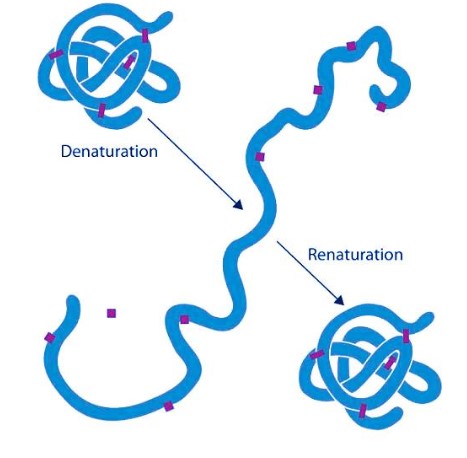
Proteins are fundamental to the myriad functions in living organisms, and their structures are intricately designed to support these functions. Changes in these structures can significantly affect their behavior and role within biological systems. Denaturation and renaturation are two such structural changes that, although might seem straightforward, involve complex molecular interactions and consequences.
Denaturation of a protein refers to the process where proteins lose their tertiary and secondary structure which is essential for their biological function, due to the influence of external factors like changes in temperature, pH, or exposure to chemicals. Conversely, renaturation is the process by which a denatured protein regains its original structure and function under suitable conditions.
These transformations are not just crucial for understanding biological processes but also have practical implications in biotechnology and medicine. For example, the renaturation process is fundamental in biopharmaceutical manufacturing, where protein drugs must be refolded into their functional forms after production.
Protein Basics
Definition and Role
Proteins are large, complex molecules that play many critical roles in the body. They do most of the work in cells and are required for the structure, function, and regulation of the body’s tissues and organs. Proteins are made up of smaller units called amino acids, which are attached to one another in long chains. There are 20 different types of amino acids that can be combined to make a protein. The sequence of amino acids determines each protein’s unique 3-dimensional structure and its specific function.
Structure Levels
Proteins have four levels of structure:
- Primary structure: This is the sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide chain.
- Secondary structure: This includes alpha helices and beta sheets that form within certain segments of the protein.
- Tertiary structure: This is the overall 3D shape of the protein molecule, formed by interactions among various side chains (R groups).
- Quaternary structure: This structure is formed when two or more protein molecules form a functional unit.
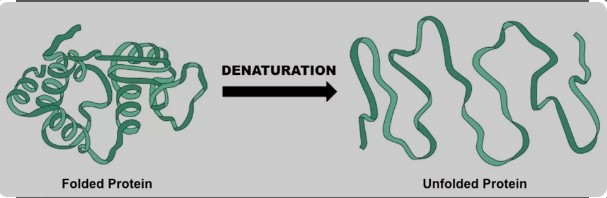
What is Denaturation?
Denaturation involves the disruption and possible destruction of both the secondary and tertiary structures. Denaturation occurs because the bonding interactions responsible for the secondary structure (hydrogen bonds to amides) and tertiary structure (disulfide bridges between cysteines) are disrupted. As a result, the protein unravels and loses its native conformation (shape), which is necessary for its proper function.
Causes of Denaturation
Heat
Elevated temperatures increase the kinetic energy and denature proteins by disrupting the weak forces that hold them. The heat alters the bonds in the enzyme and thus changes its shape. Once the shape is changed, the active site is deformed, preventing the substrate from binding and stopping the enzyme from functioning.
Chemicals
Chemicals such as urea, guanidinium chloride, and others can disrupt the environment around a protein, making it unfold or denature. These chemicals disrupt the hydrogen and disulfide bonds that hold proteins in their 3D shape.
pH Changes
Changes in pH affect the chemistry of amino acid residues and can lead to protein denaturation. The ionizable side chains of the amino acids in the protein can gain or lose protons in response to pH shifts, disrupting the bonds and thus the structure.
Effects on Protein Function
When a protein is denatured, its structure is so altered that it can no longer perform its function. For instance, enzymes, which are proteins that catalyze biological reactions, lose their catalytic activity when denatured because their active sites become deformed.
Denaturation Processes
Heat-induced Denaturation
When proteins are heated, the increased kinetic energy can cause the bonds that hold proteins together to break, leading to a loss of structure and function. This process is commonly observed when cooking eggs; the egg whites turn from clear to white as the proteins are denatured and coagulate.
Chemical-induced Denaturation
Exposure to harsh chemicals like acids or alkalis can also denature proteins. For example, adding vinegar to milk can denature the milk proteins, leading to the formation of curds.
Physical Changes
Mechanical agitation or the introduction of interfaces can also cause denaturation. For example, beating egg whites introduces air and disrupts the protein structure, allowing it to denature and form the stiff peaks of a meringue.
