Chemical reactions are fundamental to numerous industrial processes, with chlorination and sulfonation being two pivotal methods widely used across various sectors. These processes are essential for the synthesis of many chemical compounds, affecting everything from municipal water supplies to pharmaceuticals. By altering the molecular structure of substances, these reactions help in achieving desired properties and functionalities in the end products.
Chlorination involves adding chlorine to a compound, typically to disinfect or to produce chemicals for industrial use. On the other hand, sulfonation involves adding a sulfonate group to an organic compound, enhancing its solubility and reactivity. These chemical transformations are crucial for creating a wide range of products, from household cleaners to advanced medicines.
Both chlorination and sulfonation are employed to modify the chemical and physical properties of substances to suit specific needs. They play crucial roles in improving product performance, stability, and usability, influencing production strategies in industries such as water treatment, textiles, and pharmaceuticals. Understanding their differences and applications helps in optimizing their use in various industrial contexts.
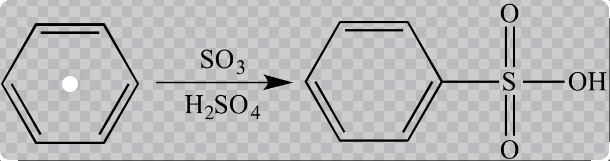
Chlorination Explained
Definition and Basics
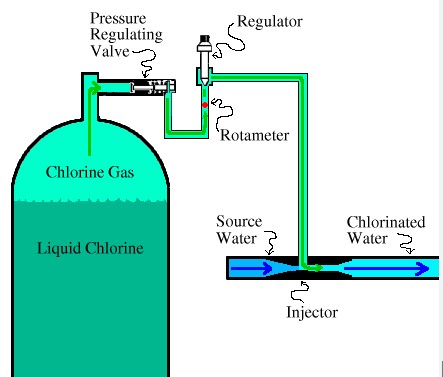
Chlorination is a chemical process where chlorine or chlorine compounds are added to water or other substances. This addition aims to achieve disinfection, bleaching, and chemical reactions that modify the properties of the original material. Chlorine, a potent oxidizer, interacts with organic material within the water, leading to microbial death or transformation of materials.
Common Uses
The most recognized use of chlorination is in water treatment. By adding chlorine to drinking water, swimming pools, and wastewater, harmful organisms such as bacteria, viruses, and protozoa are effectively killed, making the water safe for human use. Chlorination is also employed in the production of plastics, sanitation of public facilities, and in the paper industry for bleaching pulp.
Chemical Process
When chlorine is added to water, it reacts to form hypochlorous acid (HOCl) and hypochlorite ions (OCl^-). These compounds are highly effective in penetrating and destroying the cell walls of bacteria and other pathogens, ensuring the water becomes safe for consumption or use.
Types of Chlorination
Water Treatment
In water treatment, chlorination is crucial for both disinfection and oxidation. It helps remove odors, control taste, and eliminate slime bacteria, molds, and algae. The precise dosage and monitoring are essential to balance effectiveness with safety, as too much chlorine can be harmful.
Organic Synthesis
Chlorination is extensively used in organic chemistry to synthesize chlorinated compounds. This includes the production of solvents, agricultural chemicals, and pharmaceuticals. The reaction involves substituting one or more hydrogen atoms in a hydrocarbon with chlorine, under controlled conditions.
Benefits of Chlorination
Disinfection Efficacy
The primary benefit of chlorination is its ability to effectively disinfect water, making it free from harmful microorganisms. This quality is essential for public health, particularly in preventing diseases such as cholera, typhoid, and dysentery.
Cost-Effectiveness
Chlorination is a cost-effective method of water disinfection compared to other treatments like UV or ozone. The technology is simple, the chemicals are inexpensive, and the process does not require sophisticated equipment.
Sulfonation Explored
Definition and Principles
Sulfonation is the chemical process of introducing a sulfonyl group into an organic compound, making the molecule more soluble in water. This reaction is crucial for enhancing the reactivity of hydrophobic compounds and making them more amenable to further chemical reactions.
Industrial Significance
In industries, sulfonation is key to producing surfactants for detergents, dyes for textiles, and drugs in pharmaceuticals. The ability to make substances more reactive and soluble underpins many manufacturing processes, leading to high-quality products with consistent performance.
Chemical Mechanism
Sulfonation typically involves the reaction of sulfuric acid or its derivatives with an organic compound. The process forms a strong sulfonic acid group attached to the aromatic ring, dramatically altering the compound’s chemical properties.
Sulfonation Techniques
Direct Sulfonation
Direct sulfonation involves adding sulfur trioxide to an organic compound, usually in the presence of a catalyst or at elevated temperatures. This method is straightforward and commonly used for bulk chemicals.
Indirect Sulfonation
Indirect sulfonation may use chlorosulfonic acid or sulfuric acid as the sulfonating agent. This technique allows for more control over the reaction and is preferred for more delicate or complex molecules.
Advantages of Sulfonation
Product Versatility
Sulfonation increases the versatility of products. The process can modify fats, oils, and other hydrophobic compounds to become water-soluble, opening up uses in areas like detergents and personal care products.
