Genetic variation forms the core of evolutionary biology and is pivotal in the fields of medicine and public health. It enables organisms, particularly pathogens, to adapt to their environments and hosts. Among the myriad types of genetic variation, antigenic and phase variation stand out due to their profound implications on the dynamics of infectious diseases and immune evasion.
Antigenic variation refers to changes in the surface proteins of pathogens, allowing them to escape detection by the host’s immune system. Phase variation, on the other hand, involves changes in the expression of specific genes, leading to alterations in the phenotype of a microorganism that can be reversible. These mechanisms are crucial for pathogens to adapt, survive, and spread within host populations.
Understanding these variations is more than an academic pursuit; it has direct applications in developing effective vaccines and therapeutic strategies. The ability of pathogens like influenza viruses and Neisseria gonorrhoeae to vary their genetic makeup complicates the development of long-term effective medical countermeasures, highlighting the need for ongoing research and innovation in this area.
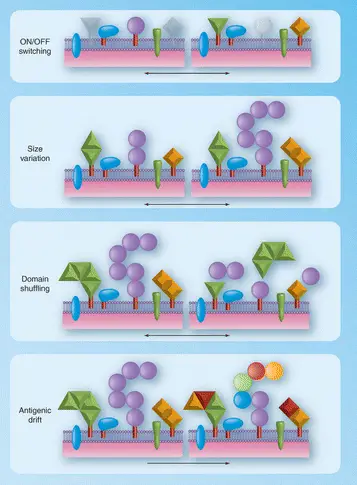
Antigenic Variation
Definition and Basics
Antigenic variation is a process where pathogens change their surface proteins to evade the host’s immune system. This ability is critical for the survival and proliferation of many infectious agents, particularly those that face a robust immune response over prolonged periods.
Biological Mechanisms
The mechanisms of antigenic variation are complex and involve several biological processes that enable pathogens to alter their genetic material effectively.
Gene Conversion
Gene conversion is a fundamental process contributing to antigenic variation. It involves the non-reciprocal transfer of genetic material from one DNA sequence to another, allowing for the rapid introduction of new genetic variants without altering the overall genomic integrity.
Hypermutation
Hypermutation is a process where the mutation rate of a genomic sequence is significantly increased. This accelerated rate of mutation can lead to rapid changes in the proteins expressed by the pathogen, particularly those involved in infection and immune system interaction.
Recombination
Recombination involves the exchange of genetic material between different molecules of DNA. In pathogens, this can lead to the creation of new gene combinations, particularly in the genes that encode surface proteins, further helping them to dodge the host’s immune defenses.
Examples in Pathogens
Influenza
Influenza viruses are notorious for their ability to undergo antigenic variation. The flu virus changes its hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA) proteins, which are critical for the virus’s attachment to host cells and subsequent entry. These changes can make previously effective vaccines less effective over time.
Trypanosomes
Trypanosomes, particularly Trypanosoma brucei, the causative agent of African sleeping sickness, utilize antigenic variation to switch their surface glycoproteins. This switch in surface proteins, driven by gene conversion and recombination, helps them evade the immune response of their host.
Phase Variation
Definition and Explanation
Phase variation is a reversible alteration in the expression of certain genes that leads to changes in the phenotype of a microorganism. Unlike antigenic variation, phase variation does not necessarily involve changes to the genetic code but rather to how certain genes are expressed.
Mechanisms Behind Phase Variation
Slipped-strand Mispairing
Slipped-strand mispairing occurs during DNA replication when DNA polymerase slips on a template strand, leading to additions or deletions in the DNA sequence. This can cause shifts in how the genetic code is read, leading to changes in the expression of genes, particularly those related to surface structures and virulence factors.
Site-specific Recombination
Site-specific recombination involves the breaking and rejoining of DNA at specific sites. This mechanism allows for the inversion or excision of DNA segments, leading to on-off switching of gene expression, particularly genes involved in pathogenicity and host interaction.
Examples in Bacteria
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Neisseria gonorrhoeae, the bacterium responsible for gonorrhea, uses phase variation to alter the expression of its pilus, a structure crucial for attachment to host cells. Changes in pilus expression help the bacterium evade immune detection and contribute to its virulence.
Salmonella typhimurium
Salmonella typhimurium employs phase variation to regulate the expression of its flagella, which are important for motility and host colonization. This regulation is crucial for its ability to infect hosts successfully and escape immune responses.
