Radiometric dating is a key tool used by scientists to determine the age of materials, from ancient artifacts to the rocks that compose our planet. By measuring the decay rate of radioactive isotopes within these materials, researchers can estimate their ages with remarkable accuracy. This process is crucial in fields such as archaeology, paleontology, and geology, offering insights into our world’s and civilization’s history.
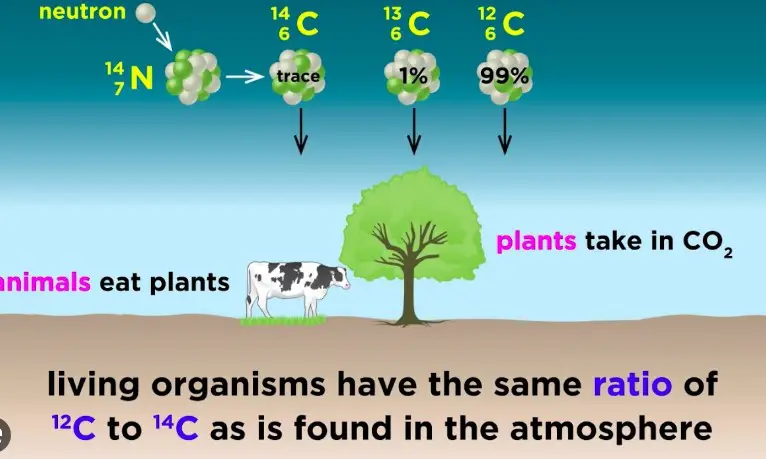
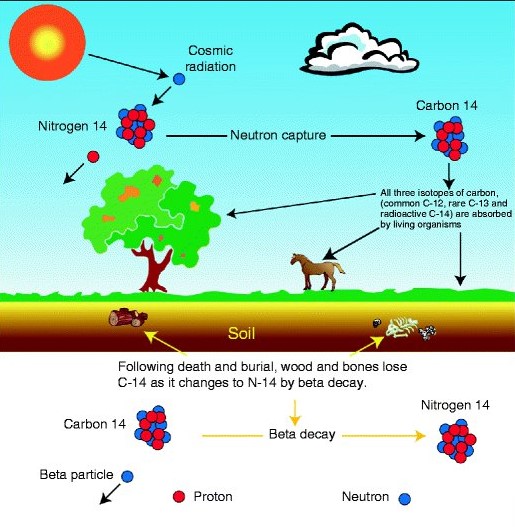
Carbon dating and uranium dating are two of the most well-known methods of radiometric dating. Carbon dating is primarily used to date relatively young, organic materials up to about 50,000 years old. In contrast, uranium dating is applied to date much older rocks and minerals, extending back billions of years. These methods utilize the decay of carbon-14 and uranium isotopes, respectively, as a “clock” to measure the passage of time since the material was formed or died.
While both carbon and uranium dating are based on the principles of radioactive decay, they differ significantly in their applications, limitations, and the types of materials they can accurately date. Carbon dating is invaluable for archaeologists studying past civilizations, whereas uranium dating provides geologists with the means to unravel the Earth’s geological history, including the age of the Earth itself.
Radiometric Dating Basics
What is Radiometric Dating?
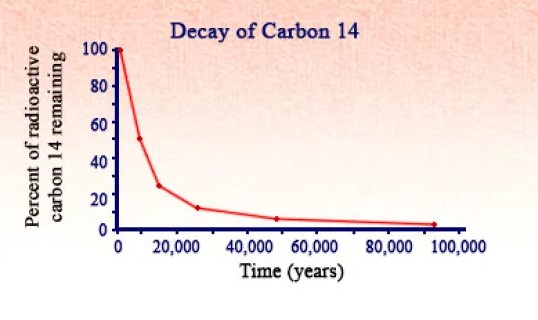
Radiometric dating is a scientific method used to determine the age of materials such as rocks or carbon, by measuring the decay rate of radioactive isotopes within them. The core principle behind radiometric dating is the consistent and predictable rate at which radioactive isotopes transform into stable isotopes. This transformation happens at a steady rate, known as the half-life, which is the time it takes for half of the radioactive isotope in a sample to decay.
