Fungal spores play a pivotal role in the reproduction and survival strategies of fungi, exhibiting a variety of forms with specific functions tailored to their environmental niches. Among these, arthrospores and chlamydospores are two types that differ significantly in their formation, structure, and ecological roles. Each type of spore ensures the continuity of fungal species under various conditions, adapting uniquely to their surroundings.
Arthrospores and chlamydospores serve distinct purposes within fungal life cycles. Arthrospores are formed by the fragmentation of hyphae, typically in response to nutrient scarcity or environmental stress, aiding in survival and dispersal. Chlamydospores, on the other hand, are thick-walled spores that act as survival units under adverse conditions, providing a means for fungi to withstand periods of nutrient deficiency and environmental extremes.
These spores are not only crucial for fungal propagation but also have significant implications in agriculture and medicine. Understanding their differences is essential for managing diseases they may cause in crops and humans, as well as for utilizing them in biological control and other biotechnological applications.
Spore Basics
Definition and Role
Fungal spores are essential for the reproduction and survival of fungi. They are analogous to seeds in plants but exist as microscopic entities capable of giving rise to new fungal colonies. Spores are produced by fungi as a means to spread and persist across diverse environments, often under conditions that would be challenging for other forms of life. Their ability to remain dormant for extended periods enhances their survival during unfavorable conditions.
Common Types of Spores
Fungi produce a variety of spore types, each adapted to specific environmental or biological roles. Some of the most common types include:
- Zoospores: Motile spores that use flagella to move through liquid environments.
- Basidiospores and Ascospores: Produced during sexual reproduction, crucial for genetic diversity.
- Conidia: Asexual spores that are abundantly produced and released to colonize new areas rapidly.
Each type plays a unique role in the life cycle of fungi, contributing to their ability to adapt to and colonize a wide range of habitats.
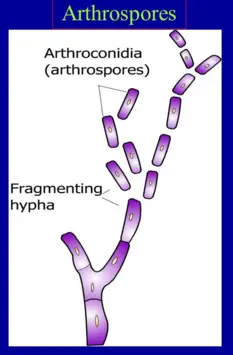
Arthrospores Explained
Formation Process
Arthrospores are formed through the fragmentation of hyphae, the thread-like structures that make up the body of a fungus. This process typically occurs when the fungus encounters adverse conditions such as nutrient scarcity or environmental stress. The hyphae segment into individual pieces that develop into mature, spore-like structures capable of forming new fungal colonies.
Characteristics
Arthrospores are known for their hardiness and resilience. Unlike other spores, they do not have a specialized spore-bearing structure but are rather segments of the fungal hyphae that harden and detach. This simplicity in their formation allows for quick and efficient reproductive responses to environmental changes.
Ecological Roles
In the ecosystem, arthrospores play critical roles in:
- Survival: They enable fungi to survive harsh conditions by lying dormant until favorable conditions return.
- Dispersal: Their resilience facilitates the spread of fungi over long distances, often aided by wind or water.
- Recolonization: Arthrospores can quickly germinate and colonize new substrates, essential for the propagation of fungal species.
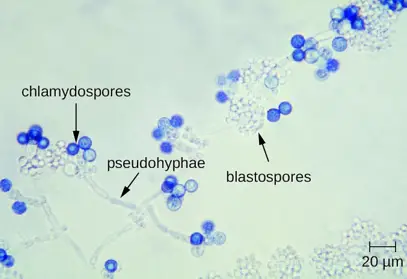
Chlamydospores Defined
Development Mechanism
Chlamydospores develop either terminally or within the strands of hyphae and are typically larger and thicker-walled than other types of fungal spores. Their development is triggered by environmental signals that indicate a need for a durable, survival-oriented spore. The thick wall of the chlamydospore is key to its role as a survival structure, providing significant resistance against desiccation and other environmental hazards.
Distinct Features
Chlamydospores are characterized by:
- Thick cell walls: Helps in protecting the spore against physical damage and dehydration.
- Energy storage: They often contain high amounts of storage compounds like lipids and glycogen, necessary for long-term survival.
- Dormancy: Capable of remaining dormant for extended periods until conditions are favorable for growth.
Environmental Significance
Chlamydospores are particularly significant in environments where conditions can suddenly become inhospitable. Their roles include:
- Soil health: They contribute to the biodiversity and stability of soil ecosystems, acting as a reserve of fungal life during extreme conditions.
