The interplay between different types of organic matter and their origins is a foundational concept in ecology that profoundly influences ecosystem dynamics. Terms like allochthonous, autochthonous, and parautochthonous, though seemingly complex, are essential in categorizing these organic materials based on their origins and impacts on various habitats. These categories help scientists and ecologists understand how energy flows through ecosystems and how organisms are supported by different sources of matter.
Allochthonous matter refers to organic material that originates outside of the ecosystem it is found in, such as leaves or logs that fall into a stream from surrounding forests. Autochthonous matter, on the other hand, is produced within the ecosystem itself, like algae in a lake. Parautochthonous matter strikes a balance between the two, being local but not entirely produced by the immediate biotic community, for example, dead plant parts that accumulate in the same place they grew.
Understanding these distinctions is not just academic; it has practical implications for conservation, management of natural resources, and restoration ecology. It affects everything from nutrient cycling and food web structures to habitat complexity and biodiversity. Recognizing the differences and interactions between allochthonous, autochthonous, and parautochthonous matter enables a deeper comprehension of ecological processes and fosters more informed decisions in environmental stewardship.
Origins of Organic Matter
Allochthonous Matter
Definition and Examples of Sources
Allochthonous matter is organic material that finds its way into an ecosystem from external locations. This type of matter originates outside the immediate area where it ends up and plays a crucial role in the nutrient cycles and energy flow within ecosystems. Common examples include leaves, wood, and other plant debris carried by wind or water into rivers, lakes, or marine environments. Another significant source is runoff from agricultural lands, which carries nutrients and organic materials into aquatic systems.
Autochthonous Matter
Definition and Sources Within Ecosystems
Autochthonous matter, in contrast, is produced within the ecosystem itself. Primary producers like algae, aquatic plants, and phytoplankton are key contributors, using photosynthesis to convert sunlight into organic materials. These organisms form the base of the food web in many aquatic systems, supplying energy and nutrients directly to various forms of aquatic life, from invertebrates to fish.
Parautochthonous Matter
Clarification of the Term and Its Role
Parautochthonous matter occupies a middle ground, being derived from the local environment but not produced by the water body’s typical biotic community. Examples include dead plant material that falls and accumulates in the water but was grown in the immediate surroundings. This type of matter emphasizes the interaction between terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems, highlighting the blurred lines where these systems meet and influence each other.
Key Differences
Source Locations
Comparison Based on Origin
- Allochthonous matter originates from outside the ecosystem.
- Autochthonous matter is produced within the ecosystem.
- Parautochthonous matter comes from the local environment but not directly from the ecosystem’s primary producers.
These distinctions are crucial for understanding how energy and nutrients move through ecosystems, impacting everything from water quality to habitat complexity.
Impact on Ecosystems
Effects of Each Type on Local Environments
- Allochthonous matter can enrich an ecosystem with nutrients but may also introduce pollutants.
- Autochthonous matter supports self-sufficiency in ecosystems, directly feeding the food web.
- Parautochthonous matter provides a link between terrestrial and aquatic systems, affecting both nutrient cycling and habitat structure.
Contribution to Food Webs
Role in Supporting Diverse Life Forms
- Allochthonous inputs can significantly augment food resources in nutrient-poor environments.
- Autochthonous production is the backbone of aquatic food webs, especially in clear, nutrient-rich waters.
- Parautochthonous matter offers unique feeding opportunities for organisms that exploit the transition zones between land and water.
Importance in Ecology
Nutrient Cycling
How Each Type Affects Nutrient Distribution
- Allochthonous matter often introduces new nutrients into aquatic systems, potentially boosting productivity.
- Autochthonous matter circulates nutrients within the ecosystem, maintaining an equilibrium.
- Parautochthonous matter can both introduce new nutrients and recycle existing ones, offering a dynamic impact on nutrient cycling.
Habitat Formation
Influence on the Physical Structure of Habitats
- Allochthonous debris like logs and leaves can create physical habitats for aquatic organisms, offering shelter and breeding grounds.
- Autochthonous growth such as aquatic plants and algae can form extensive underwater structures that serve as habitat and food sources.
- Parautochthonous deposits contribute to the sediment layer, influencing water quality and bottom habitats.
Biodiversity Support
Contribution to Species Diversity and Abundance
- Allochthonous inputs support a variety of species by providing additional resources.
- Autochthonous production is essential for sustaining endemic species that rely on the ecosystem’s primary productivity.
- Parautochthonous matter supports species that thrive in ecotones, where different ecosystems overlap and interact.
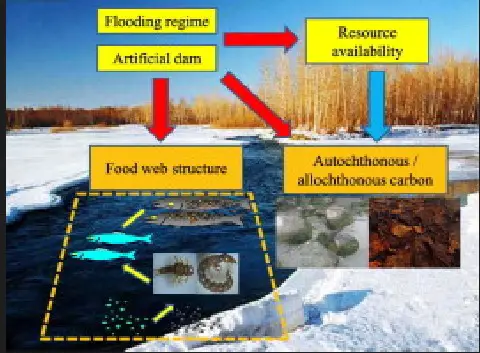
Case Studies
Freshwater Ecosystems
Role and Impact in Rivers and Lakes
In freshwater ecosystems like rivers and lakes, allochthonous matter such as fallen leaves and tree branches from surrounding forests plays a significant role in providing nutrients and habitat. This external organic matter supports diverse microbial communities and serves as food for aquatic invertebrates, which are, in turn, prey for fish and other wildlife. Autochthonous matter, generated by aquatic plants and algae, forms the basis of the food web, directly supporting fish and other aquatic organisms. Parautochthonous matter, such as dead reeds and plants that decompose in the water, creates unique microhabitats and influences nutrient cycling within these ecosystems.
