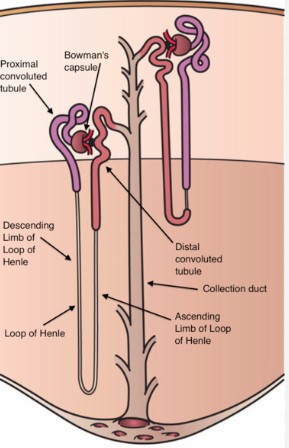
The Loop of Henle serves as a critical component of the nephron in the kidneys, playing a pivotal role in the body’s water and salt balance. Its unique structure, divided into ascending and descending limbs, facilitates the concentration and dilution of urine, an essential process for maintaining homeostasis. By adjusting the kidney’s ability to conserve water or excrete waste, the Loop of Henle exemplifies nature’s precision in human physiology.
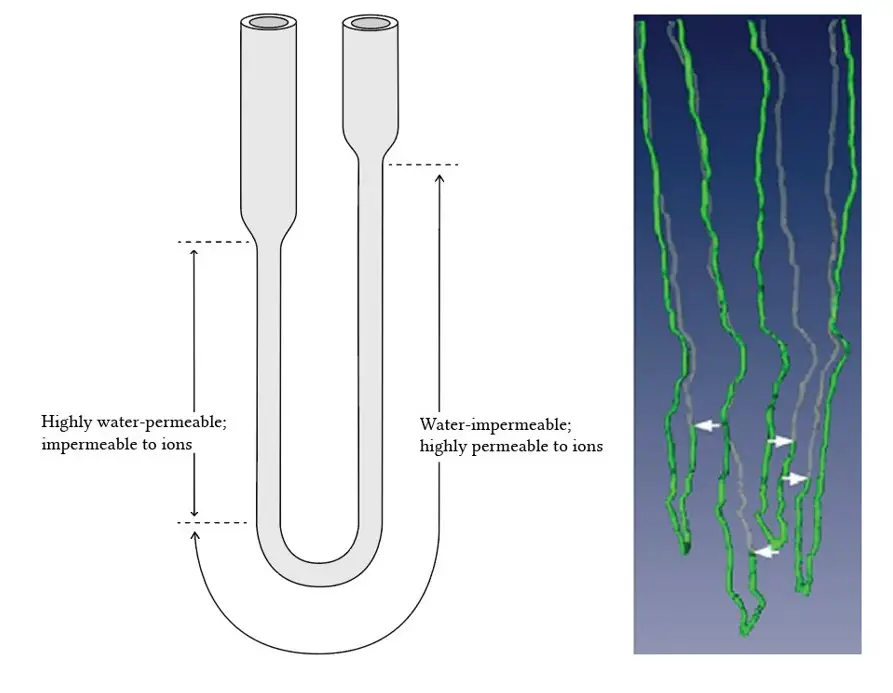
The primary difference between the ascending and descending loops of Henle lies in their permeability and functions. The ascending loop is impermeable to water but actively transports ions, particularly sodium and chloride, out of the urine. Conversely, the descending loop is permeable to water but not to ions, allowing water to be reabsorbed into the bloodstream, thereby concentrating the urine.
This specialized segment of the nephron not only illustrates the sophistication of kidney function but also highlights the intricate balance the body maintains to regulate its internal environment. Through a series of active and passive transport mechanisms, the Loop of Henle ensures the efficient removal of waste products while conserving vital nutrients and water, a testament to the evolutionary refinement of the human body.
Basic Anatomy
Overview of Nephron
The nephron is the kidney’s functional unit, tasked with removing waste from the bloodstream and balancing body fluids. Each nephron consists of a filtering unit of small blood vessels called a glomerulus and a tubule. The process of filtration, reabsorption, secretion, and excretion occurs here, resulting in urine formation.
Role of Loop of Henle
The Loop of Henle, a crucial segment of the nephron’s tubule, extends from the cortex into the medulla of the kidney. It’s essential for concentrating urine and maintaining the body’s water and salt balance. This loop works through a counter-current mechanism, which maximizes water reabsorption and solute concentration.
