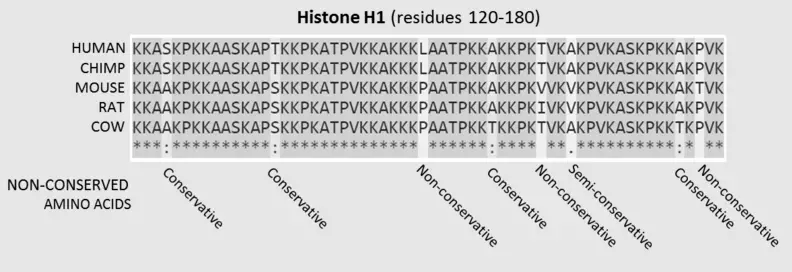
Genetic sequences are fundamental to the study of biology, serving as the blueprints that inform the development and function of living organisms. These sequences are composed of nucleotides that encode the necessary information for life processes. Among the various types of sequences studied, conserved and consensus sequences hold particular importance due to their implications in genetics and evolutionary biology.
Conserved sequences are those that have remained unchanged across different species throughout evolution, indicating their essential roles in biological functions. Consensus sequences, on the other hand, represent the idealized sequence that is most common to a set of similar sequences, reflecting a norm or a standard within a population. These sequences play critical roles in gene regulation and protein function.
The distinction between conserved and consensus sequences is not merely academic but has practical applications in fields ranging from medical research to evolutionary studies. Understanding these differences helps researchers identify crucial regions within genomes, predict molecular function, and trace the evolutionary history of organisms.
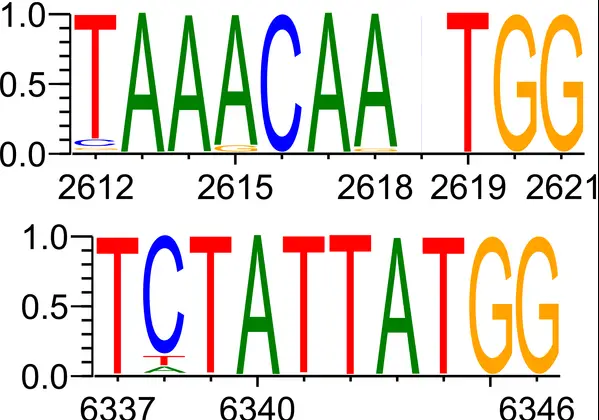
Basic Concepts
Genetic Sequences
Definition and Role
Genetic sequences are the series of nucleotides that make up DNA and RNA, the molecules responsible for storing and transmitting genetic information. Each nucleotide consists of a phosphate group, a sugar molecule (deoxyribose in DNA and ribose in RNA), and a nitrogenous base (adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine in DNA; adenine, uracil, cytosine, guanine in RNA). These sequences dictate everything from physical traits to the synthesis of proteins necessary for survival.
Conserved Sequences
Explanation and Significance
Conserved sequences are segments of DNA that have remained relatively unchanged across different species and through millions of years of evolution. Their preservation suggests that these sequences are crucial for the survival and proper functioning of organisms. Typically, these sequences are involved in critical biological processes, such as protein coding and regulatory functions, which are essential for maintaining life’s complex mechanisms.
Consensus Sequences
Explanation and Significance
Consensus sequences, in contrast, are idealized sequences derived from aligning multiple sequences that share a common function. These sequences represent the most common bases at each position in a given set of similar sequences. They are often used to identify known functional sites, such as binding sites for proteins, which are crucial for regulating gene expression and other cellular processes.
Key Differences
Sequence Composition
Core Differences in Composition
The main difference in the composition of conserved and consensus sequences lies in their derivation and representation. Conserved sequences are actual DNA segments found across different organisms, highlighting evolutionary stability. In contrast, consensus sequences are not found as contiguous sequences in nature; instead, they are theoretical constructs that represent common features of a set of similar sequences.
Biological Functions
Functional Distinctions
The functions of conserved and consensus sequences are distinct yet interconnected. Conserved sequences often encode parts of proteins crucial for basic cellular functions and are thus deeply embedded in the organism’s survival strategy. Consensus sequences, although not directly encoding for proteins, play a key role in the regulation of genes and orchestration of biological processes through their role as binding sites.
