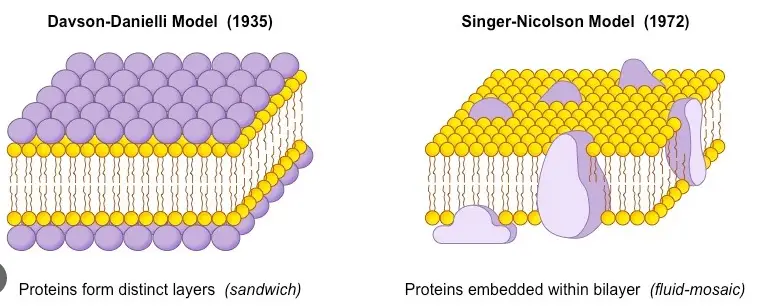
The cell membrane, a critical barrier and communication interface in cells, is described through various models, each proposing unique structural and functional aspects. Among these, the Fluid Mosaic Model and the Sandwich Model stand out due to their significant contributions to our understanding of cellular mechanisms. These models explain how biological membranes are organized and function at the molecular level, shaping decades of research and theory in cell biology.
The Fluid Mosaic Model depicts the cell membrane as a dynamic, fluid structure with proteins embedded in or attached to a bilayer of phospholipids. Contrarily, the Sandwich Model, an earlier hypothesis, suggested a more rigid structure where proteins coat the phospholipid bilayer. Although the Fluid Mosaic Model is the more accepted theory today, both models have been instrumental in guiding scientific inquiry and experimental approaches.
The exploration of these models offers insight into the evolutionary nature of scientific theories and their impact on our understanding of cell biology. As research progresses, these models adapt and are refined, reflecting new discoveries and technologies that continue to push the boundaries of science.
Cell Membrane Overview
Basic Structure and Function
The cell membrane plays a pivotal role as the protective barrier that separates the interior of all cells from the external environment. This membrane is not just a static layer; it is dynamic, selectively permeable, and involved in complex interactions. Structurally, it is primarily composed of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins, cholesterol, and other lipids that provide fluidity and mechanical support.
Phospholipids, the fundamental building blocks of the membrane, have a hydrophilic (water-attracting) head and two hydrophobic (water-repelling) tails. This arrangement causes phospholipids to align themselves in a bilayer, creating a barrier that protects cellular components from the external environment while allowing selective transport of substances in and out of the cell.
Role in Cellular Biology
The cell membrane is essential in various cellular functions, including:
- Transport: Regulates the movement of substances, ensuring that essential nutrients enter the cell and waste products are expelled.
- Communication: Contains receptors that recognize and respond to chemical signals.
- Protection: Forms a barrier against substances and pathogens that could harm the cell.
- Attachment: Helps cells adhere to each other and form tissues.
This diverse functionality not only supports the cell’s survival but also enables it to contribute to the larger functions of tissues and organs.
Fluid Mosaic Model
Definition and Origin
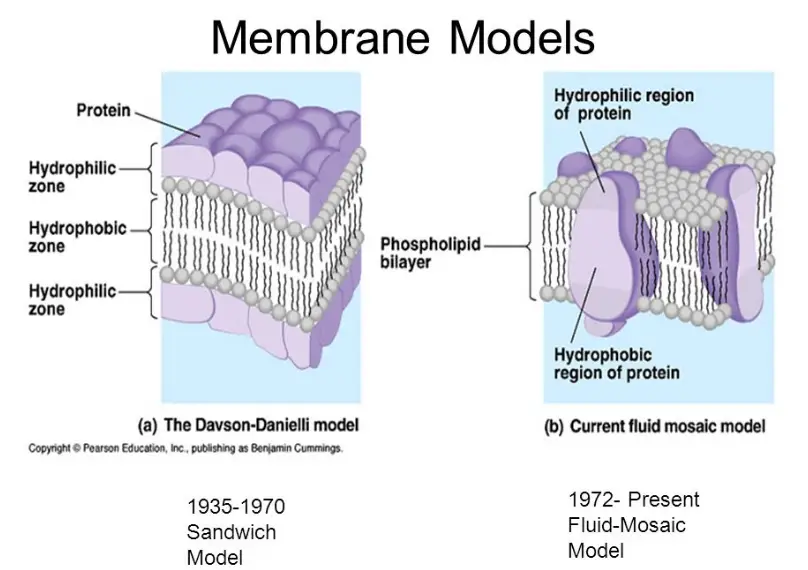
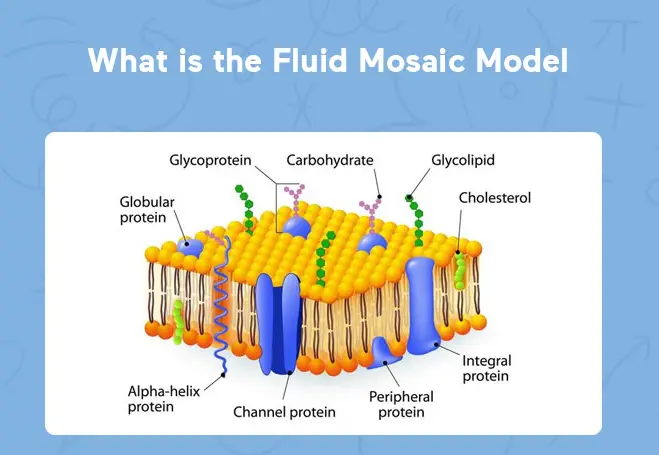
The Fluid Mosaic Model was proposed by S.J. Singer and Garth Nicolson in 1972. This model introduced the idea that the cell membrane is a fluid, dynamic mosaic of phospholipids and proteins. This concept was revolutionary as it described the membrane’s nature to be more integrated and variable, contrasting sharply with the static models previously suggested.
