Metabolic diversity among microorganisms is a cornerstone of ecological systems, enabling the recycling of nutrients and the flow of energy through different environments. Among the vast array of metabolic strategies, chemoorganotrophs and chemolithotrophs play pivotal roles, albeit through markedly different mechanisms. Their unique methods of harnessing energy underline the complexity of life and its adaptability to various ecological niches.
Chemoorganotrophs derive their energy from organic compounds, breaking these molecules down to fuel their metabolic processes. In contrast, chemolithotrophs rely on inorganic substances, utilizing often seemingly inhospitable substances to generate energy. This fundamental difference highlights the adaptability and diversity of microbial life, contributing to the balance of ecosystems by cycling organic and inorganic matter.
Understanding these two groups of organisms reveals the intricate dance of life at the microbial level. Chemoorganotrophs and chemolithotrophs not only exemplify the vast metabolic capabilities found in microorganisms but also play critical roles in maintaining the health of our planet. Through their activities, they affect everything from soil fertility and water quality to atmospheric composition, demonstrating the interconnectedness of all life forms.
Energy Sources in Microorganisms: An Overview
Microorganisms exhibit a remarkable ability to adapt to diverse environments by exploiting various energy sources. This adaptability is rooted in their metabolic diversity, allowing them to sustain life in almost every niche on Earth. Understanding these energy sources is crucial for appreciating the ecological roles of different microorganisms, including chemoorganotrophs and chemolithotrophs.
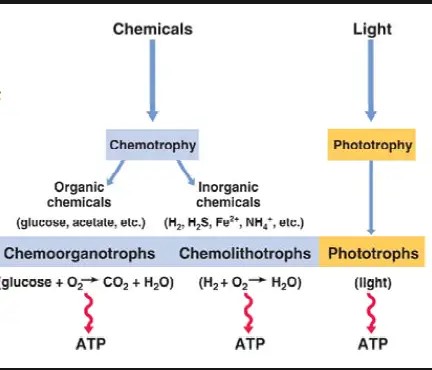
Organic vs. Inorganic Energy Sources
The distinction between organic and inorganic energy sources is foundational to microbial metabolism. Organic sources include compounds like sugars, fats, and proteins, which contain carbon-hydrogen bonds. In contrast, inorganic sources encompass minerals and other non-carbon-based substances. This fundamental difference shapes the metabolic pathways microorganisms use to harness energy, ultimately influencing their roles within ecosystems.
Chemoorganotrophs
Definition and Energy Extraction
Chemoorganotrophs are microorganisms that derive their energy from the oxidation of organic molecules. Unlike plants, which obtain energy through photosynthesis, chemoorganotrophs rely on organic compounds as their energy source, making them vital players in the decomposition of organic material.
Key Characteristics
Types of Organic Molecules Used
Chemoorganotrophs utilize a wide range of organic molecules, including:
- Sugars: Glucose and fructose are common examples.
- Fats: These are broken down into fatty acids and glycerol.
- Proteins: Amino acids from protein degradation serve as energy sources.
Environments Where They Thrive
These microorganisms are found in virtually all habitats, from soil and water to extreme environments like hot springs and the deep sea, where organic matter is present.
Role in Ecosystems
Decomposition and Nutrient Cycling
Chemoorganotrophs play a crucial role in breaking down dead organic matter, recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem. This process is essential for the health and sustainability of ecosystems.
Contribution to the Carbon Cycle
By decomposing organic material, chemoorganotrophs release carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere, a vital step in the carbon cycle. This activity ensures that carbon is not locked away but is available for use by other organisms, including plants during photosynthesis.
Chemolithotrophs
Definition and Energy Acquisition
Chemolithotrophs differ from chemoorganotrophs in their energy source. They obtain energy by oxidizing inorganic substances, such as ammonia or hydrogen sulfide. This ability allows them to inhabit environments where organic compounds are scarce.
Key Characteristics
Types of Inorganic Substrates Utilized
Common inorganic substrates include:
- Hydrogen sulfide (H2S)
- Ammonia (NH3)
- Iron (Fe2+)
Environments Where They Are Predominant
Chemolithotrophs are often found in extreme environments, such as hydrothermal vents and sulfur springs, where inorganic energy sources are abundant.
Role in Ecosystems
Importance in Geochemical Cycles
These organisms are instrumental in driving geochemical cycles, transforming inorganic compounds into forms that can be used by other life forms.
Influence on Primary Productivity
In some ecosystems, chemolithotrophs contribute to primary productivity, especially in environments where light for photosynthesis is limited or absent.
Metabolic Pathways
Chemoorganotrophic Pathways
Glycolysis and TCA Cycle Overview
Glycolysis and the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle are central to the energy extraction process in chemoorganotrophs. These pathways break down organic molecules to produce ATP, the energy currency of the cell.
