Formal charge and oxidation state are both important concepts in chemistry, but they are not the same. In this blog post, we’ll discuss the difference between formal charge and oxidation state and explain why each one is important.
By the end of this blog post, you’ll have a better understanding of the differences between formal charge and oxidation state.
How formal charge and oxidation state relate to each other
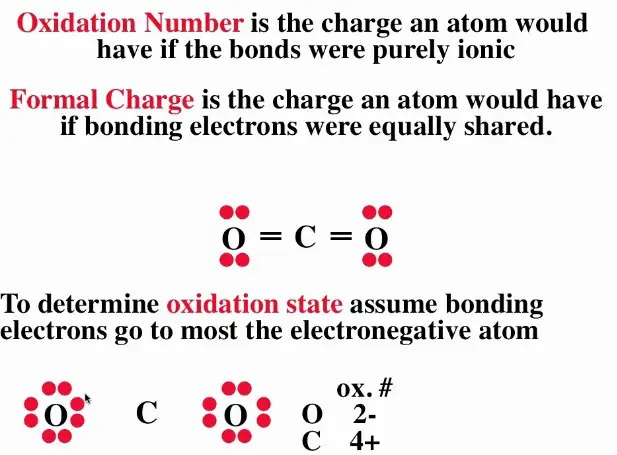
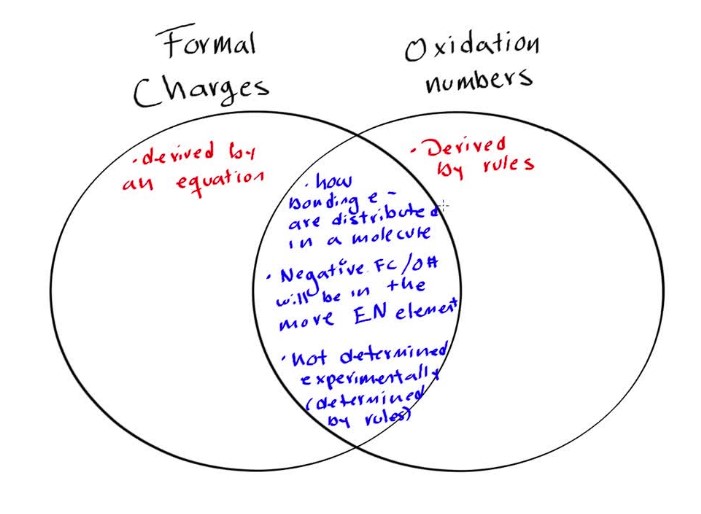
Formal charge and oxidation state are two related but distinct concepts in chemistry. While they both involve the transfer of electrons between atoms, their roles in chemical reactions are quite different. The formal charge of an atom is a measure of the difference between the number of electrons in the atom’s valence shell and the number of electrons that would be present if all the covalent bonds to the atom were purely ionic.
The formal charge of an atom is a measure of the difference between the number of electrons in the atom’s valence shell and the number of electrons that would be present if all the covalent bonds to the atom were purely ionic. On the other hand, the oxidation state of an atom is a measure of how much the atom has been oxidized or reduced in a reaction. In other words, the formal charge is indicative of the electron-sharing between atoms in a molecule, while the oxidation state is a measure of the overall change in oxidation state.
In short, the formal charge of an atom is a measure of the number of electrons in its outer shell, while the oxidation state is a measure of the overall change in oxidation state.
Factors that affect formal charge and oxidation state

When it comes to understanding formal charge and oxidation state, it’s important to know the difference between the two. The formal charge of an atom is the charge on an atom in a molecule or ion, calculated by subtracting the number of electrons surrounding the atom from the number of protons in the nucleus. The oxidation state, on the other hand, is the charge an atom would have if all the bonds to atoms of different elements were to be 100% ionic.
There are several factors that affect the formal charge and oxidation state of an atom, including the number of electrons in the atom’s valence shell, the number of lone pairs in the atom’s outer shell, and the number of bonds the atom has with atoms of different elements. The oxidation state of an atom can also be affected by the overall polarity of a molecule.
When calculating formal charge and oxidation state, it’s important to keep these factors in mind.
Examples of formal charge and oxidation state
Formal charge and oxidation state can be two of the most confusing aspects of chemistry to understand. While both are related to electron transfer, there are some key differences to keep in mind. Formal charge is the difference between the number of valence electrons of an atom in a molecule and the number of electrons the atom is actually holding.
On the other hand, oxidation state is the number of electrons a atom has lost or gained in a reaction. In essence, formal charge is the net difference between the number of electrons that an atom has, while oxidation state is the net number of electrons lost or gained.
Common misconceptions about formal charge and oxidation state
Formal charge and oxidation state are both important concepts when it comes to understanding chemistry, but they are often confused for one another. While both formal charge and oxidation state are related to the charge of an atom in a molecule, they are not the same. The main difference between formal charge and oxidation state is that formal charge is a bookkeeping tool used to keep track of electrons, while oxidation state is a measure of the oxidation number of an atom in a molecule.
Formal charge takes into account the number of valence electrons on an atom, and assigns a charge based on how many electrons an atom has gained or lost. Oxidation state, on the other hand, looks at the total number of electrons an atom has, and assigns a charge based on the total number of electrons an atom has gained or lost.
Therefore, oxidation state is a more accurate measure of an atom’s charge than formal charge.
Tips for keeping track of formal charge and oxidation state
Keeping track of formal charge and oxidation state can be a challenge for chemists, as they are two different concepts that are related but distinct. Formal charge is a way of keeping track of the electrons in a molecule, and is calculated by subtracting the number of valence electrons from the number of electrons assigned to each atom in the molecule. Oxidation state, on the other hand, is a way of keeping track of the number of bonds between atoms in a molecule and is calculated by adding the number of covalent bonds between the atoms and subtracting the number of lone electrons.
While both formal charge and oxidation state are important in predicting the properties of a molecule, it’s important to understand the difference between them in order to accurately predict the behavior of the molecule.
Final Touch
In conclusion, the difference between formal charge and oxidation state can be summarized as follows: Formal charge is the charge assigned to an atom in a molecule based on its electron configuration, whereas oxidation state is the charge assigned to an atom based on its share of electrons in a chemical reaction. Formal charge is determined by the number of electrons surrounding the atom, while oxidation state is determined by the total number of electrons in the atom. Although both are used to determine the charge of an atom in a molecule, they are calculated differently and can lead to different results.
Although both are used to determine the charge of an atom in a molecule, they are calculated differently and can lead to different results.