The functioning of our nervous system is a marvel of biological engineering, enabling everything from basic reflexes to complex thought processes. At the heart of this system’s efficiency lies the concept of refractory periods, which play a crucial role in how nerve impulses are generated and transmitted. These periods ensure that neurons communicate effectively, without the signals overlapping or merging into a chaotic noise.
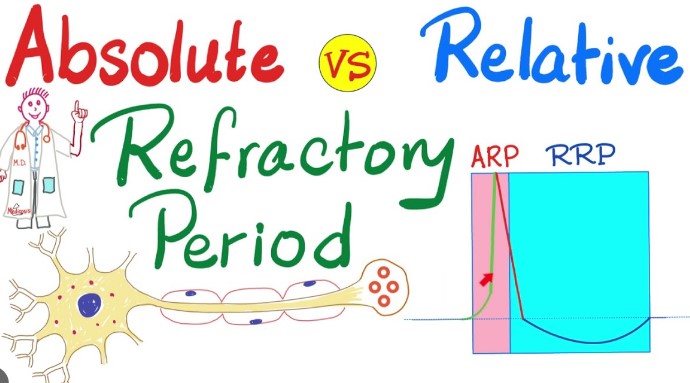
The difference between absolute and relative refractory periods is foundational to understanding how neuronal communication is regulated. The absolute refractory period is a phase during which a neuron is completely incapable of triggering another action potential, regardless of the strength of the incoming signal. On the other hand, during the relative refractory period, a neuron can be stimulated to initiate another action potential, but only by a much stronger signal than usual. This subtle but critical difference ensures the orderly propagation of nerve impulses.
Focusing on these refractory periods illuminates how neurons maintain the precision of their signaling mechanisms. By implementing a forced downtime (absolute) and a phase of heightened threshold (relative), the nervous system prevents the overlap of signals, thus safeguarding the clarity and directionality of neural communication. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for grasping the broader principles of neurophysiology and the intricate dance of electrical and chemical signals that underpin our every thought and action.
Basic Concepts
Nerve Impulses
How Nerve Impulses Are Generated and Transmitted
Nerve impulses, the electrical signals that travel along the neurons, are the cornerstone of communication within the nervous system. Their generation and transmission are intricate processes, crucial for every action we undertake, from the simplest reflex to complex thought.
- Initiation: It all begins at the neuron’s dendrites, where specific stimuli (like heat, light, or pressure) are converted into electrical signals.
- Action Potential: When the stimulus is strong enough, it triggers an action potential. This is an all-or-nothing event that temporarily reverses the charge across the neuron’s membrane, creating an electrical pulse.
- Propagation: This pulse travels down the axon, a long, slender projection of the neuron, toward the nerve endings.
- Transmission: At the axon terminals, the electrical signal prompts the release of neurotransmitters, chemicals that bridge the gap (synapse) between neurons, carrying the signal to the next neuron or muscle cell.
The ability of neurons to transmit these signals rapidly and accurately is fundamental to our survival and functioning.
Refractory Periods
Definition and Role
The refractory period is a brief time span following an action potential during which a neuron is unable to fire another action potential or its ability to do so is significantly reduced. There are two types: absolute and relative.
- The absolute refractory period ensures that each action potential is a distinct event, preventing the signals from merging into one continuous signal. This is crucial for the proper decoding of neural messages.
- The relative refractory period allows a neuron to fire again but requires a stronger stimulus. This modulation ensures that only the strongest signals, those most necessary for attention, are given priority in neural communication.
These periods play a pivotal role in maintaining the unidirectional flow of nerve impulses and in the temporal coding of information by the nervous system.
