Chemical reactions are fundamental to scientific exploration and industrial application, playing a pivotal role in everything from the creation of everyday products to advancements in pharmaceuticals. Electrocyclic and cycloaddition reactions, while perhaps less familiar to the non-specialist, are crucial in the realm of organic chemistry. These reactions involve the transformation of pi-bonded electrons into new sigma bonds, leading to the formation of cyclic products.
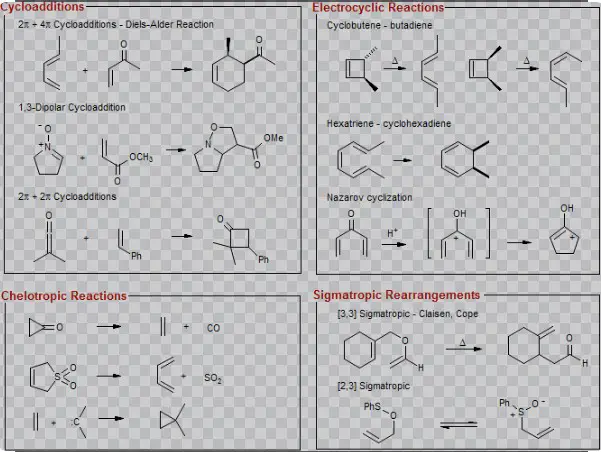
Electrocyclic reactions involve the conversion of a linear pi system into a cyclic one under the influence of heat or light, typically following a conrotatory or disrotatory motion based on specific molecular orbital symmetries. Cycloaddition reactions, on the other hand, generally refer to the process where two or more unsaturated molecules combine to form a cyclic adduct, often facilitated by the presence of a catalyst or under specific thermal conditions.
Understanding the distinctions between these two types of reactions is not just academic; it has practical implications in synthesizing complex molecular structures efficiently and with higher yields. The subtle yet significant differences in their mechanisms, applications, and conditions under which they occur offer a fascinating glimpse into the intricate dance of electrons that drives chemical transformations.
Electrocyclic Reactions
Definition and Basics
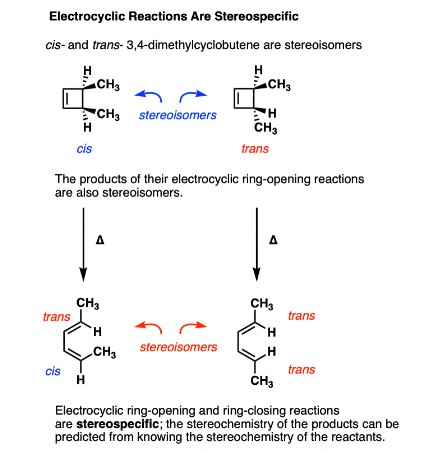
Electrocyclic reactions are a class of organic reactions where a linear pi system transforms into a cyclic one. This transformation is triggered either by heat or light and is fundamental in synthetic organic chemistry. The reaction is characterized by the movement of electrons which causes a significant structural rearrangement.
Mechanism Explained
The mechanism of electrocyclic reactions involves the breaking and forming of bonds through a concerted process. This means that all bond-making and bond-breaking events occur simultaneously in a single step without intermediates. The process is typically influenced by the electronic configuration of the molecule, which determines whether the reaction will proceed via a conrotatory or disrotatory motion:
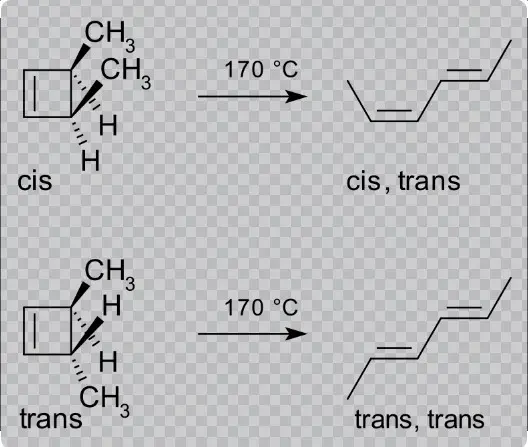
- Conrotatory motion: In this mode, the ends of the molecule rotate in opposite directions. This motion is typically observed under thermal conditions.
