glycolipids
Glycolipids perform several critical functions in cellular processes:
- Cell Recognition: Glycolipids are essential for cell-cell recognition, a process vital for the immune response and in the development of tissues.
- Signal Transmission: They play a role in signal transduction processes, helping cells respond to external signals.
- Protection: By forming part of the cell membrane, glycolipids contribute to the protective barrier against environmental stresses.
Phospholipids Explained
Structure of Phospholipids
Phospholipids are characterized by having two fatty acid chains and a phosphate-containing group attached to a glycerol backbone. This structure allows them to form bilayers that are essential for cell membranes, creating a hydrophobic interior and a hydrophilic exterior.
Components and Formation
Phospholipids are synthesized in the cell by the addition of fatty acids to a glycerol-phosphate backbone. This process takes place primarily in the cytosolic side of the endoplasmic reticulum membrane.
Functions of Phospholipids
The primary functions of phospholipids include:
- Barrier Formation: They form the double-layered membrane of cells which separates the cell from its external environment.
- Molecular Transport: Phospholipids help in the formation of vesicles for molecular transport within cells.
- Cell Signaling: They participate in cell signaling mechanisms, especially in the creation and function of lipid rafts.
Key Differences
Molecular Structure
Comparison of Structural Components
Glycolipids and phospholipids, while both essential components of cell membranes, differ markedly in their molecular makeup. Glycolipids are characterized by the presence of one or more sugar groups attached to a lipid base, typically a ceramide. This sugar moiety allows them to participate in specific biological interactions that are carbohydrate-specific. In contrast, phospholipids consist of a glycerol backbone, two fatty acid tails, and a phosphate group. The phosphate group is often linked to other organic groups, which contributes to the phospholipid’s role in cell signaling and membrane dynamics.
Biological Roles
Distinct Functions in Organisms
The distinct molecular structures of glycolipids and phospholipids translate into different functions in biological systems. Glycolipids are predominantly involved in cell recognition and communication. They facilitate interactions between cells and the external environment, playing a pivotal role in immune responses and the targeting of pathogens. Phospholipids, however, are fundamental to forming and maintaining the cellular membrane structure. They provide a barrier that protects cellular components and helps to maintain the cell’s chemical environment.
Location in Cells
Membrane Placement and Interactions
Glycolipids are typically located on the outer leaflet of the cell membrane, where they interact with the extracellular milieu. This positioning is critical for their role in cell-cell recognition and signaling. Phospholipids, meanwhile, are found in both leaflets of the bilayer but are more dynamic in their distribution. They can move between layers through processes like flip-flop, which is catalyzed by specific enzymes. This flexibility allows phospholipids to participate actively in various cellular processes, such as vesicle formation and membrane fusion.
Similarities Overview
Common Features
Shared Traits in Lipid Function
Despite their differences, glycolipids and phospholipids share several important features. Both are amphipathic, meaning they contain both hydrophilic (water-attracting) and hydrophobic (water-repelling) regions. This duality is crucial for their function in membrane architecture, allowing them to form barriers that protect cellular components from the external environment while enabling interaction with it.
Role in Membrane Architecture
Contributions to Cellular Structures
Both glycolipids and phospholipids contribute significantly to the structure and integrity of cellular membranes. Their amphipathic nature facilitates the formation of lipid bilayers, which are the foundation of all cell membranes. These layers not only provide structural support but also create the necessary barriers for the selective transport of ions and molecules, crucial for cellular function and homeostasis.
Impact in Health and Medicine
Glycolipids in Disease
Examples of Related Conditions
Glycolipids play roles in several pathological conditions, including autoimmune diseases and certain types of cancer. Their function in cell recognition makes them key players in the immune system’s ability to distinguish between self and non-self, and disruptions in this process can lead to autoimmune reactions. Additionally, changes in glycolipid expression have been linked to tumor progression and metastasis, making them targets for therapeutic intervention.
Phospholipids in Health
Essential Benefits and Supplementation
Phospholipids are essential for maintaining cellular health. They not only form the cell membrane but also contribute to fat metabolism and brain health. Dietary supplements containing phospholipids, such as lecithin, are often recommended to support brain function, liver health, and cholesterol metabolism, underscoring their importance in maintaining overall health.
Industrial and Research Applications
Glycolipids in Industry
Uses in Products and Technology
In the industrial sector, glycolipids have found applications in areas ranging from cosmetics to biotechnology. They are used as natural emulsifiers and conditioning agents in skincare products and as bio-surfactants in environmental bioremediation efforts. Their unique properties make them attractive for developing green technologies and sustainable products.
Phospholipids in Research
Advances in Drug Delivery and Therapy
Research into phospholipids has led to significant advances in drug delivery systems. Their ability to form liposomes, small vesicles that can encapsulate drugs, allows for targeted drug delivery to specific tissues or organs. This property is particularly valuable in cancer treatment, where minimizing damage to healthy tissues is crucial. Phospholipid-based carriers are also being explored for their potential to improve the bioavailability of drugs, enhancing their therapeutic efficacy and reducing side effects.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are glycolipids?
Glycolipids are lipids that have a carbohydrate molecule attached. They are primarily found in the cell membrane and play significant roles in cell recognition and immune response.
How are phospholipids structured?
Phospholipids consist of a glycerol backbone, two fatty acid tails, and a phosphate group. This structure forms the basis of cell membranes, creating a bilayer that separates internal cellular components from the external environment.
Why are glycolipids important in medicine?
Glycolipids are important in medicine because they are involved in cell-cell interactions and the immune response. Their roles in diseases, particularly autoimmune diseases and infections, make them critical targets for medical research and drug development.
How do phospholipids support cell function?
Phospholipids support cell function by forming the cell membrane’s bilayer structure, which is crucial for maintaining the integrity and environment of cells. They allow for selective permeability, which is vital for transporting substances and communicating signals.
Conclusion
The exploration of glycolipids and phospholipids reveals a fascinating aspect of biological science, emphasizing the complexity and specificity of cellular components. Understanding these lipids enhances our knowledge of cell functions and paves the way for advancements in health sciences.
The ongoing research and interest in these molecules underscore their significance in both health and disease. Insights gained from studying glycolipids and phospholipids continue to inform a wide range of applications, from therapeutic interventions to the design of more effective biomimetic materials, highlighting their indispensable roles in science and medicine.