Absolute Refractory Period
Definition
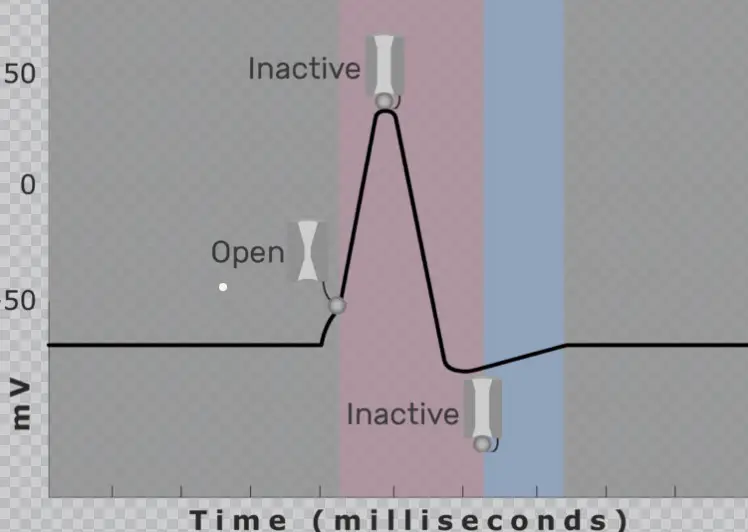
The absolute refractory period is the time during which a neuron is completely incapable of initiating another action potential. This period ensures that each nerve impulse is a separate, distinct event, allowing for the clear and orderly transmission of signals.
Mechanism
The mechanism behind this period involves the ion channels in the neuron’s membrane. During an action potential, sodium channels open first, allowing Na+ ions to enter the neuron, depolarizing the membrane. Shortly after, these channels inactivate and cannot be reopened immediately, regardless of the incoming stimuli. Concurrently, potassium channels open to repolarize the cell, further ensuring that the neuron cannot immediately fire again.
Significance
The absolute refractory period is vital for several reasons:
- It prevents the backflow of nerve impulses, ensuring signals move in only one direction—from the dendrites to the axon terminals.
- It sets a limit on the frequency of nerve impulses, allowing the neuron time to reset before firing again. This limitation is essential for the temporal resolution of neuronal communication.
Relative Refractory Period
Definition
Following the absolute refractory period is the relative refractory period, a phase during which the neuron can initiate another action potential, but only if the incoming stimulus is significantly stronger than usual. This period allows for graded responses based on the strength of the stimulus.
Mechanism
During the relative refractory period, the membrane potential is closer to the resting level, but not completely there. Some sodium channels have reset, but the potassium channels are still active, making the membrane hyperpolarized. A much stronger than normal stimulus is required to depolarize the membrane enough to reach the threshold for an action potential.
Significance
The relative refractory period plays a crucial role in the modulation of nerve impulse transmission:
- It enables neuronal adaptation to ongoing stimulation, allowing the nervous system to prioritize more significant or urgent signals.
- It contributes to the coding of stimulus intensity in the frequency of action potentials generated. Stronger stimuli can overcome the relative refractory period more easily, leading to a higher rate of nerve firing.
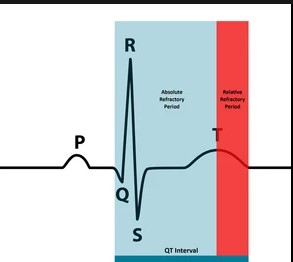
Key Differences
Trigger Conditions
The initiation of the absolute and relative refractory periods is closely linked to the cycle of an action potential. However, what triggers each of these periods to start varies significantly.
- Absolute Refractory Period: This period begins immediately after an action potential is triggered. The key factor initiating this phase is the opening of sodium channels and the subsequent influx of Na+ ions into the neuron, leading to depolarization.
- Relative Refractory Period: It starts right after the absolute refractory period, when the sodium channels start to reset to their original state, but the neuron is still not at its resting potential due to ongoing potassium outflow. This period is initiated by the neuron’s internal state being closer to the resting potential but still hyperpolarized.
Duration
The duration of these periods is a critical aspect of their function and has a profound impact on neuronal communication.
- Absolute Refractory Period: Lasts approximately 1-2 milliseconds. During this time, no matter how strong a stimulus is applied, another action potential cannot be generated.