Types of Radiometric Dating
Radiometric dating encompasses a range of techniques, each based on the specific isotopes used for measurement. These methods include:
- Carbon Dating: Targets carbon-14 in organic materials.
- Uranium-Lead Dating: Measures the decay of uranium isotopes into lead in rocks and minerals.
- Potassium-Argon Dating: Used for dating volcanic rocks by measuring the decay of potassium-40 to argon-40.
- Rubidium-Strontium Dating: Involves the decay of rubidium-87 into strontium-87, useful for dating rocks.
Each method has its unique application, depending on the age of the sample and the type of material being dated.
Carbon Dating Explained
Carbon Dating Principles
Carbon dating, also known as radiocarbon dating, is a method used to date materials that once exchanged carbon dioxide with the atmosphere; in other words, things that were once living. It is based on the decay of carbon-14, a radioactive isotope of carbon with a relatively short half-life of 5,730 years. The process of carbon dating involves measuring the amount of carbon-14 remaining in a sample and comparing it to the known rate of decay to estimate the sample’s age.
Applications of Carbon Dating
The primary use of carbon dating is in archaeology, where it helps date artifacts and sites that are up to about 50,000 years old. Key applications include:
- Dating of organic materials: Such as wood, bone, seeds, and cloth.
- Historical archaeology: To establish the age of historical structures and cultural artifacts.
- Environmental science: For analyzing past climate conditions through the dating of ice cores, ocean sediments, and tree rings.
Carbon dating has revolutionized the field of archaeology by providing a way to accurately date archaeological sites and artifacts, offering insights into human history and prehistory.
Limitations of Carbon Dating
While carbon dating is a powerful tool, it has its limitations, including:
- Age Range: Effective only for dating materials up to about 50,000 years old.
- Material Restrictions: Can only date materials that were once part of the biosphere and contain organic carbon.
- Contamination: The accuracy of carbon dating can be affected by contamination from more recent carbon sources.
Uranium Dating Uncovered
Uranium Dating Principles
Uranium dating, particularly uranium-lead dating, is based on the radioactive decay of uranium isotopes (238238U and 235235U) into stable lead isotopes (206206Pb and 207207Pb, respectively). This method utilizes the known decay rates of uranium isotopes, which have much longer half-lives than carbon-14, making uranium dating suitable for determining the age of the Earth and other ancient geological formations.
Applications of Uranium Dating
Uranium dating is instrumental in geology for dating rocks, particularly:
- Age of the Earth: Uranium dating has been crucial in estimating the Earth’s age at approximately 4.5 billion years.
- Dating of geological samples: Useful for dating zircon crystals in igneous rocks, as zircon incorporates uranium atoms into its crystalline structure but rejects lead.
- Planetary science: Helps in dating meteorites and moon rocks, providing insights into the solar system’s history.
Uranium dating’s ability to date geological samples millions to billions of years old has made it a cornerstone in understanding the timing of geological events and the age of the Earth.
Limitations of Uranium Dating
Despite its wide applications, uranium dating also faces several challenges:
- Sample Requirements: Requires samples that have remained closed systems since their formation.
- Complexity: The presence of two uranium isotopes decaying to different lead isotopes adds complexity to age calculations.
- Lead Contamination: The initial presence of lead in the sample can complicate age determinations.
Comparative Analysis
Key Differences
The main differences between carbon dating and uranium dating lie in the isotopes used and their decay rates. Carbon dating utilizes carbon-14, a radioactive isotope with a relatively short half-life of about 5,730 years. This makes it ideal for dating organic materials up to 50,000 years old. Uranium dating, on the other hand, uses uranium-238 and uranium-235 isotopes, which have much longer half-lives (4.5 billion years and 700 million years, respectively), allowing scientists to date rocks and minerals that are millions to billions of years old.