Key Components
The main components of the Fluid Mosaic Model include:
- Phospholipids: Form the fluid bilayer that is the foundation of the membrane.
- Proteins: Interspersed within the phospholipid bilayer, these proteins may be peripheral or integral, facilitating various functions such as transport, signal transduction, and enzymatic activity.
- Cholesterol: Scattered within the bilayer to stabilize membrane fluidity across temperature variations.
Mechanisms of Function
The mechanisms by which the Fluid Mosaic Model functions are crucial for cellular health and activity:
- Dynamic Movement: Components of the membrane can move laterally, allowing the cell to adapt and reorganize in response to environmental changes.
- Selective Permeability: Enables differential permeability where only specific molecules can pass through via proteins, maintaining the cell’s internal conditions.
- Signal Reception: Membrane proteins act as receptors for signaling molecules, initiating cellular responses.
Sandwich Model
Historical Context
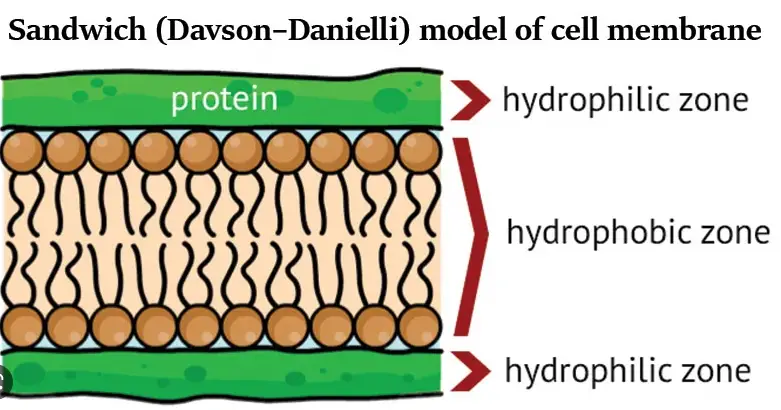
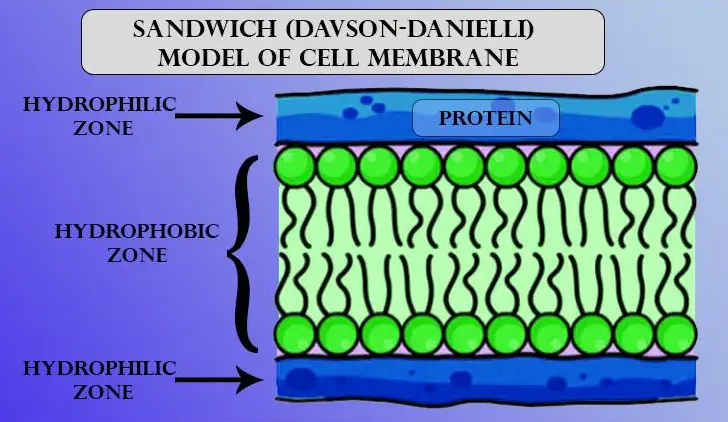
Before the Fluid Mosaic Model, the Sandwich Model proposed by Davson and Danielli in 1935 dominated the field. This model suggested that proteins coat either side of the lipid bilayer like bread on a sandwich. It was based on electron microscopy studies and was widely accepted due to the limited understanding of membrane structure at the time.
Core Concepts
The core concepts of the Sandwich Model included:
- Bilayer Core: Composed solely of lipids.
- Protein Layers: Proteins lie outside the lipid bilayer, not integrated within it.
- Static Structure: Implied a rigid, fixed arrangement of molecules.
Comparison with Later Models
The Sandwich Model was eventually replaced by the Fluid Mosaic Model due to several shortcomings:
- Inflexibility: It did not explain the dynamic nature of cellular membranes observed in later experimental studies.
- Lack of Integration: Modern techniques revealed proteins that penetrate the lipid bilayer, inconsistent with the surface-only protein placement in the Sandwich Model.