- Relative Refractory Period: This can last anywhere from a few milliseconds to tens of milliseconds, depending on the neuron type and the extent of hyperpolarization. During this phase, a stronger-than-normal stimulus can trigger another action potential.
Physiological Implications
The absolute and relative refractory periods play distinct but complementary roles in the transmission of nerve impulses, with significant physiological implications.
- Absolute Refractory Period: Ensures the unidirectional flow of nerve impulses and sets a limit on the frequency of action potentials, thus defining the maximum speed of neural communication.
- Relative Refractory Period: Allows the nervous system to encode information regarding stimulus intensity into the rate of action potentials. This period enables the neuron to respond to new, significantly stronger stimuli, facilitating graded responses to varying environmental inputs.
Clinical Relevance
Impact on Neurological Disorders
Abnormalities in the refractory periods can have profound effects on the nervous system’s ability to process and transmit information accurately, potentially leading to neurological disorders.
- Epilepsy: This condition can be linked to shortened refractory periods, where neurons are capable of firing too frequently, leading to seizures.
- Neuropathic Pain: Altered refractory periods may also contribute to the development of chronic pain conditions, where neurons fire excessively in response to non-painful stimuli.
Understanding these refractory periods’ dynamics offers insights into the pathophysiology of such conditions, highlighting the importance of their proper regulation for neural function.
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Uses
Knowledge of refractory periods not only aids in diagnosing neurological conditions but also opens avenues for therapeutic interventions.
- Diagnostic Tools: Electrophysiological tests that measure the excitability and responsiveness of neurons can help diagnose conditions like epilepsy, providing information on how quickly neurons recover after firing and how susceptible they are to repetitive stimulation.
- Therapeutic Approaches: Treatments that modulate the length of refractory periods, such as certain medications or neuromodulation techniques, can be used to restore normal neuronal firing rates. For example, anticonvulsant drugs used in treating epilepsy often work by prolonging the absolute refractory period, thus reducing the likelihood of seizure-inducing neuronal hyperactivity.
The refractory periods’ role in maintaining the integrity of neural communication makes them a focal point in understanding and treating various neurological disorders. By modulating these periods, it’s possible to influence the overall excitability of the nervous system, offering potential pathways for intervention in conditions characterized by dysregulated neural activity.
Frequently Asked Questions
What triggers the absolute refractory period?
The absolute refractory period is triggered immediately after a neuron fires an action potential. It is a direct consequence of the inactivation of sodium channels, which temporarily prevents the neuron from initiating another action potential, ensuring that each signal is distinct and directional.
How long does the relative refractory period last?
The duration of the relative refractory period can vary significantly but generally follows the absolute refractory period and lasts until the neuron returns to its resting state. This period can extend from a few milliseconds to several milliseconds, depending on the type of neuron and the context of neural activity.
Why are refractory periods important in neuronal communication?
Refractory periods are essential for maintaining the unidirectional flow of nerve impulses and preventing the chaotic overlap of signals. They ensure that neurons can reset and prepare for the next signal, contributing to the precise timing and orderliness of communication within the nervous system.
Can refractory periods influence the speed of neural transmission?
Yes, refractory periods directly influence the speed at which neurons can transmit signals. The absolute refractory period, in particular, sets a hard limit on the maximum firing rate of a neuron, thus indirectly dictating the speed of neural transmission across networks of neurons.
Conclusion
The difference between absolute and relative refractory periods is more than a mere detail in the study of neurophysiology; it is a fundamental aspect that ensures the efficient and precise operation of our nervous system. These periods enable neurons to communicate without interference, maintaining the fidelity of signal transmission across the vast and intricate networks that underlie our thoughts, behaviors, and sensations.
Understanding these differences not only deepens our appreciation for the complexity and efficiency of neuronal communication but also highlights the delicate balance maintained within our nervous system to support all aspects of human life. Through the lens of refractory periods, we gain insight into the elegant mechanisms that allow our brains to function with remarkable precision and reliability.