Age Range and Accuracy
The effective dating ranges of these methods vary significantly. Carbon dating is effective for relatively young, organic materials. It’s accuracy decreases for samples older than 50,000 years due to the rapid decrease in detectable carbon-14. Uranium dating shines in dating much older materials, with the potential to accurately measure ages up to the age of the Earth itself.
Material Suitability
When it comes to material suitability, carbon dating is used to date organic materials like wood, bone, and shell. Uranium dating is suited for dating rocks, minerals, and other inorganic materials. This distinction highlights the complementary nature of these dating methods in the field of geochronology.
Technological and Methodological Advances
Improvements in Carbon Dating
Accelerator Mass Spectrometry (AMS) represents a significant advancement in carbon dating. This technology enhances the detection of carbon-14, allowing for smaller sample sizes and greater accuracy, even in samples where the carbon-14 content is extremely low.
Advances in Uranium Dating
For uranium dating, high-precision mass spectrometry has been a game-changer. It allows for the precise measurement of uranium and lead isotopes, improving age estimations for rocks and minerals dating back billions of years. This precision is critical for understanding the geological history of the Earth.
Impact on Scientific Research
Contribution to Archaeology
Carbon dating has revolutionized archaeology by providing a reliable method for dating artifacts and sites. It has been instrumental in redefining historical timelines, from the age of ancient Egyptian mummies to the timing of Neolithic settlements.
Contribution to Geology
Uranium dating has been fundamental in geology, especially in determining the age of the Earth and the timing of geological events such as mountain formations and volcanic eruptions. This method has helped to map the geological history of the planet in unprecedented detail.
Future Prospects
Challenges and Opportunities
The future of radiometric dating lies in overcoming current limitations and harnessing new technologies. Improvements in accuracy and the development of methods capable of dating more diverse materials are among the primary challenges. The integration of machine learning and AI for data analysis presents exciting opportunities for advancing these dating techniques.
Interdisciplinary Applications
Radiometric dating, particularly carbon dating, has found interdisciplinary applications in climate change studies, helping scientists understand past climate conditions through the dating of ice cores and sediments. Similarly, uranium dating contributes to anthropology by dating cave paintings and fossilized human remains, offering insights into human evolution and migration patterns.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is radiometric dating?
Radiometric dating is a technique used to determine the age of materials such as rocks or carbon, based on the decay rate of radioactive isotopes contained within them. This method measures the time elapsed since these isotopes were formed, offering a window into the past.
How does carbon dating work?
Carbon dating works by measuring the amount of carbon-14, a radioactive isotope of carbon, remaining in organic materials. Since carbon-14 decays at a known rate, the age of the material can be estimated by calculating the ratio of remaining carbon-14 to stable carbon isotopes.
What types of materials can be dated using uranium dating?
Uranium dating is primarily used for dating rocks and minerals that contain uranium. This method is particularly useful for dating very old geological samples, as it can measure ages up to billions of years, providing insights into the Earth’s formation and the timing of geological events.
Why can’t carbon dating be used on rocks?
Carbon dating cannot be used on rocks because they do not contain organic carbon, which is necessary for carbon-14 dating. Instead, rocks are usually dated using methods like uranium dating, which rely on the decay of radioactive isotopes present in the minerals that compose the rocks.
Conclusion
The techniques of carbon dating and uranium dating serve as critical tools for scientists across various disciplines, enabling them to piece together the chronological puzzle of Earth’s history and the evolution of life. While each method has its specific applications and limitations, together they provide a comprehensive framework for understanding the timing of events and processes that have shaped our planet and the life it supports.
As scientific methods and technologies advance, the accuracy and range of radiometric dating continue to improve. These advancements promise to deepen our understanding of the natural world, offering more precise insights into the age of archaeological finds, the formation of geological features, and the history of Earth itself.