Key Differences
Structural Distinctions
The structural differences between the Fluid Mosaic Model and the Sandwich Model are pivotal in understanding how scientists view the cell membrane. The Fluid Mosaic Model suggests a flexible, ever-changing landscape where proteins and lipids move freely across the membrane’s surface. This contrasts sharply with the Sandwich Model, where the lipid bilayer is simply flanked by rigid protein layers, suggesting no intercalation of proteins within the lipid layers.
- Phospholipid Arrangement: In the Fluid Mosaic Model, phospholipids and proteins integrate seamlessly, allowing for a dynamic and adaptable membrane structure. In contrast, the Sandwich Model posits a static bilayer sandwiched by external protein layers.
- Protein Mobility: The Fluid Mosaic Model allows for protein mobility across the membrane, essential for cellular signaling and transport. The Sandwich Model lacks this dynamic interaction, depicting proteins as static and merely adjacent to the lipid core.
Functional Implications
The functional implications of these structural distinctions are vast:
- Cell Signaling: Dynamic protein placement in the Fluid Mosaic Model facilitates complex signaling pathways essential for cellular responses to environmental stimuli. The rigidity of the Sandwich Model does not support such intricate interactions.
- Membrane Fluidity: Fluidity is crucial for the membrane’s adaptability to changes in temperature and environment, supported by the Fluid Mosaic Model. The Sandwich Model’s rigid structure offers no such adaptability, which is inconsistent with observed cellular behaviors.
Scientific Acceptance and Evidence
Scientific evidence has overwhelmingly supported the Fluid Mosaic Model over the Sandwich Model. Advanced imaging techniques, such as cryo-electron microscopy and fluorescent tagging, have shown proteins moving within the lipid bilayer, a concept incompatible with the Sandwich Model. These findings have cemented the Fluid Mosaic Model’s status in scientific literature and educational materials.
Impact on Scientific Research
Influence on Membrane Studies
The adoption of the Fluid Mosaic Model has profoundly influenced membrane studies, steering research towards understanding cellular processes such as endocytosis, exocytosis, and ion channel behavior. Researchers now explore how membranes facilitate cellular communication and transport mechanisms, viewing the membrane not just as a barrier but as a dynamic participant in these processes.
Developments in Cellular Biology
The implications of the Fluid Mosaic Model extend beyond membrane studies into broader cellular biology, impacting our understanding of:
- Disease Mechanisms: Many diseases, including cystic fibrosis and some forms of cancer, involve mutations that affect membrane proteins. Understanding the dynamic nature of these proteins within the membrane can lead to targeted therapies.
- Drug Delivery Systems: Enhanced knowledge of membrane dynamics has led to better-designed lipid-based drug delivery systems that can effectively target specific cells without harming others.
Modern Understanding
Evolution of Theories
The evolution from the Sandwich Model to the Fluid Mosaic Model represents a broader shift in biological sciences from static to dynamic systems theories. This shift reflects a deeper understanding that biological entities are not static structures but dynamic systems engaging with their environment in complex ways.
Current Accepted Models
Today, the Fluid Mosaic Model remains the accepted depiction of the cell membrane structure. However, ongoing research continues to refine this model, incorporating new discoveries about the roles of various lipids and the complex nature of membrane proteins. Current research investigates the role of microdomains known as lipid rafts and their function in signaling and membrane trafficking.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Fluid Mosaic Model?
The Fluid Mosaic Model, introduced by Singer and Nicolson in 1972, describes the cell membrane as a flexible layer made of lipid bilayers interspersed with various proteins that move dynamically. This model emphasizes the fluidity and variability of the membrane’s components, essential for understanding membrane permeability and functionality.
How does the Sandwich Model differ?
The Sandwich Model, proposed earlier in the 20th century, presented the membrane as a static structure with proteins layered on either side of a lipid bilayer, like a sandwich. This model has since been deemed less accurate as it does not account for the fluid nature of most biological membranes.
Why is the Fluid Mosaic Model more accepted?
The Fluid Mosaic Model is favored because it better accommodates the diverse functions and dynamic nature of cellular membranes observed in experimental studies. It explains the presence of lipid rafts, protein mobility, and the overall heterogeneous environment of the cellular membrane, which are critical for cellular function.
What impact did these models have on biology?
Both models significantly influenced the field of cellular biology by guiding research into membrane structure and function. The Fluid Mosaic Model, in particular, has shaped modern understanding of cell interaction, signaling, and membrane permeability.
Conclusion
Reflecting on the differences between the Fluid Mosaic Model and the Sandwich Model reveals more than the evolution of scientific thought; it illustrates the process of hypothesis and refinement that is core to scientific inquiry. These models have not only provided frameworks for understanding cell membrane structure but have also prompted further questions leading to more nuanced discoveries.
The ongoing refinement of these models exemplifies the dynamic and ever-evolving nature of science, where theories are not simply replaced but built upon. Insights gained from both models continue to influence current research and teaching in cellular biology, proving the enduring value of foundational scientific models.