Arthropods, a diverse and predominant group in the animal kingdom, are renowned for their complex body structures and varied limb forms. These creatures, ranging from insects to crustaceans, exhibit significant differences in their appendages, which are critical to their survival and adaptation. The distinction between biramous and uniramous limbs represents a fundamental aspect of their evolutionary biology.
Biramous limbs are split into two branches, a common feature in many crustaceans, while uniramous limbs consist of a single series of segments extending from the body, typical of insects and spiders. This structural variance not only affects their physical capabilities but also their ecological roles, influencing how different arthropods interact with their environments.
Understanding the differences between these limb types is more than an academic pursuit; it offers insights into evolutionary strategies, ecological impacts, and the adaptive diversification of arthropods. Such knowledge is crucial for studying biodiversity and the evolutionary mechanisms that drive the success of these ubiquitous animals.
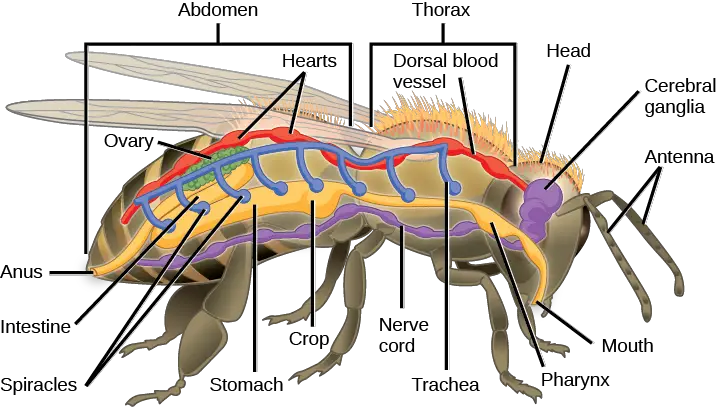
Arthropod Basics
What are Arthropods?
Arthropods are invertebrates with an external skeleton, segmented body, and jointed appendages. They form the largest phylum in the animal kingdom, encompassing a vast variety of species including insects, arachnids, myriapods, and crustaceans. These creatures are found in nearly every habitat on Earth, from the deepest ocean trenches to the highest mountain peaks, adapting to an incredible range of environments.
Main Classes within Arthropoda
Arthropoda is divided into several classes, each representing a unique evolutionary path:
- Insecta: The most diverse group, including butterflies, beetles, flies, and more.
- Arachnida: This class includes spiders, scorpions, ticks, and mites.
- Crustacea: Comprising crabs, lobsters, shrimps, and barnacles.
- Myriapoda: Consisting of centipedes and millipedes.
Each class exhibits distinctive features but shares the fundamental arthropod characteristics of jointed limbs and exoskeletons.
Anatomical Features
General Structure of Arthropod Limbs
The limbs of arthropods are primarily composed of chitin, a sturdy yet flexible material that forms the exoskeleton. A typical arthropod limb is segmented and may end in various specialized structures like claws or paddles, depending on the species’ lifestyle and environment.
Role of Limbs in Arthropod Biology
The limbs play crucial roles in mobility, feeding, and defense. They allow arthropods to interact dynamically with their environments, perform complex behaviors, and adapt to various ecological niches.
Limb Variations
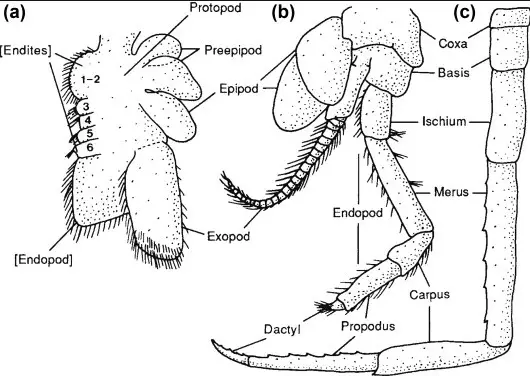
Biramous Limbs
Definition of Biramous Limbs
Biramous limbs are a distinctive type of appendage split into two branches—a basal segment that may serve as a gill and a distal segment that functions in locomotion or sensory reception. This limb type is most commonly associated with aquatic arthropods, particularly crustaceans.
Evolutionary Significance
The biramous configuration is believed to be the primitive condition of arthropod limbs, offering both respiratory and locomotive functions, which may have been crucial for survival in early aquatic environments.
Examples in Nature
Common examples include the limbs of lobsters and crayfish, which utilize these bifurcated structures for swimming and breathing under water.
Uniramous Limbs
Definition of Uniramous Limbs
Uniramous limbs consist of a single series of segments without any branching, typically found in insects and spiders. These limbs are versatile and adapted to a range of activities from walking to grasping or even jumping.
Evolutionary Perspectives
The shift from biramous to uniramous limbs is a significant evolutionary step, often associated with the transition from aquatic to terrestrial life, where streamlined and flexible limbs offered better support and mobility on land.
Examples in the Animal Kingdom
Spiders use their uniramous limbs for intricate web construction, while insects like grasshoppers have powerful hind legs adapted for jumping.