What is Renaturation?
Renaturation Explained
Renaturation is the process by which a denatured protein regains its native structure and function when the denaturing influence is removed. This process is not always complete or possible, as some interactions that stabilize the protein in its native form may not reform, or may reform incorrectly.
Conditions for Renaturation
Successful renaturation depends on the protein itself and the conditions under which the denaturation occurred. Factors such as temperature, pH, and the concentration of salts and other chemicals in the solution can influence whether a protein can renature.
Renaturation Mechanisms
Reversing Heat Effects
Renaturation after heat denaturation is sometimes possible by slowly cooling the protein solution. This gradual process allows the protein molecules to refold back to their functional structures. Key steps typically include:
- Cooling the solution slowly to avoid abrupt changes that might trap the protein in a non-functional state.
- Gradually restoring the environment to one that resembles the protein’s natural conditions, which may include adjusting pH and ionic strength.
Neutralizing Chemicals
For proteins denatured by chemicals, removal or neutralization of the chemicals can lead to renaturation. This is typically achieved by:
- Dialysis to remove small-molecule denaturants.
- Adding protective agents like glycerol, which can help stabilize the correct folding of the protein chains.
Factors Affecting Renaturation
Protein Type
The complexity and size of the protein play critical roles in its ability to renature. Smaller, less complex proteins are generally more likely to renature than larger, multi-domain proteins.
Environmental Conditions
The conditions under which renaturation is attempted significantly influence the success of the process. Important factors include:
- Temperature: Optimal temperatures help proteins refold without aggregating or degrading.
- pH levels: Correct pH levels are crucial for maintaining the right charge on amino acids, facilitating correct folding.
- Ionic strength: The presence of salts can shield electrostatic interactions and help proteins fold correctly.
Time Factor
The time allowed for renaturation can also affect the outcome. Some proteins may require longer periods to successfully refold into their active configurations.
Biological Implications
In Vivo Relevance
In living organisms, proteins may undergo reversible denaturation and renaturation as part of their functional cycle. For example, heat shock proteins help other proteins fold correctly in response to stress conditions, demonstrating the dynamic nature of protein structures in biological systems.
Industrial Applications
Renaturation is particularly important in industrial processes where recombinant proteins are produced in bacterial hosts and need to be refolded for therapeutic uses. Applications include:
- Pharmaceuticals: Producing active forms of protein-based drugs.
- Biotechnology: Enzymes used in industrial processes are often renatured to their active forms after expression in host cells.
Key Challenges
Limitations in Renaturation
Not all proteins can be successfully renatured due to the permanent alterations that might occur during the initial denaturation. The challenges include:
- Protein aggregation: Misfolded proteins tend to aggregate, making renaturation difficult.
- Scrambled disulfide bonds: Incorrectly paired cysteine residues can prevent proper folding.
Research and Innovations
Ongoing research aims to overcome the limitations of protein renaturation. Innovations include:
- Use of chaperone proteins that assist in the folding of other proteins to improve yields of correctly folded proteins.
- Advanced biochemical techniques like high-pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC) and mass spectrometry to analyze and optimize conditions for renaturation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes protein denaturation?
Protein denaturation can be triggered by various factors such as heat, pH changes, and exposure to certain chemicals. These disrupt the weak forces holding the protein’s structure, leading to a loss of its functional conformation.
Can all proteins be renatured?
Not all proteins can be renatured once denatured. The ability to renature depends on the protein’s complexity and the conditions under which denaturation occurred. Simpler proteins have a higher chance of successful renaturation.
How does pH affect protein denaturation and renaturation?
pH levels can significantly influence protein structure. Extreme pH levels lead to denaturation by disrupting ionic bonds within the protein. Adjusting the pH to an optimal level can sometimes help in renaturing the protein.
What are the applications of protein denaturation?
Protein denaturation has applications in food science, where it affects the texture and digestibility of foods, and in research, where it helps in studying protein structures. It is also used in the denaturation of pathogens in vaccine development.
Why is renaturation important in biotechnology?
Renaturation is crucial in biotechnology for the recovery of active proteins from inclusion bodies formed during protein expression in bacteria. It is essential for ensuring that biopharmaceuticals retain their therapeutic efficacy after production.
Conclusion
Denaturation and renaturation of proteins are pivotal concepts that not only enhance our understanding of biological functions but also have extensive applications across various scientific fields. These processes illustrate the delicate balance and complexity inherent in protein structures.
The exploration of these protein transformations continues to evolve, offering promising insights and innovative solutions particularly in medicine and biotechnology. Understanding these processes in depth can pave the way for advancements in drug development and therapeutic interventions, highlighting the integral role of protein structure in the blueprint of life.