Enzymes are fundamental to the myriad of biochemical processes that sustain life. Among the many enzymes operating within living organisms, catalase and peroxidase stand out due to their crucial roles in managing reactive oxygen species, protecting cells from oxidative damage. Each enzyme, while similar in function, has distinct characteristics and applications that make them vital to both health and industry.
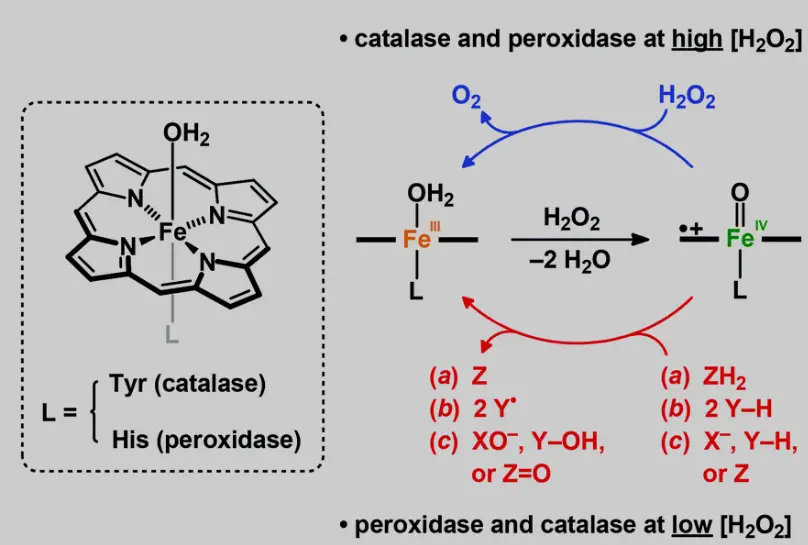
Catalase and peroxidase are enzymes that catalyze the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide, a common byproduct of cellular metabolism that can be harmful in high concentrations. Catalase converts hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen gas rapidly, while peroxidase typically uses it to oxidize other molecules, often in the presence of a reducing agent like iodide.
These enzymes not only protect cellular components from oxidative damage but also have significant applications in various industries ranging from medicine to environmental management. Their ability to handle reactive molecules makes them invaluable in scientific and medical fields, leading to advancements in treatments and technologies that leverage their unique properties.
Enzyme Basics
Definition and Functions
Enzymes are proteins that act as catalysts within living organisms, speeding up chemical reactions without being consumed in the process. Every enzyme is specific to a particular reaction or type of reaction, playing a critical role in facilitating metabolic pathways. They help convert substrates—the molecules at the beginning of a process—into different molecules known as products. Enzymes are vital for processes like digestion, energy production, and other metabolic functions within the body.
Role in Cellular Metabolism
Enzymes are indispensable in cellular metabolism, ensuring that essential reactions occur at speeds conducive to life. They enable the body to perform complex chemical transformations at relatively low temperatures and with incredible speed and precision. For example, they are key in synthesizing molecules, generating energy, and breaking down waste products. In the absence of enzymes, these reactions would occur too slowly to sustain life.
Catalase Explained
Structure and Properties
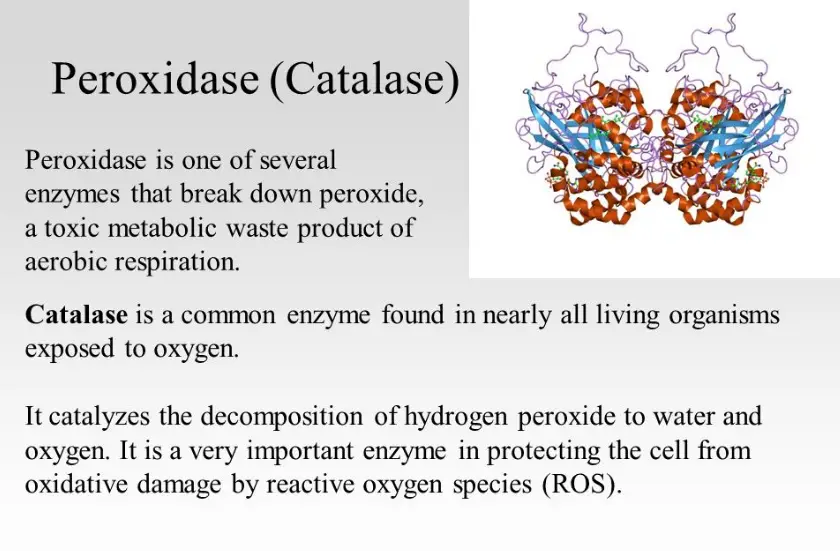
Catalase is a common enzyme found in nearly all living organisms that are exposed to oxygen, where it catalyzes the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen. It is a tetramer of four polypeptide chains, each over 500 amino acids long. The active site, containing a heme group bound to iron, is where the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide occurs.