Comparing Variations
Key Differences
Antigenic and phase variations, though both mechanisms of genetic flexibility in pathogens, differ significantly in their function and impact. Antigenic variation primarily changes the proteins on the surface of pathogens, directly affecting how these organisms interact with the host’s immune system. In contrast, phase variation influences the expression levels of certain genes, which can turn on or off traits such as virulence factors and adhesion capabilities.
Impact on Immune Evasion
The ability to evade the immune system is a crucial survival strategy for pathogens, and both types of variation play critical roles in this process. Antigenic variation allows pathogens like the influenza virus to repeatedly infect the same host by presenting new antigens that the host’s immune system has not previously encountered. Phase variation helps organisms like Neisseria gonorrhoeae adapt to different environments within the host by changing the expression of surface structures, thus avoiding immune detection.
Role in Infection and Transmission
Both variations directly affect a pathogen’s capacity to cause disease and spread. Antigenic variation can lead to more effective spread within a population by creating new strains against which the population has no immunity. Phase variation can influence the transmission dynamics by enabling the pathogen to adapt to different host environments, enhancing its infectiousness and survivability.
Scientific and Medical Implications
Vaccine Development Challenges
The shifting landscape of pathogen antigens due to antigenic variation presents a significant hurdle in vaccine design. Vaccines based on specific viral or bacterial strains become less effective as these pathogens evolve. For instance, the annual changes required for influenza vaccines reflect the rapid antigenic shifts of the virus. Phase variation complicates this further by altering the expression of vaccine targets, necessitating adaptable and broadly protective vaccine strategies.
Diagnostic and Treatment Considerations
Diagnostics and treatments also must adapt to the variability introduced by both antigenic and phase variations. Standard tests may fail to detect a pathogen if it has altered its surface proteins or gene expression profiles significantly. Similarly, treatments targeting specific bacterial virulence factors may become ineffective if these factors are no longer expressed. This dynamic requires continuous updates and innovations in medical approaches, such as the development of broad-spectrum drugs and universal diagnostic tests.
Advances in Research
Recent Studies on Genetic Variation
Recent research has provided deeper insights into how genetic variations affect pathogen behavior and impact public health. Studies on the genome plasticity of Salmonella show how its ability to switch between different types of flagella helps it evade immune responses. Similarly, research on Trypanosoma brucei highlights how its surface protein variations thwart long-term immune defenses, complicating efforts to control sleeping sickness.
Technological Advancements Aiding Research
Technological advancements have significantly boosted our ability to study and combat the effects of genetic variations. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) technologies allow for rapid, high-throughput analysis of genetic changes across entire populations of pathogens. CRISPR-Cas systems provide tools not only for detailed genetic studies but also for potentially rectifying genetic changes in pathogens or modifying host responses.
FAQs
What is Antigenic Variation?
Antigenic variation is a mechanism by which pathogens alter their surface proteins to evade the immune response of their host. This evolutionary strategy is particularly observed in viruses and certain protozoa, enabling them to persist within the host and avoid immune clearance.
How Does Phase Variation Affect Bacteria?
Phase variation affects bacteria by altering the expression of genes, which can switch on and off, leading to changes in characteristics such as virulence and the ability to form biofilms. This variability plays a crucial role in bacterial adaptation and survival, especially in hostile environments.
Why is Studying Genetic Variation Important?
Studying genetic variation is essential for understanding how pathogens evolve and adapt to host defenses. This knowledge is crucial for the development of vaccines and treatments that can effectively target evolving strains of pathogens.
How Do Variations Impact Vaccine Development?
Genetic variations, particularly antigenic variation, pose significant challenges in vaccine development as they can lead to the emergence of vaccine-resistant strains. This necessitates continuous updates to vaccine formulations to maintain their effectiveness against new strains.
Conclusion
The study of antigenic and phase variation provides essential insights into the adaptive mechanisms of pathogens, underscoring the challenges and opportunities in managing infectious diseases. As pathogens evolve, so must our strategies in combating them, requiring a dynamic approach to vaccine development and public health planning.
Continued research into genetic variations not only enhances our understanding of pathogen biology but also informs the development of more effective interventions. By anticipating and responding to these genetic shifts, medical science can stay one step ahead in the ongoing battle against infectious diseases.