Organic chemistry, a branch of science focused on the study of carbon compounds, plays a crucial role in various industrial and pharmaceutical applications. Among the diverse group of organic compounds, dihalides stand out due to their unique chemical properties and applications. Dihalides are categorized based on the position of halogen atoms attached to the carbon atoms within the molecule.
Geminal and vicinal dihalides are two types of dihalides differentiated by the placement of their halogen atoms. Geminal dihalides have two halogen atoms attached to the same carbon atom, while vicinal dihalides have their halogen atoms on adjacent carbon atoms. This distinction influences their chemical reactivity, stability, and practical applications in significant ways.
Understanding the differences between these compounds is essential for chemists and industries that utilize these substances. The molecular structure, formation process, and reactivity vary between geminal and vicinal dihalides, affecting how they are used in synthesis and production processes across different sectors of the chemical industry.

Basic Concepts
Definitions and Terminology
Dihalides are a class of organic compounds where two halogen atoms are bonded to carbon atoms within a molecule. These halogens include fluorine, chlorine, bromine, and iodine, each contributing unique characteristics to the dihalide based on their chemical nature.
What are Dihalides?
In organic chemistry, dihalides are categorized by the number and position of halogen atoms attached to the carbon skeleton. The term “dihalide” signifies that two halogen atoms are involved, which are key to the chemical behavior and applications of these compounds.
Key Chemical Properties
The presence of halogen atoms in dihalides significantly affects their chemical reactivity, polarity, and physical properties such as boiling and melting points. Dihalides are generally more reactive than their corresponding alkanes due to the electronegative nature of the halogens that attract electrons towards themselves, creating polar bonds.
Types of Dihalides
Distinguishing between different types of dihalides depends on the arrangement of halogen atoms relative to each other.
Geminal Dihalides
Geminal dihalides, often abbreviated as “gem-dihalides,” have both halogen atoms attached to the same carbon atom. This setup can lead to interesting reactivity patterns due to the increased electron density at that carbon center.
Vicinal Dihalides
In contrast, vicinal dihalides feature halogen atoms on adjacent carbon atoms. This configuration allows for reactions that can bridge or split the carbons, offering versatile options in synthetic chemistry.
Geminal Dihalides
Structure and Formation
Molecular Structure
The molecular structure of geminal dihalides involves a carbon atom doubly bonded to two halogen atoms. This configuration can create a significant strain due to the crowding around the carbon atom and the repulsion between the large halogen atoms.
How They are Formed
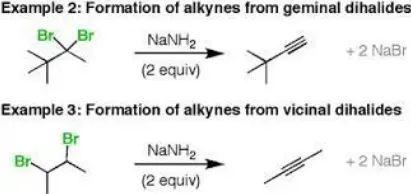
Geminal dihalides are typically formed through the halogenation of alcohols or ketones where a dihalogen molecule reacts with a corresponding precursor, introducing two halogen atoms to the same carbon.
Chemical Properties
Reactivity
The reactivity of geminal dihalides is heightened by the presence of two electron-withdrawing groups (the halogens) attached to a single carbon. This arrangement can lead to instability and makes these compounds excellent candidates for further chemical transformations.
Stability Factors
The stability of geminal dihalides is generally lower than their vicinal counterparts due to steric strain and the potential for halogen repulsion.
Common Uses
Industrial Applications
Geminal dihalides are crucial in the synthesis of various chemicals, including solvents, pharmaceuticals, and agrochemicals, due to their reactivity.
Role in Synthesis
In organic synthesis, geminal dihalides serve as intermediates in the preparation of more complex molecules, including cyclopropanes and other cyclic structures.
Vicinal Dihalides
Structure and Formation
Molecular Structure Differences
Vicinal dihalides differ from geminal dihalides in that the halogens are bonded to adjacent carbon atoms. This spatial arrangement reduces the electron density stress and offers different reactivity.
Formation Processes
Vicinal dihalides are often produced by the halogenation of alkenes, where the addition of a dihalogen across the double bond results in halogens attaching to neighboring carbon atoms.
Chemical Properties
Unique Reactivity
The reactivity of vicinal dihalides includes the ability to participate in reactions that can open or rearrange the carbon framework, such as dehalogenation or reactions leading to ring formations.
Stability under Various Conditions
Vicinal dihalides tend to be more stable than geminal dihalides due to less crowding around any single carbon atom, making them suitable for different chemical environments and storage conditions.
Common Uses
Uses in Industry
Vicinal dihalides find applications in the manufacture of polymers, pesticides, and other industrial chemicals. Their ability to transform into different chemical structures easily makes them valuable in complex chemical manufacturing processes.
Importance in Organic Synthesis
In organic synthesis, vicinal dihalides are essential for constructing halogenated intermediates that are precursors to many important compounds and catalysts in chemical reactions.
Comparative Analysis
Structural Differences
Bond Placement and Angles
The spatial arrangement of atoms within geminal and vicinal dihalides significantly influences their molecular architecture. In geminal dihalides, the two halogen atoms are bonded to the same carbon atom, often leading to increased angular strain due to the repulsion between the large electron clouds of the halogens. This strain can affect the bond angles, typically making them smaller than in a standard tetrahedral geometry found in less crowded molecules.