- Disrotatory motion: Here, the ends rotate in the same direction, often induced by photochemical conditions.
Common Examples
Examples of electrocyclic reactions are widespread in the synthesis of various organic compounds:
- Ring-closing of hexatriene to cyclohexadiene is a classic example, showcasing the conversion of a linear structure into a cyclic one.
- Synthesis of vitamin D utilizes an electrocyclic reaction to form the core ring structure essential for its biological activity.
Cycloaddition Reactions
What They Are
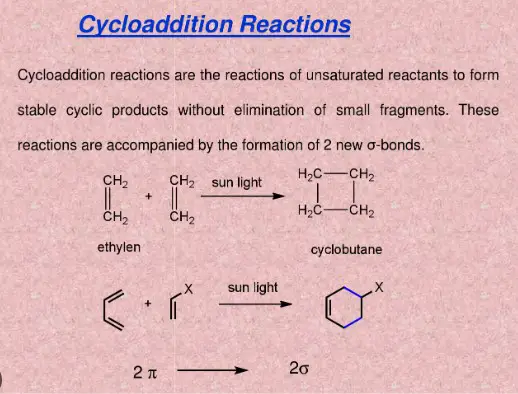
Cycloaddition reactions represent another critical category of chemical reactions where two or more unsaturated molecules, or parts of the same molecule, combine to form a cyclic compound. These reactions are vital for creating complex ring systems in an efficient and stereospecific manner.
Reaction Mechanism
The mechanism of cycloaddition reactions involves the formation of new sigma bonds through the overlap of pi orbitals, resulting in a cyclic product. These reactions are typically described by the [4+2] cycloaddition or Diels-Alder reaction, which is one of the most well-known examples:
- [4+2] cycloaddition: Involves a diene and a dienophile reacting to form a six-membered ring.
Key Examples
Key examples include:
- Diels-Alder reaction: A diene and dienophile react to produce a six-membered ring containing new sigma bonds.
- 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition: Used in the synthesis of various heterocyclic compounds, involving a dipole and a dipolarophile.
Key Differences
Reaction Pathways
The pathways of electrocyclic and cycloaddition reactions differ primarily in their mechanisms and the types of bonds formed. Electrocyclic reactions involve a single molecule forming a ring, typically through a conrotatory or disrotatory path. Cycloaddition reactions, however, typically involve two different molecules or moieties coming together to form a new ring.
Energy Changes
Energy changes in these reactions are crucial for understanding their spontaneity and feasibility:
- Electrocyclic reactions often release energy as the system moves to a more stable, cyclic state.
- Cycloaddition reactions may either absorb or release energy, depending on the specific reactants and conditions.
Product Formation
The products of these reactions are cyclic compounds, but their formation differs:
- Electrocyclic reactions result in single-ring products with various substituents depending on the starting material.
- Cycloaddition reactions can produce complex multi-ring systems and are highly useful in synthesizing intricate molecular architectures.
Thermodynamic Considerations
Activation Energy
Activation energy is a critical factor determining the rate and feasibility of a chemical reaction. For both reaction types, the lower the activation energy, the faster and more likely the reaction is to occur under given conditions.
Reaction Conditions
Reaction conditions such as temperature, pressure, and the presence of catalysts significantly affect the outcome of both electrocyclic and cycloaddition reactions. For instance:
- Electrocyclic reactions might require heat or light to proceed.
- Cycloaddition reactions are often catalyzed by Lewis acids or bases to increase the reaction rate and selectivity.
Kinetic Aspects
Rate of Reaction
The rate of reaction is a fundamental aspect of chemical kinetics that determines how quickly reactants convert to products. In both electrocyclic and cycloaddition reactions, this rate can vary widely depending on the molecular structure, type of reactants, and the external conditions under which the reaction is carried out. Factors such as the alignment of molecular orbitals and the stability of transition states play critical roles in influencing the reaction rates. For instance, in electrocyclic reactions, the symmetry of the molecule and the orbital alignments dictate whether the reaction will proceed rapidly or sluggishly.