Comparative Analysis
Structural Differences
Detailed Comparison of Limb Anatomy
Biramous limbs typically feature two branches that can serve dual functions—locomotive and respiratory—whereas uniramous limbs are more streamlined for specialized tasks. The structural simplicity of uniramous limbs often leads to greater specialization in terrestrial environments.
Adaptive Functions of Each Limb Type
- Biramous: Dual functionality helps in balancing and respiration in aquatic settings.
- Uniramous: Specialization allows for enhanced mobility, manipulation, or sensory perception on land.
Evolutionary Trajectories
Evolutionary Theories Explaining Limb Diversification
The evolution from biramous to uniramous limbs is thought to reflect arthropods’ adaptive responses to changing environmental demands, enabling more efficient land colonization.
Impact on Habitat and Lifestyle Adaptations
This evolutionary shift has allowed arthropods to exploit new ecological niches, from terrestrial to aerial, significantly impacting their distribution and ecological roles across the globe.
Significance in Ecology
Ecological Roles of Biramous Arthropods
Case Studies of Specific Species
One notable example is the American lobster (Homarus americanus), which utilizes its biramous limbs for locomotion and manipulating its environment. This species plays a crucial role in maintaining the health of seabed ecosystems by consuming dead organisms and organic waste.
Impact on Ecosystems
Biramous limbs allow arthropods like crabs and shrimp to burrow and alter the sediment structure, which enhances the habitat for other marine organisms. This activity increases the biodiversity and productivity of marine ecosystems.
Ecological Roles of Uniramous Arthropods
Case Studies and Ecological Impacts
The desert locust (Schistocerca gregaria), with its powerful uniramous hind legs, can travel vast distances, impacting agriculture profoundly by consuming large amounts of vegetation. Despite their destructive power, locust swarms contribute to nutrient cycling across their migration routes.
Impact on Ecosystems
Insects with uniramous limbs, such as bees and ants, play pivotal roles in pollination and soil aeration, respectively. Their activities are essential for plant reproduction and soil health, influencing ecological stability and productivity.
Impact on Biodiversity
Genetic and Morphological Diversity
The variation in limb types among arthropods has led to a broad range of adaptations, allowing them to inhabit diverse ecological niches. This morphological diversity is linked to genetic variations that enhance species survival and adaptation.
Role in Evolutionary Resilience
The ability to evolve different limb structures has provided arthropods with the flexibility to survive environmental changes and mass extinction events. This evolutionary resilience underscores the importance of limb diversification in their long-term survival.
Implications for Conservation
Conservation Concerns for Rare Species
Certain arthropods with unique limb adaptations are increasingly threatened by habitat loss and climate change. Protecting these species is crucial for maintaining ecological balance and genetic diversity within their habitats.
Importance of Limb Types in Ecological Balance
The diversity of limb structures among arthropods affects their roles in ecosystems, from predators and scavengers to pollinators and decomposers. Conserving this diversity helps maintain the stability and functionality of ecosystems.
Future Research Directions
Genetic Studies
Future research could focus on uncovering the genetic mechanisms behind limb variation and adaptation. Understanding these genetic factors can provide insights into the evolutionary history of arthropods and their potential responses to environmental pressures.
Environmental Impact Studies
How Changing Environments Might Affect Limb Adaptations
- Climate Change: As global temperatures rise, arthropods may experience shifts in limb functionality, potentially affecting their survival and distribution.
- Habitat Alteration: Changes in land use, such as deforestation and urbanization, might impact the natural habitats of arthropods, necessitating adaptations in their limb structures to cope with new environments.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are Biramous Limbs?
Biramous limbs are a type of appendage found in some arthropods, characterized by their bifurcated structure; they branch into two, with one branch typically bearing the gill and the other functioning as a limb. This configuration is primarily seen in crustaceans, like lobsters and shrimp.
What are Uniramous Limbs?
Uniramous limbs, in contrast to biramous, do not split into branches but extend as a single appendage from the body. This design is typical in arthropods such as insects and spiders, where each limb is unbranched and often adapted for walking, climbing, or other specialized functions.
How do Limb Types Affect Arthropod Ecology?
The type of limbs an arthropod possesses impacts its ecological role by influencing its mobility, habitat preference, and feeding strategies. Biramous limbs often facilitate swimming and carry respiratory functions, whereas uniramous limbs are more versatile for terrestrial environments.
Why is the Study of Arthropod Limbs Important?
Studying the limb structures of arthropods helps scientists understand evolutionary patterns, species adaptation, and ecological dynamics. These insights are crucial for conservation efforts and in understanding the environmental changes affecting these organisms.
Conclusion
The intricate differences between biramous and uniramous limbs underscore the rich tapestry of life within the arthropod phylum. These variations not only illuminate the evolutionary paths of these organisms but also their adaptability and survival strategies in diverse environments. As we explore these distinctions, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity of life and the delicate balance of ecosystems.
In summary, the study of arthropod limb differences offers valuable perspectives on biodiversity, evolution, and the ecological roles of these creatures. It enhances our understanding of the natural world and our strategies for preserving it, highlighting the interconnectedness of structure, function, and environmental adaptation.

