Reflection, a fundamental phenomenon observed in the realms of physics, extends its significance far beyond just producing mirror images. It encompasses a vast spectrum of scientific disciplines, from materials science to engineering and optics, showcasing the diverse nature of light interaction with different surfaces. This versatility not only enhances our understanding of the physical world but also paves the way for numerous technological advancements.
Bragg’s Reflection and Ordinary Reflection represent two distinct manifestations of this phenomenon, each governed by unique principles and equations. Bragg’s Reflection, primarily observed in crystal structures, involves the diffraction of waves, such as X-rays or neutrons, leading to constructive interference under specific conditions defined by Bragg’s Law. In contrast, Ordinary Reflection describes the simple bouncing back of light from surfaces, adhering to the law of reflection, which is familiar in everyday life through mirrors and shiny objects.
The essence of these reflections lies in their contribution to scientific research and technological innovation. Bragg’s Reflection plays a crucial role in the analysis of crystal structures, significantly impacting the field of materials science, while Ordinary Reflection finds its applications in designing optical devices and enhancing architectural aesthetics. Understanding these phenomena not only enriches our scientific knowledge but also opens doors to new technological possibilities.
Reflection Basics
What is Reflection?
At its core, reflection is the process by which light waves bounce off a surface. The law of reflection plays a pivotal role here, stating that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. This fundamental principle finds application in a multitude of everyday phenomena, from the clarity of a mirror image to the way light scatters off a rough surface, illuminating our surroundings.
Reflection is not just a passive observation but a key concept in optics, influencing the design of lenses, mirrors, and even architectural spaces, to harness light effectively for various purposes, including illumination, imaging, and even in art.
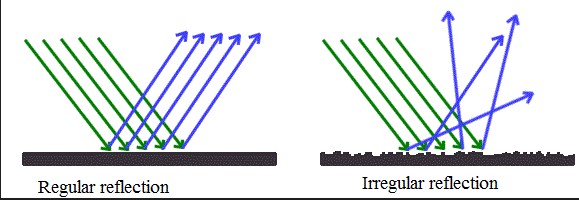
Types of Reflection
Specular Reflection
Specular or mirror-like reflection occurs when light beams reflect off a smooth surface, maintaining their coherence and direction. This type of reflection is responsible for the formation of clear images in mirrors, where each ray of light reflects in a single direction, preserving the appearance of the original object.
Diffuse Reflection
Contrastingly, diffuse reflection happens when light hits a rough surface, scattering the rays in multiple directions. This scattering effect causes the reflected light to lose its coherent image-forming capability, which is why we cannot see our reflection in a sidewalk or a plastered wall. Despite this, diffuse reflection is crucial for indirect lighting, helping illuminate spaces more evenly by dispersing light across a wider area.
Bragg’s Reflection
The Concept
Bragg’s Reflection, named after William Henry Bragg and his son William Lawrence Bragg, who first proposed it in 1913, is a specialized form of reflection observed in crystal structures. Unlike ordinary reflection, Bragg’s Reflection involves the diffraction of waves, such as X-rays or neutrons, which then interfere constructively under specific conditions, revealing the atomic structure of the material.
This phenomenon is essential in the field of crystallography, providing insights into the atomic and molecular structure of crystals, which in turn helps in understanding their physical properties and behaviors.
Bragg’s Law
Bragg’s Law mathematically defines the conditions under which Bragg’s Reflection occurs. It relates the wavelength of the incident waves to the angle of incidence and the distance between the crystal planes, offering a precise method to analyze the atomic structure of crystals. The law is elegantly simple yet powerful, enabling scientists to decode the arrangement of atoms within a material, which is critical for the development of new materials and the study of substances at the molecular level.
Applications
The applications of Bragg’s Reflection are vast and varied, touching upon numerous scientific disciplines:
- X-ray Crystallography: Perhaps the most notable application, allowing the determination of the atomic structure of crystals.
- Materials Science: Understanding the microstructure of materials to predict their properties and behaviors.
- Semiconductor Fabrication: Analyzing the crystal quality and defects that affect the performance of semiconductors.
Ordinary Reflection
The Concept
Ordinary Reflection, the more commonly observed form of reflection, occurs when light rays bounce off surfaces, such as mirrors, water, or polished metal. The principle is straightforward, governed by the law of reflection, which makes it a fundamental concept in optics and various practical applications.
Physical Principles
The physical principles underlying Ordinary Reflection are governed by the law of reflection, which states that the incident light ray, the reflected light ray, and the normal to the surface at the point of incidence all lie in the same plane, with the angle of incidence equaling the angle of reflection. This principle is critical in designing optical devices, ensuring accurate reflection and imaging.
Applications
The practical applications of Ordinary Reflection are extensive, influencing both technology and architecture:
- Mirrors: From personal grooming to scientific instruments, mirrors rely on ordinary reflection to provide clear images.
- Optical Devices: Cameras, telescopes, and microscopes use specially designed mirrors and lenses to direct light precisely, capturing images or focusing on distant or tiny objects.