Structure Differences
The Loop of Henle is divided into two parts: the ascending loop and the descending loop. The descending loop is thin and permeable to water but not to ions, allowing water to be reabsorbed into the bloodstream. Conversely, the ascending loop is impermeable to water but actively transports ions, such as sodium and chloride, into the surrounding medullary tissue, aiding in the regulation of urine concentration and volume.
Ascending Loop
Function Overview
The ascending loop of Henle plays a pivotal role in the kidney’s ability to concentrate urine. Unlike its descending counterpart, it is equipped to actively transport ions while being impermeable to water, which helps in the generation of an osmotic gradient essential for water reabsorption elsewhere in the nephron.
Ion Transport
Active transport mechanisms in the ascending loop move sodium, potassium, and chloride ions out of the tubular fluid. This ion removal is crucial for establishing the osmotic gradient that the kidney uses to reabsorb water from the collecting duct, thereby concentrating the urine.
Water Permeability
The ascending loop’s impermeability to water is key to its function. Because it does not allow water to follow the transported ions by osmosis, the tubular fluid becomes more dilute as it moves up the loop. This mechanism is fundamental in the kidney’s ability to produce urine that is less concentrated than the body fluids, allowing for the excretion of waste without excessive water loss.
Role in Concentrating Urine
The ascending loop’s activities are central to the countercurrent multiplication system, which concentrates urine. By actively transporting salts and creating a high osmolarity in the kidney medulla, it enables water reabsorption from the collecting duct, crucial for producing concentrated urine and maintaining hydration.
Descending Loop
Function Overview
The descending loop of Henle contrasts with the ascending loop by being highly permeable to water but not to ions. This part of the loop facilitates the passive reabsorption of water back into the bloodstream, driven by the osmotic gradient created by the ascending loop, thereby concentrating the tubular fluid.
Water Transport
In the descending loop, water exits the tubular fluid passively due to the osmotic pressure gradient established by the ascending loop’s ion transport. This process significantly increases the concentration of the tubular fluid as it moves deeper into the medulla, preparing it for ion reabsorption in the ascending loop.
Ion Permeability
The descending loop’s impermeability to ions ensures that only water is reabsorbed, maintaining the osmotic gradient necessary for the kidney’s concentrating function. This selective permeability is crucial for the loop’s role in the concentration of urine.
Role in Diluting Urine
While the primary role of the descending loop is to concentrate the tubular fluid by removing water, this action sets the stage for the subsequent dilution process in the ascending loop. The interplay between the descending and ascending loops facilitates the kidney’s ability to excrete waste in a highly efficient manner, regardless of the body’s state of hydration.
Comparative Analysis
Ion Absorption Variance
The Loop of Henle showcases a significant variance in ion absorption between its ascending and descending limbs. The ascending loop actively transports sodium, potassium, and chloride ions out of the tubular fluid, which is a process that consumes energy. This active transport is crucial for setting up the osmotic gradient needed for water reabsorption in other parts of the nephron. Conversely, the descending loop, being impermeable to ions, does not partake in ion transport, highlighting a clear functional divergence between the two segments.
Water Reabsorption Contrast
The contrast in water reabsorption capabilities between the two loops is stark. The descending loop of Henle is highly permeable to water, allowing significant water reabsorption into the bloodstream, driven by the osmotic gradient created by the ascending loop’s ion transport activities. This permeability facilitates the concentration of urine as it descends deeper into the medulla. On the other hand, the ascending loop’s impermeability to water prevents water from leaving the tubule, leading to the dilution of the tubular fluid as ions are actively removed.
Contribution to Osmotic Gradient
Both loops contribute distinctly to the establishment and maintenance of the osmotic gradient in the kidney’s medulla. The ascending loop’s active ion transport increases the osmolarity of the surrounding medullary tissue, which is essential for the functioning of the countercurrent multiplication system. The descending loop complements this by allowing water to exit the tubular fluid, thereby increasing the fluid’s osmolarity as it moves down. Together, these processes create a steep osmotic gradient that enables the kidney to vary urine concentration according to the body’s hydration needs.
Physiological Implications
Impact on Blood Pressure
The Loop of Henle has a significant impact on blood pressure through its role in regulating the body’s fluid volume and sodium balance. The ascending loop’s ability to remove sodium from the tubular fluid without accompanying water loss leads to a reduction in the fluid volume, impacting blood pressure. Furthermore, the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, which controls blood pressure and fluid balance, is influenced by the ion concentration gradients established by the Loop of Henle, illustrating its vital role in cardiovascular health.