Biological Functions
Catalase has a crucial protective function in cells, preventing damage by decomposing hydrogen peroxide, a toxic byproduct of many metabolic reactions. In human beings, catalase is present in nearly every organ, with particularly high concentrations found in the liver, kidneys, and erythrocytes (red blood cells). These locations highlight the enzyme’s vital role in protecting cells from oxidative stress.
Sources in Nature
Catalase is ubiquitous in nature, found in various organisms including mammals, birds, plants, and fungi. It serves as a key defense mechanism against oxidative stress, which can damage cells and lead to various diseases.
Peroxidase Overview
Structure and Properties
Peroxidases are a large group of enzymes that typically catalyze reactions involving hydrogen peroxide as a substrate to oxidize a variety of compounds, including toxic substances and phenols. These enzymes are found across different species, including plants, animals, and bacteria. Their structure allows them to bind to substrates through a heme group similar to that of hemoglobin.
Biological Roles
In biological systems, peroxidases play a pivotal role in processes such as growth regulation, stress response, and pathogen defense. For example, in plants, peroxidases are involved in the growth and hardening of the cell wall, whereas in humans, they are essential for immune responses through the oxidation of pathogens.
Common Sources
Peroxidases are abundantly present in many living organisms. In plants, they are crucial for growth and response to environmental stressors. In animals, they are mostly found in the liver, where they detoxify chemicals.
Key Differences
Chemical Structure
Catalase and peroxidase differ significantly in their chemical structure. While catalase has a unique tetrameric structure enabling it to interact with hydrogen peroxide molecules efficiently, peroxidases vary greatly in structure, adapting to a wider range of substrates.
Reaction Mechanisms
The key difference in reaction mechanisms lies in their interaction with hydrogen peroxide. Catalase directly decomposes hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen, acting almost exclusively on this molecule. In contrast, peroxidases use hydrogen peroxide to oxidize other substances, making them more versatile in substrate interaction.
Substrate Specificity
Catalase exhibits high specificity towards hydrogen peroxide, whereas peroxidases can act on a broader range of substrates using hydrogen peroxide. This functional diversity allows peroxidases to participate in a wider variety of biological and chemical processes compared to catalase.
Biological Impacts
Impact on Human Health
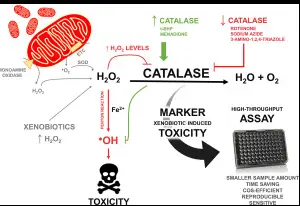
Catalase and peroxidase enzymes play pivotal roles in maintaining human health by managing oxidative stress, a condition caused by an excess of free radicals that can damage cells and lead to chronic diseases such as cancer, diabetes, and heart disease. Catalase helps protect cells from oxidative damage by converting hydrogen peroxide, a potentially harmful byproduct of cellular metabolism, into water and oxygen. This reaction is crucial in cellular defense, particularly in organs like the liver and kidneys, which are exposed to higher levels of reactive oxygen species.
Peroxidase enzymes, on the other hand, are involved in various bodily functions including immune response and hormone synthesis. They help break down harmful substances in the bloodstream, contributing to detoxification processes. Peroxidases in white blood cells help to kill bacteria and other pathogens by producing oxidants, which are part of the body’s defense mechanism.