- Disease resistance: In agricultural settings, understanding the formation and spread of chlamydospores can help in developing strategies to manage plant diseases caused by pathogenic fungi.
- Ecological resilience: They enhance the resilience of fungal populations by ensuring survival during adverse environmental changes.
Comparative Analysis
Structural Differences
When comparing arthrospores and chlamydospores, the key structural differences lie in their formation and resilience. Arthrospores are simpler, formed from the fragmentation of hyphae without requiring significant energy or resources to develop specialized structures. In contrast, chlamydospores develop thick walls filled with reserves that aid in longevity and resistance, making them more complex and robust compared to the relatively fragile arthrospores.
Functional Variances
Functionally, arthrospores are primarily adapted for rapid dispersal and colonization under stressful conditions, whereas chlamydospores are geared towards long-term survival. This functional divergence highlights the evolutionary adaptability of fungi, with each spore type serving a strategic role in fungal lifecycle and survival strategies.
Adaptation to Habitats
Adaptation to various habitats also reflects these differences:
- Arthrospores: Thrive in transient, nutrient-poor environments due to their rapid colonization capabilities.
- Chlamydospores: Excel in stable, nutrient-limited environments where long-term survival is crucial.
Detection and Identification
Microscopic Examination
Identifying these spores typically involves microscopic examination where distinct features are noted:
- Arthrospores: Identified by their segmented hyphae appearance.
- Chlamydospores: Recognized by their enlarged, thick-walled structure.
Chemical and Biological Markers
Advanced techniques involve using chemical and biological markers to distinguish between spore types. Specific staining methods can highlight the structural differences, making it easier to identify and categorize the spores accurately.
Implications in Agriculture
Impact on Crop Health
Both arthrospores and chlamydospores can significantly impact crop health. Arthrospores may lead to rapid disease spread, especially in crowded agricultural settings. Chlamydospores contribute to persistent infections due to their ability to survive in soil for extended periods.
Management Strategies
Effective management strategies include:
- Crop rotation: Helps disrupt the life cycles of fungi producing harmful spores.
- Fungicides: Selected based on their effectiveness against specific spore types.
- Biological control: Introducing beneficial fungi to compete with harmful species.
Medical Relevance
Infections and Treatments
In a medical context, diseases caused by fungi with these spore types can be challenging to treat due to their resilience and adaptability. Treatments often involve antifungal medications tailored to target specific fungal structures and reproductive mechanisms.
Research and Developments
Recent developments in fungal research have focused on:
- Genetic understanding: Identifying genes involved in spore development can lead to targeted treatments and management strategies.
- Biotechnology applications: Utilizing fungal spores in industry, such as in the production of antibiotics or enzymes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are fungal spores?
Fungal spores are microscopic biological particles used by fungi for reproduction and survival. They can be dispersed through air, water, or living carriers, enabling fungi to colonize new environments and form new colonies.
How do arthrospores form?
Arthrospores form through the segmentation of pre-existing hyphae, typically as a response to environmental stress or nutrient depletion. This fragmentation helps the fungus spread and survive under challenging conditions.
What distinguishes chlamydospores?
Chlamydospores are characterized by their thick walls and ability to form in various parts of the fungal hyphae, either terminally or intercalary. They are specialized for long-term survival during unfavorable conditions.
How do arthrospores and chlamydospores impact agriculture?
In agriculture, these spores can influence crop health through their role in the spread of fungal diseases. Effective management of arthrospores and chlamydospores is crucial for controlling outbreaks and minimizing crop losses.
Can chlamydospores cause human disease?
Yes, certain fungi that produce chlamydospores can cause diseases in humans, particularly in immunocompromised individuals. Recognizing and treating these infections early is vital for effective medical management.
Conclusion
Fungal spores such as arthrospores and chlamydospores are integral to the adaptive strategies of fungi, playing crucial roles in their life cycles and interactions with the environment. Their unique characteristics and behaviors underline the complexity of fungal biology and its implications across various fields, from agriculture to medicine.
The study of these spores not only enhances our understanding of fungal ecology but also supports the development of new techniques for managing fungal diseases in crops and humans. Continued research and education on fungal spores will further our ability to harness their properties for beneficial applications and mitigate their impacts on our lives and livelihoods.