In contrast, vicinal dihalides feature halogens on adjacent carbons, which generally adhere more closely to the ideal tetrahedral angle of 109.5 degrees. This difference in bond placement impacts the overall flexibility and torsional strain of the molecule.
Impact on Molecular Shape
The shape of a molecule in geminal dihalides tends to be more compact and strained compared to vicinal dihalides. This compactness can lead to higher reactivity, as the molecule may seek to relieve strain. Conversely, the more extended shape of vicinal dihalides allows for greater rotational freedom, which can influence their behavior in chemical reactions and physical properties like boiling points and solubility.
Reactivity and Stability
Comparative Reactivity
Geminal dihalides are generally more reactive due to the strain and polarization caused by having two halogens on the same carbon. They are particularly susceptible to nucleophilic attack, where a nucleophile targets the carbon center to displace one or both halogens.
Vicinal dihalides, however, often participate in elimination reactions, where the adjacent halogens leave, forming a double bond. This difference in reactivity patterns opens various pathways in synthetic chemistry, making each type uniquely valuable depending on the reaction conditions and desired products.
Stability in Different Environments
The stability of dihalides varies significantly with their environment. Geminal dihalides may decompose under less strenuous conditions due to internal stress, whereas vicinal dihalides typically exhibit greater thermal stability. This stability makes vicinal dihalides more versatile for use in conditions that require a higher threshold for decomposition.
Applications Contrast
Divergent Uses in Industry
The unique properties of geminal and vicinal dihalides dictate their specific applications in industry. Geminal dihalides are often used in the synthesis of fine chemicals, where high reactivity and specific outcomes are required. They serve as key intermediates in pharmaceutical manufacturing and specialty polymers.
Vicinal dihalides are more commonly employed in the production of larger scale industrial chemicals. Their robust nature makes them suitable for processes like the production of PVC (polyvinyl chloride) through the polymerization of vinyl chloride, a product of vicinal dihalide processing.
Synthesis Importance
In organic synthesis, the choice between using geminal or vicinal dihalides can impact the efficiency, yield, and purity of the final product. Geminal dihalides are crucial for reactions that require high reactivity, while vicinal dihalides are preferred for reactions that benefit from their stability and propensity for controlled reactions such as eliminations and substitutions.
Practical Implications
Synthesis Challenges
Challenges in Synthesizing Geminal and Vicinal Dihalides
The synthesis of both geminal and vicinal dihalides presents distinct challenges. For geminal dihalides, the major difficulty lies in controlling the reaction conditions to prevent overreaction or degradation of the carbon-halogen bonds. This requires precise temperature control and careful selection of reagents.
Vicinal dihalides challenge chemists in terms of regioselectivity, where the specific positioning of halogens must be controlled to ensure the correct structure. This often necessitates the use of specific catalysts or protective groups to guide the reaction pathway.
Overcoming These Challenges
Advancements in chemical synthesis techniques have provided strategies to mitigate these challenges:
- Use of specialized catalysts that enhance selectivity and control reaction rates.
- Development of new synthetic methods that offer greater control over the reaction environment, such as microwave-assisted synthesis and flow chemistry.
- Implementation of computational modeling to predict reaction outcomes and optimize conditions before empirical testing.
Future Prospects
Emerging Research
Research in the field of dihalides is continuously evolving, with new discoveries focusing on improving the sustainability and efficiency of synthesis methods. Innovations such as greener reagents and solvent-free reactions are paving the way for more environmentally friendly chemistry.
Potential New Applications
The ongoing development in dihalide chemistry holds promise for new applications in areas like materials science, where advanced polymers and composites require tailored molecular structures for enhanced properties. Additionally, the pharmaceutical industry continues to explore dihalides for novel drug synthesis, particularly in the design of molecules with improved efficacy and reduced side effects.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are Geminal Dihalides?
Geminal dihalides, or gem-dihalides, are compounds in which two halogen atoms are bonded to the same carbon atom. They are often used in various chemical reactions and processes due to their unique reactivity, which can be leveraged to synthesize other complex molecules.
What are Vicinal Dihalides?
Vicinal dihalides contain halogen atoms attached to adjacent carbon atoms within a molecule. They are crucial in organic synthesis, especially in the preparation of other important organic compounds through reactions like halogenation and dehalogenation.
How do Geminal and Vicinal Dihalides Differ in Reactivity?
The reactivity of geminal and vicinal dihalides differs primarily due to their structural configurations. Geminal dihalides generally exhibit higher reactivity because the presence of two halogen atoms on the same carbon atom creates significant electronic and steric strain.
What are the Industrial Applications of Dihalides?
Dihalides are extensively used in the chemical industry for manufacturing a wide range of products, including pharmaceuticals, agricultural chemicals, and polymers. Their unique properties make them valuable for various chemical synthesis processes.
Conclusion
The study of geminal and vicinal dihalides offers fascinating insights into the field of organic chemistry. Their distinct properties not only distinguish them in terms of chemical reactivity and stability but also underline their importance in industrial applications. Recognizing these differences is crucial for chemists and industries that rely on precise chemical synthesis techniques.
By further exploring and understanding these compounds, the chemical industry can continue to innovate and improve the efficiency of synthesis processes, paving the way for the development of new products and technologies. This exploration not only enriches our understanding of organic chemistry but also contributes to advancements in multiple scientific and industrial fields.