Catalyst Effects
Catalysts are substances that speed up chemical reactions without being consumed in the process. They are especially important in cycloaddition reactions, where their presence can dramatically enhance both the rate and selectivity of the reaction. Catalysts like Lewis acids can stabilize the transition state, reduce the activation energy required for the reaction, and help control the stereochemistry of the product. In electrocyclic reactions, photochemical catalysts can be used to initiate and direct the reaction pathway via specific wavelengths of light.
Applications in Synthesis
Pharmaceuticals
The synthesis of pharmaceutical compounds often relies on the principles of electrocyclic and cycloaddition reactions. These reactions are crucial for constructing complex cyclic structures that are commonly found in natural products and drug molecules. For example:
- Antibiotics such as macrolides are synthesized using cycloaddition reactions to form their large macrocyclic structures.
- Anticancer drugs often incorporate cycloaddition methodologies to efficiently build up the complex rings and frameworks necessary for biological activity.
Material Science
In material science, these chemical reactions contribute to the development of new materials with enhanced properties. Polymers, for instance, can be synthesized through cycloaddition reactions to create new types of plastics and resins with specific characteristics like increased heat resistance or improved mechanical strength. Electrocyclic reactions are employed in the synthesis of organic conductive materials, which are essential for creating innovative electronic devices.
Challenges and Solutions
Common Challenges
One of the major challenges in utilizing electrocyclic and cycloaddition reactions in synthesis is the requirement for precise conditions to achieve desired outcomes. The reactivity of precursors, the stereochemical outcome of the reactions, and the scalability of the processes can often pose significant hurdles. Additionally, the sensitivity of certain reactants to light, heat, or moisture may limit the practicality of these reactions in industrial applications.
Overcoming Difficulties
To address these challenges, chemists employ a variety of strategies:
- Advanced catalysts are developed to enhance the efficiency and selectivity of reactions. These catalysts are designed to be more robust and versatile, capable of facilitating reactions under milder conditions.
- Computational modeling tools are increasingly used to predict the outcomes of electrocyclic and cycloaddition reactions, helping chemists to fine-tune the reaction conditions before performing actual experiments.
- Microreactor technology has been introduced to carry out reactions that are difficult to scale using traditional methods. These microreactors allow for precise control over reaction conditions, which can significantly improve the yield and purity of the products.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are Electrocyclic Reactions?
Electrocyclic reactions are a type of organic reaction where a linear pi-bonded molecule undergoes a transformation to form a cyclic product. This reaction is often driven by heat or light and involves a clear, predictable change in the electronic configuration of the molecule.
How do Cycloaddition Reactions Work?
Cycloaddition reactions involve the joining of two or more unsaturated molecules, such as alkenes or alkynes, to form a new ring structure. These reactions are pivotal in forming complex cyclic structures and are highly valued for their precision and the diversity of compounds they can help synthesize.
Why are these Reactions Important in Synthesis?
Both electrocyclic and cycloaddition reactions are key in synthetic chemistry for creating complex, cyclic compounds that form the basis of many drugs, plastics, and other advanced materials. Their ability to efficiently and selectively form new bonds makes them indispensable in many manufacturing processes.
What Determines the Pathway of an Electrocyclic Reaction?
The pathway of an electrocyclic reaction, whether it follows a conrotatory or disrotatory course, depends on the number of pi electrons involved and the temperature or light conditions under which the reaction occurs. These factors influence the symmetry and movement of electrons during the reaction.
Conclusion
The exploration of electrocyclic and cycloaddition reactions illuminates a crucial area of chemistry that impacts a variety of fields, from medicinal chemistry to material science. These reactions not only enhance our understanding of chemical processes but also improve our ability to design and synthesize new molecules with desired properties.
Continued research and application of these chemical reactions promise further breakthroughs in creating more effective and efficient synthesis pathways. As chemistry advances, the nuanced understanding of these processes will undoubtedly lead to significant innovations and solutions across multiple industries.