Marine Ecosystems
Differences in Contribution to Oceans
In marine ecosystems, the contribution of allochthonous matter is relatively less compared to autochthonous sources due to the vastness of oceans and their separation from large terrestrial sources of organic material. Here, autochthonous matter, primarily produced by phytoplankton, forms the base of a complex marine food web. Phytoplankton’s role in capturing sunlight and converting it into energy through photosynthesis is crucial for supporting marine life from zooplankton to large whales. Parautochthonous matter is less defined in marine systems but can include materials from coastal vegetation like mangroves and seagrasses that fall and accumulate on the ocean floor, providing critical habitats and nurseries for a multitude of marine species.
Forest Ecosystems
Impact on Forest Floor and Overall Health
Forest ecosystems offer a clear demonstration of the interaction between allochthonous, autochthonous, and parautochthonous matter. Leaf litter and deadwood from the forest canopy (allochthonous matter) fall to the forest floor, where they decompose and enrich the soil with nutrients, supporting the growth of forest plants (autochthonous matter). This cycle of decay and growth underpins the health and sustainability of forest ecosystems, driving biodiversity and ecosystem productivity. Parautochthonous matter, such as decaying logs that retain their location, becomes a nursery for new forest growth, illustrating the cyclical nature of organic matter in these ecosystems.
Challenges in Study
Differentiating Between Types
Methods and Difficulties in Classification
Differentiating between allochthonous, autochthonous, and parautochthonous matter in an ecosystem presents significant challenges. The primary method involves tracing the origin of organic materials through chemical markers or isotopic signatures. However, these techniques require sophisticated equipment and can be complicated by the overlapping signatures of different organic matter types. Additionally, the dynamic nature of ecosystems means that the classification of organic matter can change over time as materials move or transform, adding another layer of complexity to their study.
Measuring Impact
Tools and Techniques for Assessing Ecological Effects
Assessing the ecological effects of different types of organic matter involves a variety of tools and techniques, from field observations to laboratory experiments. Researchers may use biomarkers, remote sensing technology, and ecosystem modeling to understand how organic matter influences nutrient cycling, biodiversity, and ecosystem health. Despite these advanced tools, measuring the long-term impact remains challenging due to the complexity of ecosystems and the multitude of factors that influence ecological processes.
Future Directions
Research Needs
Gaps in Current Understanding and Knowledge
Future research needs to focus on improving our understanding of the interactions between allochthonous, autochthonous, and parautochthonous matter within ecosystems. This includes developing better methods for tracking the flow of organic matter, understanding its chemical transformation, and assessing its impact on ecosystem services. There is also a need for more long-term studies to observe the effects of climate change and human activities on the dynamics of organic matter in ecosystems.
Conservation Efforts
How Knowledge of These Types Can Aid in Ecosystem Preservation
Understanding the roles and impacts of different types of organic matter is essential for effective ecosystem conservation and management. Knowledge of how allochthonous matter supports aquatic ecosystems can inform strategies to protect watersheds and maintain healthy water flows. Recognizing the importance of autochthonous matter in supporting food webs can lead to efforts to preserve key habitats, such as wetlands and coral reefs. Furthermore, understanding parautochthonous matter’s role can help in the design of conservation strategies that bridge terrestrial and aquatic environments, ensuring the preservation of ecotones and transitional habitats. Integrating this knowledge into conservation planning will be crucial for maintaining biodiversity, enhancing ecosystem resilience, and supporting the services that ecosystems provide to humanity.
FAQs
What is allochthonous matter?
Allochthonous matter is organic material that originates outside of the ecosystem where it is found. Typically, this includes materials such as fallen leaves, branches, or logs from terrestrial environments that are carried into aquatic ecosystems by wind or water. This external source of organic matter plays a crucial role in the nutrient cycles and energy flows of receiving ecosystems, often providing a significant source of food and habitat for aquatic organisms.
How does autochthonous matter differ from allochthonous?
Autochthonous matter is generated within the ecosystem itself, in contrast to allochthonous matter, which comes from outside. This can include things like aquatic plants, algae, and photosynthetic bacteria in water bodies. These organisms produce organic matter through photosynthesis, contributing directly to the ecosystem’s internal food web. Autochthonous matter is vital for maintaining the self-sufficiency of aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems by providing a base level of productivity.
Why is understanding these concepts important for ecology?
Understanding the difference between allochthonous, autochthonous, and parautochthonous matter is crucial for ecology because it influences how ecosystems function, including nutrient cycling, energy flow, and food web structures. These concepts help ecologists predict changes in ecosystems resulting from natural events or human activities, design effective conservation strategies, and restore damaged ecosystems by mimicking natural processes.
What role does parautochthonous matter play in ecosystems?
Parautochthonous matter consists of organic materials that are neither strictly produced within the ecosystem (like autochthonous matter) nor originated from an external ecosystem (like allochthonous matter). It includes materials such as dead leaves and stems that accumulate where they grew. This type of matter provides a nuanced understanding of ecosystem dynamics, indicating a middle ground that contributes to local nutrient cycles and supports a diverse array of microhabitats within ecosystems.
Conclusion
Recognizing the nuanced differences between allochthonous, autochthonous, and parautochthonous matter is more than an exercise in academic terminology; it is a window into the intricate operations of natural ecosystems. These distinctions help clarify the origins of organic materials that fuel the complex web of life, influence nutrient cycling, and sustain biodiversity. In essence, they allow us to appreciate the delicate balance and interconnectedness of nature.
As we strive to protect and restore our planet’s diverse ecosystems, understanding these fundamental ecological concepts becomes imperative. It equips us with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions that foster healthy, resilient ecosystems. Through this lens, we can better appreciate the importance of each type of organic matter, not just for the health of individual ecosystems, but for the global environment as a whole.