Evolutionary Implications
Evolutionary Role and Importance
From an evolutionary perspective, conserved sequences are indicators of essential biological functions that are so fundamental that any significant mutations could be detrimental to the organism’s viability. Consensus sequences, however, offer insights into the regulatory mechanisms that may evolve more rapidly to adapt to environmental changes or new evolutionary pressures.
Detection Methods
Laboratory Techniques
Common Techniques for Identification
Laboratory techniques for detecting conserved and consensus sequences include:
- DNA Sequencing: Determines the exact sequence of bases in a DNA molecule.
- Gel Electrophoresis: Separates DNA fragments based on their size to infer sequence similarities.
- Southern Blotting: Detects specific DNA sequences within a DNA sample by hybridization.
These methods allow scientists to pinpoint the precise location and sequence of these important genetic elements.
Computational Tools
Software and Algorithms Used
In the digital era, computational tools have become indispensable in the study of genetic sequences. Software and algorithms used to identify conserved and consensus sequences include:
- BLAST (Basic Local Alignment Search Tool): Compares gene sequences against a database to find regions of local similarity.
- Clustal Omega: Used for multiple sequence alignment which helps in identifying conserved and consensus sequences.
- MEME Suite: Discovers motifs (consensus sequences) in large datasets of biological sequences.
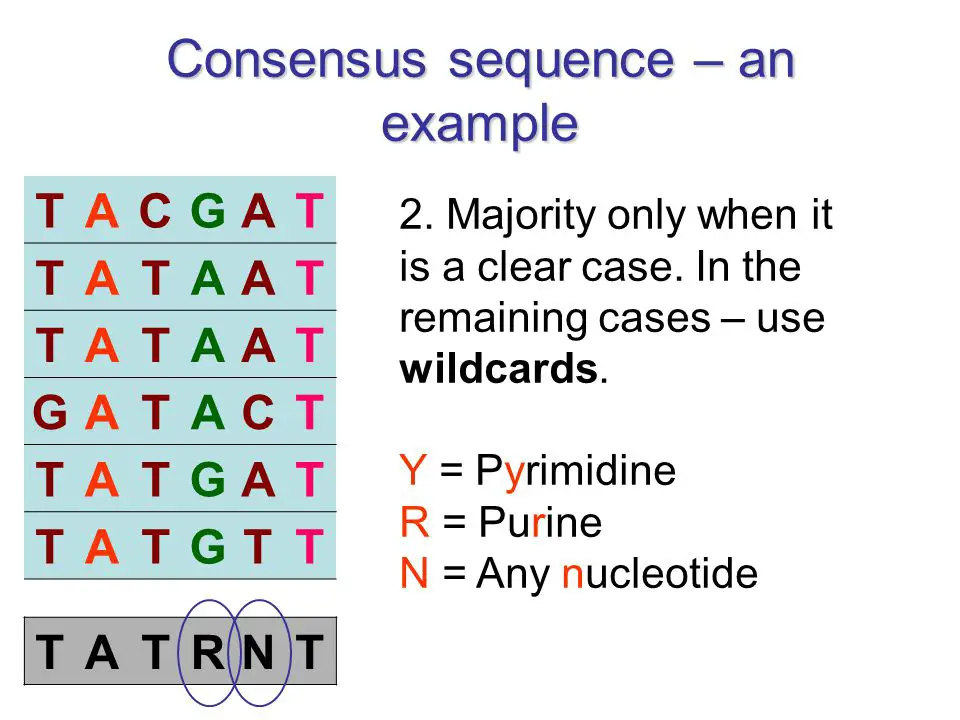
Applications in Research
Medical Research
Role in Disease Understanding and Treatment
Conserved and consensus sequences play pivotal roles in medical research, particularly in the understanding and treatment of diseases. By studying these sequences, scientists can identify genetic markers linked to diseases and develop targeted therapies. For example, conserved sequences in genes associated with hereditary diseases, like cystic fibrosis or sickle cell anemia, help researchers understand the genetic basis of these conditions and guide the development of gene therapy strategies.
Consensus sequences are crucial in designing synthetic biology tools, such as CRISPR-Cas9, which relies on a guide RNA that must bind to a specific DNA sequence in the genome. By targeting consensus sequences that control gene expression, researchers can potentially turn off the genes responsible for disease or modify them in beneficial ways.