Environmental Significance
Enzymes such as catalase and peroxidase also have significant roles in environmental health. These enzymes are involved in the biodegradation of pollutants and thus are integral to the process of bioremediation. Peroxidases are particularly effective in breaking down industrial pollutants, including phenols and aromatic compounds, which are prevalent in wastewater from chemical plants.
Catalase, by maintaining oxygen levels and managing hydrogen peroxide, helps in the aerobic degradation of organic pollutants. This ability makes it valuable in treatments where oxygenation is crucial for breaking down complex organic molecules in polluted sites.
Industrial Applications
Use in Medical Diagnostics
Both catalase and peroxidase are extensively used in clinical settings:
- Catalase testing is a standard procedure to identify the presence of catalase-positive microorganisms, such as Staphylococcus aureus, which can cause a range of infections. A simple test involving the application of hydrogen peroxide to a culture can indicate the presence of catalase, as the rapid release of oxygen bubbles suggests a positive result.
- Peroxidase activity is exploited in various diagnostic tests, such as those used to detect blood in fecal samples. The peroxidase-like activity of hemoglobin enables the use of simple, cost-effective tests for medical diagnostics and forensic applications.
Roles in Biotechnology
In biotechnology, the unique properties of these enzymes are harnessed for innovative applications:
- Catalase is used in the synthesis of biodegradable polymers and in the food industry to remove hydrogen peroxide used as a sterilant, thereby ensuring product safety without chemical residues.
- Peroxidases are utilized in the synthesis of fine chemicals, including certain dyes and aromatic compounds. Their ability to function in mild conditions without requiring harsh chemicals or extreme temperatures makes them ideal for green chemistry applications.
Research Insights
Recent Studies on Catalase
Recent research on catalase has focused on its potential in gene therapy, especially for treating conditions caused by oxidative stress, such as Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative disorders. Scientists are exploring how catalase, delivered via viral vectors, might help protect neurons from oxidative damage by improving cellular detoxification pathways.
Latest Findings on Peroxidase
In the field of peroxidase research, recent advancements have highlighted the enzyme’s potential in developing anti-cancer strategies. Studies have shown that certain peroxidase inhibitors can effectively slow down the growth of cancer cells, particularly in leukemia and breast cancer models. Moreover, peroxidase is being studied for its role in wound healing, as it can help in tissue regeneration and repair by modulating oxidative stress levels in damaged tissues.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is catalase?
Catalase is an enzyme found in nearly all living organisms exposed to oxygen. It catalyzes the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen, thus protecting cells from oxidative damage caused by peroxide, which is a byproduct of many metabolic reactions.
How does peroxidase differ from catalase?
While both catalase and peroxidase enzymes break down hydrogen peroxide, peroxidase’s function involves using hydrogen peroxide to oxidize other substrates, including various toxins and biomolecules, in the presence of a reducing agent. This makes peroxidase versatile in substrate specificity compared to catalase.
What are the industrial uses of catalase?
Catalase is widely used in the textile industry to remove hydrogen peroxide from fabrics after bleaching, ensuring material strength and longevity. It is also employed in food processing to eliminate residual hydrogen peroxide used as a sterilizing agent.
Why is peroxidase important in environmental science?
Peroxidase enzymes are crucial in bioremediation processes as they can break down harmful pollutants, including phenols and industrial dyes, thus mitigating environmental damage. They help in cleaning up pollutants effectively and naturally without the use of harsh chemicals.
Can catalase and peroxidase help in medical diagnostics?
Both enzymes are used in clinical diagnostics; catalase to assess the presence of catalase-positive bacteria and peroxidase for various assays, including those measuring glucose or cholesterol levels in blood samples.
Conclusion
Catalase and peroxidase play pivotal roles not just within the biological realms they originate from but also extend their utility to industrial and environmental applications. Their unique abilities to manage and manipulate reactive oxygen species offer incredible benefits across various fields.
Understanding and utilizing these enzymes can lead to significant advancements in healthcare, environmental management, and beyond. The ongoing research and development in leveraging catalase and peroxidase’s properties promise further innovative solutions to some of today’s most pressing challenges.
You