Chemolithotrophic Pathways
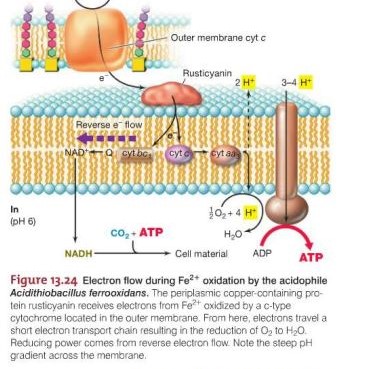
Calvin Cycle and Reverse Electron Flow
Chemolithotrophs often utilize the Calvin cycle for carbon fixation but rely on reverse electron flow for energy conservation, a process unique to their metabolic pathways.
Differences in Energy Conservation Mechanisms
The energy conservation mechanisms of chemoorganotrophs and chemolithotrophs highlight the diversity of microbial metabolic strategies. While chemoorganotrophs primarily generate ATP through substrate-level phosphorylation and oxidative phosphorylation, chemolithotrophs have evolved specialized mechanisms, such as reverse electron flow, to harness energy from inorganic compounds.
Ecological Impacts
Chemoorganotrophs’ Impact
Role in Organic Matter Decomposition
Chemoorganotrophs are crucial in breaking down organic materials, turning complex molecules into simpler compounds that can be reused by other organisms. This process:
- Enhances soil fertility by recycling nutrients.
- Reduces the accumulation of organic waste in the environment.
Chemolithotrophs’ Impact
Contribution to Biogeochemical Transformations
Chemolithotrophs influence key biogeochemical cycles, including the nitrogen and sulfur cycles, by:
- Transforming inorganic compounds into forms accessible to other organisms.
- Maintaining the balance of essential elements in ecosystems.
Industrial and Environmental Applications
Chemoorganotrophs in Biotechnology
Waste Degradation and Bioremediation
Chemoorganotrophs are harnessed for:
- Breaking down pollutants in water and soil, reducing environmental hazards.
- Converting waste into biogas, a renewable energy source.
Chemolithotrophs in Industry
Bioleaching and Bioremediation of Inorganic Pollutants
Applications of chemolithotrophs include:
- Extracting metals from ores through bioleaching, offering an eco-friendly alternative to traditional mining.
- Removing harmful inorganic compounds from environments, aiding in the cleanup of industrial waste sites.
Adaptations and Evolution
Survival Strategies
Adaptations to Extreme Environments
Microorganisms exhibit remarkable adaptations, such as:
- Thermophiles: Thriving in hot environments by stabilizing their proteins and DNA.
- Acidophiles: Surviving in acidic conditions by maintaining internal pH balance.
Evolutionary Perspectives
Significance in the Evolution of Life on Earth
The metabolic diversity of microorganisms like chemoorganotrophs and chemolithotrophs highlights their:
- Contribution to the oxygenation of the Earth’s atmosphere.
- Role in the early stages of life, providing evidence of the adaptability and resilience of life.
Challenges and Future Directions
Research Challenges
Studying Extremophiles and Unculturable Species
Key challenges in microbial research include:
- Developing techniques to culture and study extremophiles in laboratory conditions.
- Utilizing genomic and metagenomic approaches to understand unculturable microorganisms.
Potential for Biotechnological Applications
Sustainable Solutions for Environmental Challenges
The future of microbial application lies in:
- Enhancing the efficiency of microbial processes for waste degradation and energy production.
- Exploring novel microorganisms for bioremediation of emerging pollutants.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are chemoorganotrophs?
Chemoorganotrophs are microorganisms that obtain their energy by oxidizing organic compounds, including sugars, fats, and proteins. They are pivotal in decomposing organic matter, recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem. This process is essential for the breakdown of dead material and the continuation of life cycles within various habitats.
How do chemolithotrophs generate energy?
Chemolithotrophs generate energy by oxidizing inorganic substances, such as hydrogen sulfide, ammonia, or iron. This unique metabolic pathway allows them to thrive in environments where organic compounds are scarce, such as deep-sea vents, hot springs, and other extreme habitats. Their ability to convert inorganic compounds into usable energy forms the basis of some ecosystems, supporting a range of life forms.
Why are these metabolic processes important?
The metabolic processes of chemoorganotrophs and chemolithotrophs are crucial for the cycling of nutrients and energy through ecosystems. They contribute to the decomposition of organic matter, the detoxification of harmful substances, and the production of oxygen through the oxidation of inorganic compounds. Understanding these processes is key to appreciating the complexity and resilience of life on Earth.
Can these organisms help in bioremediation?
Yes, both chemoorganotrophs and chemolithotrophs can play significant roles in bioremediation efforts. By exploiting their natural metabolic processes, scientists and environmentalists can harness these microorganisms to break down pollutants, such as oil spills and toxic metals, making them invaluable tools in restoring contaminated environments.
Conclusion
The exploration of chemoorganotrophs and chemolithotrophs offers a window into the remarkable adaptability and diversity of life. These microorganisms underscore the complexity of biological systems and their capacity to exploit a vast array of energy sources. Through their roles in energy conversion and ecosystem maintenance, they highlight the interconnectedness of life and the environment.
Their study not only enriches our understanding of microbial life but also opens avenues for biotechnological applications, including environmental cleanup and sustainable energy solutions. The ongoing research and application of these organisms’ unique metabolic capabilities promise to contribute significantly to our ecological and technological advancement, showcasing the enduring importance of microbial life in shaping our world.