- Architectural Design: Architects use reflective surfaces to enhance natural lighting, create visual effects, or improve the aesthetics of a building.
Key Differences
Nature of Reflection
At the heart of the comparison between Bragg’s and Ordinary Reflections lies a fundamental difference in their nature and mechanisms. Ordinary Reflection, often encountered in daily life, involves light rays hitting a surface and bouncing back, adhering to the law of reflection. This principle is most commonly observed with surfaces such as mirrors, where a clear image is formed due to the uniform reflection of light.
Bragg’s Reflection, on the other hand, is a more complex process that involves the diffraction of X-rays or neutrons by the closely spaced lattice of atoms in a crystal. This phenomenon is not about the simple bouncing back of light rays but the constructive interference of wavefronts reflected from different planes within a crystalline structure, leading to intensified reflection at certain angles.
Mathematical Description
The mathematical formulations governing these two types of reflections further highlight their distinctions. The law of reflection, governing Ordinary Reflection, is relatively straightforward, stating that the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. This simplicity allows for easy prediction and manipulation of light paths in various applications, from designing optical instruments to architectural planning.
Conversely, Bragg’s Reflection is described by Bragg’s Law, a more complex equation that relates the angle at which waves are diffracted with their wavelength and the spacing between the diffracting planes in the crystal. This law is pivotal in fields such as crystallography and materials science, where understanding the internal structure of materials at the atomic or molecular level is crucial.
Practical Applications
The practical applications of these reflections diverge significantly, rooted in their underlying principles. Ordinary Reflection’s simplicity and predictability make it indispensable in everyday devices like mirrors, optical lenses, and sensors, where controlling the path of light is essential. Its applications span across various sectors, including visual arts, architecture, and photography, leveraging the straightforward nature of light reflection.
Bragg’s Reflection, with its specificity to crystalline structures, finds its applications in more specialized fields. X-ray crystallography, a technique crucial for the determination of the atomic structure of molecules, relies heavily on Bragg’s Reflection. This method has profound implications in chemistry, biology, and materials science, facilitating breakthroughs in drug development, the discovery of complex molecular structures, and the design of novel materials with tailored properties.
Advanced Considerations
Limitations and Challenges
While the principles of Bragg’s and Ordinary Reflections have broad applications, they are not without their limitations and challenges. The effectiveness of Ordinary Reflection in practical applications can be hindered by the quality of the reflective surface, where imperfections can distort images or reduce efficiency in devices that rely on precise optical paths.
Bragg’s Reflection, being reliant on highly ordered crystalline structures, faces challenges in materials with significant disorder or complexity beyond simple crystals. Moreover, the requirement for specific wavelengths of X-rays or neutrons limits the accessibility of this technique, necessitating sophisticated equipment and expertise.
Recent Developments
The continuous evolution of technology and scientific understanding brings with it advancements that enhance both the theoretical framework and practical applications of these reflections. In the realm of Bragg’s Reflection, recent research has focused on exploring new materials and structures, such as quasicrystals and nanoscale lattices, which exhibit unique diffractive properties. These studies not only broaden our understanding of material properties but also open up new avenues for device fabrication, from more efficient solar cells to advanced optical sensors.
Innovation in materials and fabrication techniques has also led to improvements in Ordinary Reflection applications. Developments in nano-texturing surfaces, for example, have enabled the creation of ultra-reflective or superhydrophobic materials, pushing the boundaries of optical design and surface engineering.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Bragg’s Law?
Bragg’s Law explains the condition under which maximum reflection occurs from crystal planes, crucial in determining the crystal structure through X-ray diffraction techniques. It relates the wavelength of incident waves to the angle of incidence and the distance between crystal planes, enabling scientists to decipher atomic arrangements in solids.
How does Ordinary Reflection differ from Bragg’s Reflection?
Ordinary Reflection occurs when light waves bounce off a surface, following the law of reflection. This type of reflection is commonly observed with mirrors or glossy surfaces. Bragg’s Reflection, however, is a more complex phenomenon involving the diffraction of waves such as X-rays by crystal lattices, resulting in constructive interference under specific conditions.
Can Bragg’s Reflection be observed with visible light?
Bragg’s Reflection is typically observed with X-rays or neutrons due to their wavelengths being comparable to the spacing between crystal planes in solids. While it’s theoretically possible with visible light under certain conditions, practical observations are rare due to the much larger wavelength of visible light compared to atomic spacings in crystals.
Conclusion
The exploration of Bragg’s and Ordinary Reflections uncovers the intricate ways in which light and matter interact, highlighting the profound implications these phenomena have on scientific research and technological advancements. Their distinct principles not only facilitate a deeper understanding of material properties but also inspire innovative applications, from analyzing crystal structures to enhancing the efficiency of optical devices.
As we continue to unravel the mysteries of light reflection, the knowledge gleaned from these studies not only enriches our scientific comprehension but also fuels the development of new technologies. By appreciating the differences and applications of Bragg’s and Ordinary Reflections, we gain valuable insights into the fundamental nature of light, opening new horizons in the exploration of the material world.