Application in Detergents
The sulfonated products are key ingredients in detergents. They help the detergent mix better with water, allowing it to remove dirt and oils more effectively from clothing and surfaces. This characteristic is essential for the cleaning industry, ensuring products are effective even in hard water conditions.
Comparison of Processes
Chlorination vs. Sulfonation
While both chlorination and sulfonation are essential chemical processes in various industries, they serve different purposes and operate under different chemical principles. Chlorination primarily aims at disinfection and oxidation, crucial for water treatment and ensuring microbial safety. In contrast, sulfonation increases the solubility and reactivity of organic compounds, which is vital in industries like pharmaceuticals and detergents.
Key Chemical Differences
Chlorination involves the addition of chlorine, leading to the formation of hypochlorous acid and other byproducts that kill bacteria and viruses. Sulfonation, however, introduces a sulfonate group to an organic molecule, enhancing its affinity for water and its overall stability in chemical reactions.
Environmental Impact
- Chlorination: While effective, chlorination can create byproducts like trihalomethanes (THMs) and haloacetic acids (HAAs), which have been linked to health risks such as cancer.
- Sulfonation: Sulfonation uses strong acids and can result in acidic waste that needs careful handling to prevent environmental damage.
Process Efficiency
Reaction Conditions
Chlorination reactions typically require simple conditions and are not heavily dependent on catalysts. Sulfonation, however, often needs more stringent control over temperature and the presence of catalysts to guide the reaction pathway efficiently.
Yield Comparisons
Chlorination yields can vary widely based on the type of organic compound being treated and the specific conditions applied. Sulfonation tends to have higher yields due to the specificity of the reaction, especially in controlled industrial environments.
Safety and Risks
Handling and Storage
Both chlorine and sulfur trioxide (used in sulfonation) are hazardous materials requiring strict safety protocols during handling and storage. Chlorine gas, in particular, is extremely toxic and can be lethal in high concentrations.
Hazard Mitigation
Safety measures for both processes include proper ventilation, use of protective equipment, and rigorous training for all personnel involved in the chemical handling and processing.
Applications in Industry
Chlorination in Water Treatment
Chlorination remains the backbone of water disinfection strategies worldwide. Its ability to efficiently neutralize pathogenic microbes makes it indispensable for public health.
Sulfonation in Pharmaceutical
In the pharmaceutical industry, sulfonation is used to improve the solubility and efficacy of certain drugs, making them more effective in treatment applications.
Sector-Specific Uses
Plastics and Polymers
- Chlorination: Used in the modification of polyethylene and PVC to enhance properties like flexibility, temperature resistance, and durability.
- Sulfonation: Plays a role in enhancing the qualities of styrene polymers, improving their use in various applications, including automotive parts and household goods.
Agricultural Chemicals
Chlorination is used to produce effective pesticides and soil treatments that protect crops from pests and diseases. Sulfonation contributes to the production of bioactive compounds that improve the effectiveness of agrochemicals.
Future Perspectives
Technological Advancements
Emerging technologies are expected to enhance the efficiency and safety of both chlorination and sulfonation processes. Innovations in catalyst development and reaction control systems are likely to improve yields and reduce unwanted byproducts.
Sustainable Practices
The future of industrial chemical processes lies in sustainability. Efforts are increasing to minimize environmental impacts through green chemistry principles, such as reducing the use of hazardous substances and optimizing energy use in production cycles.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Chlorination?
Chlorination is a chemical process where chlorine is added to water or organic compounds, primarily for disinfection and sterilization purposes. It effectively kills bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens, making it essential for ensuring safe drinking water and in the manufacture of various chemicals.
How does Sulfonation work?
Sulfonation is a chemical reaction where a sulfonic acid group is introduced into a molecule to increase its solubility in water and its overall reactivity. This process is widely used in the production of detergents, dyes, and pharmaceuticals, where enhanced solubility and chemical stability are required.
Why compare Chlorination and Sulfonation?
Comparing chlorination and sulfonation is essential to understand their specific uses and benefits in different industrial applications. While both are used to alter chemical properties, their distinct mechanisms and outcomes serve unique purposes across various sectors, from sanitation to synthetic chemistry.
What are the environmental impacts of these processes?
Both chlorination and sulfonation can have significant environmental impacts. Chlorination by-products may include harmful compounds if not managed correctly, while sulfonation can lead to issues with waste management and toxicity. Understanding and mitigating these impacts is crucial for sustainable industrial practices.
Conclusion
Chlorination and sulfonation are critical chemical processes with distinct roles and benefits in various industrial sectors. Their effective use not only enhances the functionality and safety of products but also drives innovation in chemical synthesis and application. By exploring their differences and applications, industries can better utilize these reactions to meet specific needs and improve product performance.
Future research and technological advancements will likely focus on making these processes more efficient and environmentally friendly, further broadening their applications and minimizing their ecological footprint. Emphasizing sustainable practices will be key in maximizing the benefits while mitigating potential environmental and health risks associated with these chemical processes.