Influence on Electrolyte Balance
The electrolyte balance within the body is tightly regulated by the kidney, with the Loop of Henle playing a crucial role. The selective transport of ions in the ascending loop and the differential permeability to ions and water in the descending loop ensure that essential electrolytes like sodium and potassium are conserved or excreted as needed. This ability to adjust electrolyte excretion based on bodily needs is fundamental to maintaining homeostasis and preventing conditions such as hyponatremia or hyperkalemia.
Role in Urine Concentration
The Loop of Henle’s primary role in urine concentration cannot be overstated. Its unique mechanism allows the kidneys to produce urine that is either more concentrated or more diluted than the blood, depending on the body’s hydration status. This flexibility is vital for the conservation of water in times of dehydration and the elimination of excess water in states of overhydration, demonstrating the loop’s critical function in fluid balance.
Clinical Relevance
Link to Diuretic Action
Diuretics are medications that increase urine production and are often used to manage conditions like hypertension and heart failure. The Loop of Henle, especially the ascending loop, is the target of one of the most potent classes of diuretics, known as loop diuretics. These drugs inhibit the sodium-potassium-chloride cotransporter in the ascending loop, reducing the reabsorption of these ions and thereby increasing water excretion. This mechanism highlights the clinical importance of the Loop of Henle in managing fluid overload conditions.
Association with Kidney Diseases
Dysfunctions in the Loop of Henle can lead to or exacerbate various kidney diseases. For example, alterations in the loop’s ability to concentrate urine can result in disorders like nephrogenic diabetes insipidus, where the kidney fails to concentrate urine properly, leading to excessive water loss. Similarly, impairments in ion transport can contribute to electrolyte imbalances and acid-base disorders, underscoring the loop’s significance in renal pathology.
Implications for Treatment
Understanding the specific functions of the ascending and descending loops of Henle has significant implications for treatment strategies in kidney diseases and conditions affecting fluid balance. Therapies that target the loop’s ion transport mechanisms, such as the administration of loop diuretics, can be tailored to manage fluid retention effectively. Additionally, insights into the loop’s operation can guide the development of new treatments aimed at enhancing or mimicking its natural functions, offering hope for patients with chronic kidney diseases or acute kidney injuries.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Loop of Henle’s function?
The Loop of Henle primarily functions to concentrate or dilute urine, depending on the body’s hydration status. By selectively reabsorbing water and solutes, it plays a crucial role in maintaining the body’s electrolyte balance and blood pressure, illustrating its vital role in kidney function and overall homeostasis.
How does the Loop of Henle affect blood pressure?
The Loop of Henle indirectly affects blood pressure through its role in regulating the body’s fluid balance and electrolyte levels. By adjusting the concentration of urine, it influences the volume of blood, which, in turn, impacts blood pressure. Its ability to transport sodium is particularly significant in this regulation.
Can Loop of Henle dysfunctions lead to disease?
Yes, dysfunctions in the Loop of Henle can lead to various kidney diseases and disorders. For instance, impairments in ion transport can result in electrolyte imbalances, while issues with water reabsorption can cause problems with urine concentration, leading to conditions such as nephrogenic diabetes insipidus or acute kidney injury.
What role does the Loop of Henle play in diuretic therapy?
The Loop of Henle is a key target for certain diuretics, especially loop diuretics. These medications work by inhibiting sodium, potassium, and chloride reabsorption in the ascending loop, increasing urine output. This mechanism is used in treating conditions like hypertension and edema by reducing fluid overload and influencing blood pressure.
Conclusion
The Loop of Henle’s ability to fine-tune the body’s internal environment showcases the remarkable efficiency of kidney physiology. Its distinct segments, the ascending and descending loops, each play a critical role in urine concentration and volume regulation, underlying the importance of this nephron part in maintaining homeostasis.
Understanding the differences and functions of the ascending and descending loops of Henle not only provides insights into the fundamental processes of the human body but also emphasizes the complexity and elegance of our physiological systems. As research advances, the potential for new therapeutic strategies targeting this essential kidney structure continues to expand, promising improvements in treating various renal and systemic conditions.