Evolutionary Biology
Insights into Species Evolution
In evolutionary biology, conserved and consensus sequences offer invaluable insights into the evolutionary trajectories of species. Conserved sequences reveal genetic features that are crucial for survival and have been preserved through natural selection. Studying these sequences across different species helps scientists trace the lineage and evolutionary history of organisms, providing evidence of common ancestry and adaptive evolution.
Consensus sequences are used to compare genetic diversity within and between species populations. By examining these sequences, researchers can infer evolutionary pressures, migration patterns, and speciation events, contributing to a deeper understanding of biodiversity and ecosystem dynamics.
Case Studies
Conserved Sequence Case
Detailed Example and Analysis
A well-documented case of a conserved sequence involves the Homeobox (HOX) genes, which play a crucial role in determining the body plan of an organism during embryonic development. These genes are remarkably conserved across a wide range of species, from fruit flies to humans, indicating their critical role in developmental processes. Research on these genes has helped elucidate how complex body structures evolve and maintain themselves through evolutionary history.
Consensus Sequence Case
Detailed Example and Analysis
An example of a consensus sequence can be seen in the TATA box, a component of the promoter region of genes in eukaryotic cells. The TATA box has a consensus sequence (TATAAA), which is crucial for the initiation of transcription. Studies on variations of this sequence have shown how slight changes can affect gene expression levels and impact cellular function, offering insights into gene regulation and its evolutionary adaptations.
Challenges and Limitations
Common Challenges in Studying These Sequences
Studying conserved and consensus sequences presents several challenges:
- High Complexity: The biological functions and interactions of these sequences can be complex, involving multiple genetic pathways and environmental factors.
- Technological Limitations: Although sequencing technology has advanced, accurately identifying and characterizing these sequences across multiple species or within large populations can still be technically challenging and costly.
Limitations in Current Research Methodologies
Current methodologies for studying these sequences also face limitations:
- Incomplete Genomic Data: Despite the vast amounts of genomic data available, there are still numerous species and genetic variations that are poorly understood or not yet discovered.
- Bias in Data: Research often focuses on model organisms, which may not always represent other species or genetic contexts accurately.
Future Directions
Emerging Trends and Potential Research Areas
The future of research in conserved and consensus sequences is promising and includes several emerging trends:
- Enhanced Computational Models: Improved algorithms and computational models that can predict the functional implications of sequence variations more accurately.
- Integration of Genomic with Phenotypic Data: Combining genomic data with real-world phenotypic expressions to better understand the functional outcomes of conserved and consensus sequences.
- Personalized Medicine: Using knowledge of conserved and consensus sequences to tailor medical treatments to individual genetic profiles, potentially revolutionizing healthcare.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are conserved sequences?
Conserved sequences are stretches of DNA which are similar or identical across different species. Their conservation suggests a crucial role in fundamental biological processes, often being involved in crucial functions like DNA binding and protein interactions.
What are consensus sequences?
Consensus sequences are synthesized from a set of similar sequences and represent the most common recurring pattern or sequence among them. These sequences are key to understanding how genetic expression is controlled and how it varies among populations.
How are conserved sequences identified?
Conserved sequences are identified using comparative genomics, where DNA sequences of different organisms are compared. Areas that show high similarity are marked as conserved, indicating essential functions preserved through evolutionary time.
Why are consensus sequences important?
Consensus sequences are important because they help predict the binding sites of DNA-binding proteins, such as transcription factors. By understanding these sites, researchers can infer regulatory mechanisms controlling gene expression.
How do conserved and consensus sequences impact evolution?
Conserved sequences impact evolution by maintaining essential biological functions across different species, suggesting their importance in survival and adaptation. Consensus sequences offer insights into the variability and regulatory mechanisms within populations, influencing evolutionary trajectories.
Conclusion
The study of conserved and consensus sequences bridges the intricate relationship between genetic makeup and functional output across various life forms. By examining these sequences, scientists unravel the complexities of genetic regulation and evolutionary conservation. These insights not only enhance our understanding of biological diversity and coherence but also pave the way for innovations in medical and genetic research.
Exploring these sequences offers a window into the past evolutionary events and a roadmap for future genetic discoveries. As research progresses, the importance of distinguishing between conserved and consensus sequences will undoubtedly grow, underscoring their significance in both basic and applied biological sciences.